0% found this document useful (0 votes)
80 views33 pagesDNA: The Blueprint of Life Explained
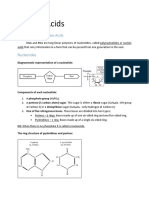
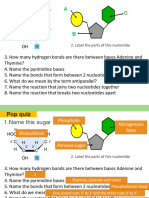
The document discusses DNA and its structure and function. It explains that DNA contains genetic instructions encoded in genes and is made up of nucleotides containing nitrogenous bases that form base pairs. The structure of DNA was discovered in 1953 by Watson and Crick to be a double helix. RNA is also discussed as being single-stranded and involved in protein synthesis, with mRNA carrying DNA instructions to the ribosomes. The genetic code is universal and some codons specify the same amino acids.
Uploaded by
ryan valerioCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
80 views33 pagesDNA: The Blueprint of Life Explained
The document discusses DNA and its structure and function. It explains that DNA contains genetic instructions encoded in genes and is made up of nucleotides containing nitrogenous bases that form base pairs. The structure of DNA was discovered in 1953 by Watson and Crick to be a double helix. RNA is also discussed as being single-stranded and involved in protein synthesis, with mRNA carrying DNA instructions to the ribosomes. The genetic code is universal and some codons specify the same amino acids.
Uploaded by
ryan valerioCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd