0% found this document useful (0 votes)
595 views35 pagesOverview of Digital Radiography Techniques
This document discusses digital radiology techniques including computed radiography (CR) and direct digital radiography using flat panel detectors. CR utilizes photostimulable phosphor plates that are scanned with a laser to produce a digital image. Direct digital systems directly convert x-rays to electrical signals without the use of phosphor plates. Digital images allow for processing, transmission, archiving and retrieval advantages over conventional films. Attention must be paid to potential increases in patient dose from digital radiology.
Uploaded by
Ahmed shabanCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
595 views35 pagesOverview of Digital Radiography Techniques
This document discusses digital radiology techniques including computed radiography (CR) and direct digital radiography using flat panel detectors. CR utilizes photostimulable phosphor plates that are scanned with a laser to produce a digital image. Direct digital systems directly convert x-rays to electrical signals without the use of phosphor plates. Digital images allow for processing, transmission, archiving and retrieval advantages over conventional films. Attention must be paid to potential increases in patient dose from digital radiology.
Uploaded by
Ahmed shabanCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Introduction to Digital Radiology: Overview and aim of digital radiology in projection imaging and fluoroscopy, setting the study's goals.
- Transition from Conventional to Digital Radiology: Explains how digital images differ from conventional ones, focusing on image processing and transmission.
- Dynamic Range in Digital Imaging: Discusses dynamic range and how it relates to image quality in digital systems compared to traditional systems.
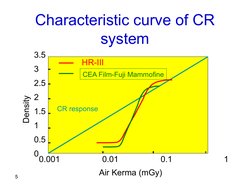
- CR System Characteristics: Features a characteristic curve to explain CR system response and its significance in imaging.
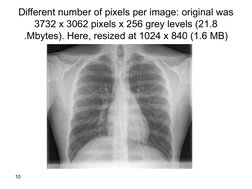
- Understanding Digital Radiology: Defines digital radiology, focusing on how it uses matrices to represent and process images.
- Digital Radiology Process: Details the digital radiology workflow, including acquisition, processing, display, archiving, and retrieval.
- Digitizing Conventional Films: Explores conversion of conventional images to digital, implications, and post-processing possibilities.
- Scintillation-based Digital Radiography: Illustrates the setup and use of scintillation materials, particularly gadolinium oxy-sulphide detectors, in digital radiography.
- Digital Radiography Systems: Distinguishes between computed radiography and digital radiography systems and their technology bases.
- Computed Radiography: Describes computed radiography, focusing on phosphor luminescence and image plate characteristics.
- Principles of PSP: Details the photostimulable phosphor (PSP) system principles, including excitation and emission processes.
- DR Detecting Systems: Introduction to digital radiography detecting systems and technologies employed in their function.
- Digital Radiography Technologies: Covers various digital radiography detector technologies, emphasizing materials and methodologies.
- Digital Fluoroscopy: Explains digital fluoroscopy systems and the transformation from analog to digital methods.
- Radiology Department Components: Outlines additional infrastructure components like RIS and PACS supporting digital radiology operations.
- DICOM Standard: Discusses the DICOM standard for digital imaging and communication, crucial for medical image management.