Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Entomology-Iii: Dr. Marina Vaidya Shrestha
Uploaded by
Deepraj Giri0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views26 pages1. Fleas are small, wingless insects that feed on blood and can transmit diseases like plague and typhus. Common flea species include rat fleas, human fleas, and dog and cat fleas.
2. Sandflies are smaller than mosquitoes and can transmit diseases like kala-azar and sandfly fever through their bites.
3. Bugs can transmit Chagas disease and their bites may cause irritation. Rodents can transmit bacterial diseases like plague, viral diseases, and parasitic infections to humans. Controlling rodents involves sanitation measures, trapping, and use of rodenticides.
Original Description:
Original Title
Untitled
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1. Fleas are small, wingless insects that feed on blood and can transmit diseases like plague and typhus. Common flea species include rat fleas, human fleas, and dog and cat fleas.
2. Sandflies are smaller than mosquitoes and can transmit diseases like kala-azar and sandfly fever through their bites.
3. Bugs can transmit Chagas disease and their bites may cause irritation. Rodents can transmit bacterial diseases like plague, viral diseases, and parasitic infections to humans. Controlling rodents involves sanitation measures, trapping, and use of rodenticides.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views26 pagesEntomology-Iii: Dr. Marina Vaidya Shrestha
Uploaded by
Deepraj Giri1. Fleas are small, wingless insects that feed on blood and can transmit diseases like plague and typhus. Common flea species include rat fleas, human fleas, and dog and cat fleas.
2. Sandflies are smaller than mosquitoes and can transmit diseases like kala-azar and sandfly fever through their bites.
3. Bugs can transmit Chagas disease and their bites may cause irritation. Rodents can transmit bacterial diseases like plague, viral diseases, and parasitic infections to humans. Controlling rodents involves sanitation measures, trapping, and use of rodenticides.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 26
ENTOMOLOGY-III
Dr. Marina Vaidya Shrestha
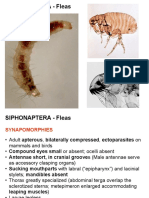
Flea
Flea
• Belong to order Siphonaptera.
• Widely distributed all over globe.
• Small,bilaterally compressed ,wingless insects with a
hard exoskeleton and covered with backwardly directed
strong bristles.
Types of Fleas
• Rat fleas(oriental): Xenopsylla cheopis
Xenopsylla astia
• Xenopsylla braziliensis
• Rat fleas(Temperate zone): Nosopsylla fasciatus
• Human fleas: Pulex irritans
• Dog and Cat fleas: Ctenocephalus canis
Ctenocephalus felis
• Sand fleas: Tunga penetrans
• Rat fleas are of greatest importance(vectors of plague
and typhus)
“sensilium”
=
“pygidium”
“ctenidium” = “comb”, e.g. “genal
comb” = “genal ctenidium”
Habits
• Found on their normal hosts and in the nests, burrows
and layers of their hosts.
• Found in dwellings, ground, cracks and crevices and
under carpet.
• Both sexes bite and suck blood.
• Feed on frequent interval, usually once a day and
sometimes more often.
• Can not fly but jump
• Passively transported by host, transport vehicles ,
humans, movement of goods like grain, cotton, bags etc.
Flea indices
• General flea index: average no.of fleas of all species per
rodent.
• Specific flea index: average no. of fleas of each species
found per rodent.
• Percentage incidence of flea species: percentage of
fleas of each species found per rodent.
• Rodent infestation rate: percentage of rodents infested
with various flea species.
Diseases
• Known to transmit the following diseases:
1. Plague
2. Endemic and Murine Typhus
3. Chigerrosis
4. Hymenolepis diminuta
Mode of transmission
• Biting:(mode of transmission in plague )
ingest plague bacilli and multiply in proventriculus or
stomach (blocked fleas)
Blockage of food passage
Hungry flea bite more ferociously
Injects plague bacilli in wound
• Mechanical :takes from proboscis of the fleas
• Faeces: fleas defecate while feeding.fecal drops may
contain numerous bacilli.When host scratches over flea
bitten area
Control of fleas
• Insecticidal control: Previously DDT (10%), Diazinon
(2%),malathion(5%)
• Sprays should be applied to floors and walls up to ht of 1
feet.
• Insecticidal sprays dust be sprayed to rodents burrows.
• Repellents:Diethyltoluamide is an effective flea repellent.
Benzyl benzoate is also a good repellent.
Rodent control
Sandfly
Sandfly
• Small insect ,light and dark brown in colour.
• Smaller than mosquitoes measuring 1.5 to 2.5 mm
• Species :phlebotomus argentipes ,P.papatasii , P.sergenti
Sergentomypia punjabensis.
General characteristics
• Head,thorax and abdomen.
• Sandflies may be distinguished from mosquitoes by the
following characteristics:
• Size:sandfly are smaller than mosquitoes
• Wings: second longitudinal vein on the wings branches
twice
• Legs: legs are longer compare to body
• Sandfly is hairy insect
• Hopping: Sandfly hop about and do not fly by choice.
Habits
• Nocturnal pets
• Bite is irritating and painful.
• Infest dwelling during night, take shelter during holes ,
trees, dark rooms.
• Females alone bite as they require blood meal every third
or fourth day.
Diseases transmitted
• Kalaazar
• Sandfly fever
• Oriental shore
Control
• Insecticides: DDT/Lindane once in 3 months.
• Sanitation: removal of shurbs and vegetation
• Filling up of cracks, crevices in walls and floors
• Location of cattle sheds and poultry away from human
habitation.
Bugs
• Vectors of Chagas disease
• Large size, wings in adult
• Live in cracks, fissures and other hiding places in walls
• Frequently attack man and bite may cause itching ,
nausea ,flushed face, palpitation.
• Residual spraying with HCH.
Rodents
2 groups:
1.Domestic rodents: black rat, Norway rat, house mouse
2.Wild rodents: Tatera indica,B.indica
Rodents and disease
• Bacterial: plague, tularaemia
• Viral: Lassa fever,haemorrhagic fever, encephalitis
• Rickettsial: scrub typhus ,murine typhus, rickettsial fever
• Parasitic: hymenolepis diminuata, Leismaniasis,
amoebiasis
Mode of transmission
• Directly through rat bite
• Contamination through food and water
Antirodent measures
• Sanitation measure
• Trapping
• Rodenticides: barium carbonate, Zinc Phosphide,
warfarin.
You might also like
- Entomology - Members of Class Insecta, Order DipteraDocument88 pagesEntomology - Members of Class Insecta, Order Dipteramiki100% (1)
- Control of Insects and RodentsDocument21 pagesControl of Insects and RodentsZam PamateNo ratings yet
- Insecta of Medical Importance - Siphonaptera (Fleas)Document21 pagesInsecta of Medical Importance - Siphonaptera (Fleas)CLEMENT100% (2)
- Vectors of Public Health ImportanceDocument31 pagesVectors of Public Health ImportanceJoseph Stans Kasirye75% (4)
- Arthropods of Medical ImportanceDocument6 pagesArthropods of Medical ImportanceMiren Sofia Jordana0% (1)
- Roles of Insects For HumanDocument58 pagesRoles of Insects For Humannovita manaluNo ratings yet
- Myiasis and Strike: Dr. Thahsin Farjana Associate Professor Dept. of Parasitology BAUDocument33 pagesMyiasis and Strike: Dr. Thahsin Farjana Associate Professor Dept. of Parasitology BAUChuramoni Saha100% (1)
- 015Document9 pages015Ayesha AtifNo ratings yet
- Medical EntomologyDocument13 pagesMedical EntomologyMusfeera KhanNo ratings yet
- House FlyDocument45 pagesHouse FlysanthiyasandyNo ratings yet
- Tsetse FlyDocument15 pagesTsetse FlyGiri PrasadNo ratings yet
- 5 Rat FleaDocument5 pages5 Rat Flea173Swapnaneil BujarbaruahNo ratings yet
- 12.bedbug and Kissing BugDocument25 pages12.bedbug and Kissing BugOsman Mohamed MuhumedNo ratings yet
- General Study Guide - 2: - For Each Insect/pathogen CombinationDocument20 pagesGeneral Study Guide - 2: - For Each Insect/pathogen CombinationHerold Riwaldo SNo ratings yet
- Pre Travel Mosquitos SnakesDocument59 pagesPre Travel Mosquitos SnakesIsrael EspinNo ratings yet
- Lecture 17 Tsetse OestridsDocument26 pagesLecture 17 Tsetse OestridsUgee KurniawanNo ratings yet
- 5 Worms 3 - Dla StudDocument49 pages5 Worms 3 - Dla StudurjaNo ratings yet
- Infestation: ScabiesDocument16 pagesInfestation: ScabiesBrix ValdrizNo ratings yet
- Rodent Control: Clores, Shira Geolinne Nicor, Nerrizza ReiDocument31 pagesRodent Control: Clores, Shira Geolinne Nicor, Nerrizza ReiEosNo ratings yet
- Phthiraptera: Johari Jalinas Medical and Urban EntomologyDocument15 pagesPhthiraptera: Johari Jalinas Medical and Urban EntomologyjoharijalinasNo ratings yet
- Unit-5, Pest ControlDocument9 pagesUnit-5, Pest ControlPuja PandeyNo ratings yet
- Ticks, Mites, Fleas, Lice As A VectorDocument24 pagesTicks, Mites, Fleas, Lice As A VectorAditya Rachman Van Der ArjunaqueeNo ratings yet
- Diptera 6Document26 pagesDiptera 6erica williamsNo ratings yet
- Protozoan Parasites: Gwy-Am Shin Office: Suite 2335, 4225 Roosevelt Phone: 206-543-9026 Email: Gwyam@u.washington - EduDocument35 pagesProtozoan Parasites: Gwy-Am Shin Office: Suite 2335, 4225 Roosevelt Phone: 206-543-9026 Email: Gwyam@u.washington - EduHazhar OmerNo ratings yet
- The Science Which Deals With The Relation of Insects, Arachnids, and Other Arthropods To Parasitic Infestations and Diseases of Man and AnimalsDocument44 pagesThe Science Which Deals With The Relation of Insects, Arachnids, and Other Arthropods To Parasitic Infestations and Diseases of Man and AnimalsRabin BaniyaNo ratings yet
- Pathogens in The Environment: - Viruses and Prions - Bacteria and Rickettsiae - Fungi and Algae - Protozoans - HelminthsDocument34 pagesPathogens in The Environment: - Viruses and Prions - Bacteria and Rickettsiae - Fungi and Algae - Protozoans - HelminthsEnaANo ratings yet
- Chigger MitesDocument25 pagesChigger MitesKoleen Lopez ÜNo ratings yet
- Arthropods of Medical ImportanceDocument6 pagesArthropods of Medical ImportanceMarlon Ursua BagalayosNo ratings yet
- Rodent and Mice ControlDocument14 pagesRodent and Mice Controljuan dela cruzNo ratings yet
- 22 SiphonapteraDocument16 pages22 SiphonapteraSmpp MondhaNo ratings yet
- Ticks: Ixodidae - Hard Ticks Argasidae - Soft TicksDocument20 pagesTicks: Ixodidae - Hard Ticks Argasidae - Soft TickssanthiyasandyNo ratings yet
- .Vektor Nyamuk Dan PenyakitnyaDocument96 pages.Vektor Nyamuk Dan PenyakitnyaAngga AgustinoNo ratings yet
- 1 Intro To Exotics 7-2023Document56 pages1 Intro To Exotics 7-2023Hailey WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Class Nematoda - The Roundworms: Blood and Tissue-Dwelling NematodesDocument33 pagesClass Nematoda - The Roundworms: Blood and Tissue-Dwelling NematodesMayank TiwariNo ratings yet
- FleaDocument27 pagesFleau2004969No ratings yet
- Bakul K13 Ectoparasite - RevisiDocument28 pagesBakul K13 Ectoparasite - RevisiagnesNo ratings yet
- 4 - Infectious Pets DiseasesDocument19 pages4 - Infectious Pets DiseasesMohamed ElsamolyNo ratings yet
- Tabani DsDocument10 pagesTabani Dssalmalissu0No ratings yet
- (K33) Pengendalian Artropoda Lain 2016Document22 pages(K33) Pengendalian Artropoda Lain 2016defaNo ratings yet
- Chairuddin P. Lubis Department of Pediatrics Faculty of Medicine University of Sumatera Utara MedanDocument46 pagesChairuddin P. Lubis Department of Pediatrics Faculty of Medicine University of Sumatera Utara MedanVinod RajNo ratings yet
- 2015 Leishmania and Leishmaniasis HabilDocument82 pages2015 Leishmania and Leishmaniasis Habilesammm350No ratings yet
- 5 Glossinidae Tsetse FlyDocument14 pages5 Glossinidae Tsetse FlyVasimNo ratings yet
- BIOL 286 Lecture 1 Introduction Part BDocument20 pagesBIOL 286 Lecture 1 Introduction Part Bevahhassane2003No ratings yet
- NematoDocument15 pagesNematoRen Zo ImpelidoNo ratings yet
- Plague Presentation FinalDocument41 pagesPlague Presentation FinalMazlan MansorNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Types of PestsDocument26 pagesLecture 1 Types of PestsArooj Fatima100% (1)
- 15 Theorical Entomology1Document91 pages15 Theorical Entomology1hhupNo ratings yet
- ZOONOSISDocument53 pagesZOONOSISBiManda Rizki NurhidayatNo ratings yet
- L37 Medical Entomology L1Document19 pagesL37 Medical Entomology L1Soon SheedNo ratings yet
- ParasitesDocument52 pagesParasitesAmmara NaeemNo ratings yet
- DR Yuni - Insect Bite ReactionsDocument9 pagesDR Yuni - Insect Bite Reactionsyuliana khairiNo ratings yet
- Tsetse Flies: Faculty of Health SciencesDocument39 pagesTsetse Flies: Faculty of Health SciencesOsman Mohamed MuhumedNo ratings yet
- Seminar Presentation Plus Ultra 10%Document10 pagesSeminar Presentation Plus Ultra 10%Adaeze Ezem-NjokuNo ratings yet
- RabiesDocument9 pagesRabiessanjay prajapatiNo ratings yet
- Ticks: October 17 & 18, 2017 VM 141 CLASS Entomology & Protozoology DR Criselda Silvestre-Battad LecturerDocument33 pagesTicks: October 17 & 18, 2017 VM 141 CLASS Entomology & Protozoology DR Criselda Silvestre-Battad LecturerDylan Warmfuzzies SalesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3.nature of Biological Control AgentsDocument80 pagesChapter 3.nature of Biological Control AgentsExposer NBNo ratings yet
- Pendahuluan ParasitologiDocument29 pagesPendahuluan ParasitologiTri Ayu Mega SaraswatiNo ratings yet
- 4-Parasitic Zoonosis: Toxoplasmosis Hydatid Cyst LeishmaniasisDocument44 pages4-Parasitic Zoonosis: Toxoplasmosis Hydatid Cyst LeishmaniasisSaher AliNo ratings yet
- Parasitology 3 PDFDocument24 pagesParasitology 3 PDFEdgar MandengNo ratings yet
- Infestation!: Roaches, Bedbugs, Ants, and Other Insect InvadersFrom EverandInfestation!: Roaches, Bedbugs, Ants, and Other Insect InvadersNo ratings yet