0% found this document useful (0 votes)
91 views29 pagesTypes and Methods of Piling Explained
Here are the answers to the questions about the document on types of piling:
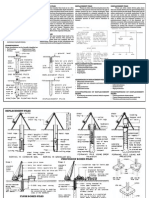
1. End bearing piles and friction piles
2. Bored piles
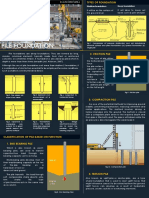
3. c. 9 types of piling
4. d. Concrete piles
5. b. 2 main steps (dropping weight and vibration)
6. Screw piles
Uploaded by
MDanish AimanCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
91 views29 pagesTypes and Methods of Piling Explained
Here are the answers to the questions about the document on types of piling:
1. End bearing piles and friction piles
2. Bored piles
3. c. 9 types of piling
4. d. Concrete piles
5. b. 2 main steps (dropping weight and vibration)
6. Screw piles
Uploaded by
MDanish AimanCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd