Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 2 Scientific Investigation and Business Research Process
Uploaded by
reda gadCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 2 Scientific Investigation and Business Research Process
Uploaded by
reda gadCopyright:
Available Formats
Business Research Methods All Rights Reserved
© Oxford Fajar Sdn. Bhd. (008974-T), 2012 2– 1
PART 1
CHAPTER 2
Business Research Process
Business Research Methods All Rights Reserved
© Oxford Fajar Sdn. Bhd. (008974-T), 2012 2– 2
LEARNING OUTCOMES
After studying this chapter, you should be able to:
Differentiate between two different types of thought
process—deduction and Induction
Differentiate between quantitative and qualitative
research
Know the different scientific stages of business
research process
Business Research Methods All Rights Reserved
© Oxford Fajar Sdn. Bhd. (008974-T), 2012 2– 3
2.1 Approaches to business
Research
Two different thought processes:
Reasoning
1. Induction (Inductive Reasoning)— general principles are
inferred from specific observations to arrive at valid
conclusions.
Investigating a Specific problem to come up with general solution
Employee high turn over new salary structure
Business Research Methods All Rights Reserved
© Oxford Fajar Sdn. Bhd. (008974-T), 2012 2– 4
Inductive—Bottom Up Approach
Conclusion
Hypothesis
Specific
Observation
Business Research Methods All Rights Reserved
© Oxford Fajar Sdn. Bhd. (008974-T), 2012 2– 5
2.1 Approaches to Research
(cont.)
2. Deduction (Deductive Reasoning)—deductive
reasoning relies on specifics are inferred from
general principles/theory to arrive at valid
conclusions.
Use general model to solve a Specific problem
Use hierarchy of need theory Categorize employees
needs
Business Research Methods All Rights Reserved
© Oxford Fajar Sdn. Bhd. (008974-T), 2012 2– 6
Deductive—Top Down Approach
Theory
Hypothesis
observation
Confirmation
Business Research Methods All Rights Reserved
© Oxford Fajar Sdn. Bhd. (008974-T), 2012 2– 7
2.2 Quantitative vs Qualitative
Research
Quantitative research to describe and understand
phenomena focusing on statistical analysis of
numerical data using large-scale survey research
method, and data collection methods of
questionnaire and/or structured interview.
Business Research Methods All Rights Reserved
© Oxford Fajar Sdn. Bhd. (008974-T), 2012 2– 8
2.2 Quantitative vs Qualitative
Research (cont.)
Qualitative research attempts to explore and
explain phenomena related to people’s beliefs,
experiences, attitudes, behaviour and interactions
through methods
using case study and/or observation research
method, and data collection methods of direct or
participant observation and/or un-structured
interview.
Business Research Methods All Rights Reserved
© Oxford Fajar Sdn. Bhd. (008974-T), 2012 2– 9
Both have their strengths and
weaknesses
One of the advantages of quantitative research is
that of generalisation of research findings to the
population through the statistical analysis
On the other hand, the qualitative research does
not necessarily seek to choose the sample that is
representative of the target population. However, it
provides in-depth information which is not possible
with quantitative data
Business Research Methods All Rights Reserved
© Oxford Fajar Sdn. Bhd. (008974-T), 2012 2– 10
2.3.1 Problem Identification
Desires to find information needed to fulfil a need.
In this context, a research is needed to address a
problem. If there is no problem then there is no
need for a research.
Don’t confuse the research phenomenon with the
research problem
Business Research Methods All Rights Reserved
© Oxford Fajar Sdn. Bhd. (008974-T), 2012 2– 11
2.3.1 Problem Identification
Match items of group A with the most relevant counterpart from group B
(Group A) (Group B)
1.Absenteeism 1.misleading Market segmentation
2.Confusing Consumer needs 2.Excessive Paperwork
3.Bottlenecks 3.Demotivated Employees
4.High material costs 4.Low Productivity
5.High Employee turn over 5.Incorrect Demand Forecasting
6.Bankruptcy 6.Low Employee awareness
7.Low Inventory turn over 7.Weak Attendance Policy
8.Employee Dissatisfaction 8.Inappropriate On - Job - Training
9.Low skilled employees 9.Incentive plan
Business Research Methods All Rights Reserved
© Oxford Fajar Sdn. Bhd. (008974-T), 2012 2– 12
2.3.2 Defining the Research
Objective / question
Need to be very focused to identify the research
objectives
The objectives’ action verb should be clear
– Understand (describe) – What
– Explain – Why
– Explore – How
Business Research Methods All Rights Reserved
© Oxford Fajar Sdn. Bhd. (008974-T), 2012 2– 13
2.3.3 Research Design
Provides the framework to be used as a guide in
collecting and analysing data
Match a research problem with appropriate
research design
– Descriptive research design
– Causal research design
– Exploratory research design
Business Research Methods All Rights Reserved
© Oxford Fajar Sdn. Bhd. (008974-T), 2012 2– 14
Descriptive research design
Can be either (a) longitudinal or (b) cross-sectional.
–A. Longitudinal: Taking multiple measures from the same
sample over an extended period of time—from a few months to
a few years (ex: market share, productivity and inventory
turnover over 4 quarters)
–B. cross-sectional : Takes place at a single point in time and
aims to describe the relationship between variables (ex:
market share, productivity and inventory turnover over on
December 2017)
Business Research Methods All Rights Reserved
© Oxford Fajar Sdn. Bhd. (008974-T), 2012 2– 15
Causal /experimental research
design
Seeks to establish the cause and effect relationship
among the variables of interest
Ex. The impact of work design on the individual
performance
Business Research Methods All Rights Reserved
© Oxford Fajar Sdn. Bhd. (008974-T), 2012 2– 16
Exploratory research design
Is to generate hypotheses for further study
Provide insight on how to do more conclusive
research
Ex. Business process models (BPMs)
Business Research Methods All Rights Reserved
© Oxford Fajar Sdn. Bhd. (008974-T), 2012 2– 17
2.3.4 Designing Research
Methodology
Major parts of research methodology are:
1. Research method: primary/secondary
2. Method of data collection (instruments)
3. Sampling plan OR complete census
4. Fieldwork plan
5. Analysis plan
Business Research Methods All Rights Reserved
© Oxford Fajar Sdn. Bhd. (008974-T), 2012 2– 18
2.3.5 Budget and Cost
Estimation
Three basic parameters which provide an estimate of
how much a study is going to cost.
Sample size.
How difficult it is to find the sampling units
(respondents) and their geographical dispersion?
Who will do the fieldwork?
Business Research Methods All Rights Reserved
© Oxford Fajar Sdn. Bhd. (008974-T), 2012 2– 19
2.3.6 Presentation, Report and
Decision-making
A business research starts with problem
identification and ends with an
actionable/formal report.
Business Research Methods All Rights Reserved
© Oxford Fajar Sdn. Bhd. (008974-T), 2012 2– 20
Business Research Process:
An Overview
Defining
Opportunity and
information research
need felt objectives
Designing
Managerial research
decision and method
action
Diagrammatic
Representation of the
Business Research
Process
Plan and do
Report primary
writing and research
presentation
Plan and do
Tabulation secondary
and analysis research
Business Research Methods All Rights Reserved
© Oxford Fajar Sdn. Bhd. (008974-T), 2012 2– 21
You might also like
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Comp and Ben PresentationDocument11 pagesComp and Ben Presentationreda gadNo ratings yet
- Part 3 - Equity ValuationDocument21 pagesPart 3 - Equity Valuationreda gadNo ratings yet
- Managerial 1Document136 pagesManagerial 1reda gadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 CitationDocument33 pagesChapter 6 Citationreda gadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Population & SamplingDocument9 pagesChapter 7 Population & Samplingreda gadNo ratings yet
- Green HRDocument23 pagesGreen HRreda gadNo ratings yet
- ROI TrainingDocument63 pagesROI Trainingreda gadNo ratings yet
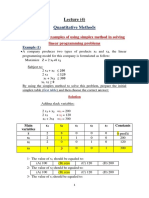
- Quantitative Methods: LectureDocument12 pagesQuantitative Methods: Lecturereda gadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Developing Theoretical FrameworkDocument30 pagesChapter 4 Developing Theoretical Frameworkreda gadNo ratings yet
- Pert - Lec 8Document10 pagesPert - Lec 8reda gadNo ratings yet
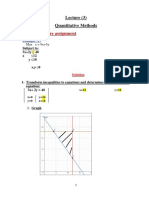
- Assignment Model: Quantitative MethodsDocument6 pagesAssignment Model: Quantitative Methodsreda gadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction To Business ResearchDocument13 pagesChapter 1 Introduction To Business Researchreda gad100% (1)
- Chapter 3 Preliminary Information Gathering and Problem DefinitionDocument12 pagesChapter 3 Preliminary Information Gathering and Problem Definitionreda gadNo ratings yet
- Quantitative MethodsDocument9 pagesQuantitative Methodsreda gadNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Methods: Instructor: DR: Abdelhamid MostafaDocument22 pagesQuantitative Methods: Instructor: DR: Abdelhamid Mostafareda gadNo ratings yet
- Linear Programming (Graph Method) : - : Quantitative MethodsDocument13 pagesLinear Programming (Graph Method) : - : Quantitative Methodsreda gadNo ratings yet
- Previous Lecture AssignmentDocument13 pagesPrevious Lecture Assignmentreda gadNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Methods: LectureDocument13 pagesQuantitative Methods: Lecturereda gadNo ratings yet
- Principles of Economics 3Document34 pagesPrinciples of Economics 3reda gadNo ratings yet
- PresentationCH 1Document35 pagesPresentationCH 1reda gadNo ratings yet
- Principles of Economics 1Document36 pagesPrinciples of Economics 1reda gadNo ratings yet
- Principles of Economics 4Document51 pagesPrinciples of Economics 4reda gadNo ratings yet
- Principles of Economics2Document39 pagesPrinciples of Economics2reda gadNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Backtesting CampbellHarvingNov222013 PDFDocument25 pagesBacktesting CampbellHarvingNov222013 PDFArvind KothariNo ratings yet
- Take Home Exam UkpDocument4 pagesTake Home Exam Ukpvkey_viknes2579No ratings yet
- CH 05Document30 pagesCH 05曾書瑋No ratings yet
- Testul Fisher ExactDocument33 pagesTestul Fisher ExactgeorgianapetrescuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - One Sample Test of HypothesisDocument37 pagesChapter 4 - One Sample Test of HypothesisJahid Khan Rahat (171011211)No ratings yet
- Test Bank For Industrial-Organizational Psychology Understanding The Workplace 5th Edition by Levy PDFDocument26 pagesTest Bank For Industrial-Organizational Psychology Understanding The Workplace 5th Edition by Levy PDFMARIE ROSE L. FUNTANARNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Variance ANOVADocument3 pagesAnalysis of Variance ANOVAnorhanifah matanogNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9. Statistical Inference For Two SamplesDocument39 pagesChapter 9. Statistical Inference For Two SamplesNguyen Thi Lan Anh (K15 HL)No ratings yet
- Unit 5: Test of Significance/Hypothesis Testing (Topics 20, 22, 23)Document24 pagesUnit 5: Test of Significance/Hypothesis Testing (Topics 20, 22, 23)Riddhiman PalNo ratings yet
- Econometrics QP CalicutDocument17 pagesEconometrics QP CalicutMadonaNo ratings yet
- Apendiks A: Data Dan Jadual StatistikDocument5 pagesApendiks A: Data Dan Jadual StatistikMohd Farhan MakhlisNo ratings yet
- SW 2e Ex ch05Document5 pagesSW 2e Ex ch05Nicole Dos AnjosNo ratings yet
- Kare, Kumar Rajuldevi, VeeramachaneniDocument88 pagesKare, Kumar Rajuldevi, VeeramachaneniReshma Mariya TomyNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3Document2 pagesTutorial 3Pitchamuthu Vethandamoorthy ThillanyNo ratings yet
- Simple Linear Regression AnalysisDocument7 pagesSimple Linear Regression AnalysiscarixeNo ratings yet
- Chap8 HM PDFDocument114 pagesChap8 HM PDFaboudy noureddineNo ratings yet
- Engineering Statistics Handbook 7. Product and Process ComparisonsDocument144 pagesEngineering Statistics Handbook 7. Product and Process Comparisonsagbas20026896No ratings yet
- Case Study Report Tut 1 Group 4 Mrs. Hoai PhuongDocument22 pagesCase Study Report Tut 1 Group 4 Mrs. Hoai Phuong2004040009No ratings yet
- Christopher Coker - The Improbable War - China, The United States and Logic of Great Power Conflict (2015, Oxford University Press)Document230 pagesChristopher Coker - The Improbable War - China, The United States and Logic of Great Power Conflict (2015, Oxford University Press)MujahidNo ratings yet
- 09 Power & Sample SizeDocument16 pages09 Power & Sample SizeafonsopilarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document7 pagesChapter 3niczclueNo ratings yet
- Statistics 578 Assignment 5 HomeworkDocument13 pagesStatistics 578 Assignment 5 HomeworkMia Dee100% (5)
- CH 13 Reasoning & Decision MakingDocument60 pagesCH 13 Reasoning & Decision MakingbbsuperNo ratings yet
- Grene, Depew - The Philosoph y of Biology - Unknown PDFDocument437 pagesGrene, Depew - The Philosoph y of Biology - Unknown PDFworstwardho100% (2)
- Anova Two WayDocument2 pagesAnova Two WayNikhitha AdluriNo ratings yet
- One Way ANOVA, Two Way ANOVA and Interaction ANOVADocument25 pagesOne Way ANOVA, Two Way ANOVA and Interaction ANOVAShil ShambharkarNo ratings yet
- BADM 299 Exam 3 Chaps 009 & 011-Review QuestionsDocument6 pagesBADM 299 Exam 3 Chaps 009 & 011-Review QuestionsStatistics LearningNo ratings yet
- Practice Problems - Part 1Document6 pagesPractice Problems - Part 1Pratip BeraNo ratings yet
- 8 33、8 35Document1 page8 33、8 35ly21171007cynthiaNo ratings yet
- Aristotle Rhetoric PDFDocument247 pagesAristotle Rhetoric PDFaco6999No ratings yet