Professional Documents
Culture Documents
كيميا لاب
كيميا لاب
Uploaded by
Suzan Salim0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
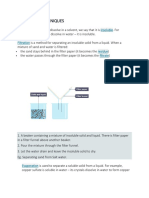
10 views4 pagesPaper chromatography is a technique used to separate and identify relatively small chemical substances such as amino acids, small peptides and sugars. The technique works by applying substances to be identified to a strip of filter paper and allowing a solvent to move up the paper, carrying the substances along at different rates depending on their size. Spots are visualized either by their inherent color or through the use of a locating agent to identify the positions of colorless substances on the chromatography paper.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentPaper chromatography is a technique used to separate and identify relatively small chemical substances such as amino acids, small peptides and sugars. The technique works by applying substances to be identified to a strip of filter paper and allowing a solvent to move up the paper, carrying the substances along at different rates depending on their size. Spots are visualized either by their inherent color or through the use of a locating agent to identify the positions of colorless substances on the chromatography paper.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views4 pagesكيميا لاب
كيميا لاب
Uploaded by
Suzan SalimPaper chromatography is a technique used to separate and identify relatively small chemical substances such as amino acids, small peptides and sugars. The technique works by applying substances to be identified to a strip of filter paper and allowing a solvent to move up the paper, carrying the substances along at different rates depending on their size. Spots are visualized either by their inherent color or through the use of a locating agent to identify the positions of colorless substances on the chromatography paper.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
Facters
• Chromatography separates small molecules in a mixture on the basis of
size
• As the solvent moves up the paper, molecules move at different rates
• When the spots are colourless (most amino acids), a locating agent is needed to
visualise their positions on the chromatography paper
Paper chromatography is a technique used for the separation & identification
of relatively small chemical substances by a moving solvent on sheets or strips
of filter paper
Substances to be identified are ‘spotted’ near one end of the filter paper
As the solvent moves up the paper, different molecules move at different rates
with the smallest molecules moving the fastest
The technique is used for small molecules such as amino acids, small peptides and
sugars
Hydrate
· Ionic compounds that contain specific ratios of loosely bound
water molecules, called waters of hydration.
· Waters of hydration can be removed by heating.
· Compounds that differ only in the
numbers of waters of hydration
can have very different properties.
Copyright 2007 Pearson Benjamin Cummings. All rights reserved.
PROPERTIES ASSOCIATED WITH WATER
HYDRATES: Solids that contain water molecules as part of their
crystalline structure. The water in the hydrate is known as the water of
hydration or the water of crystallization.
HYGROSCOPIC: A substance is hygroscopic if it readily absorbs water
from the atmosphere and forms a hydrate.
DELIQUESCENT: A substance is deliquescent if it absorbs water from the
air until it forms a solution.
DESICCANTS: Compounds that absorb water and are used as drying
agents.
EFFLORESCENCE: The process by which crystalline materials
spontaneously lose water when exposed to air.
You might also like
- Separation TechniquesDocument7 pagesSeparation TechniquesPriyanka WadhwaniNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 2 - Separating MixturesDocument7 pagesChemistry 2 - Separating MixturesNaseeb AliNo ratings yet
- Elements, Compounds and Mixtures PowerpointDocument13 pagesElements, Compounds and Mixtures PowerpointMaxime Van ElslanderNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument41 pagesChemistryAnne kimNo ratings yet
- Separation TechniquesDocument27 pagesSeparation Techniquescarresha applewhaiteNo ratings yet
- Purity of A SubstanceDocument13 pagesPurity of A SubstanceAlly Bin AssadNo ratings yet
- Separating MixturesDocument13 pagesSeparating Mixturesver_at_workNo ratings yet
- ChemDocument5 pagesChemJoelle SwaisNo ratings yet
- Organic ChemistryDocument39 pagesOrganic Chemistryh2312416No ratings yet
- Separating Mixtures PDFDocument4 pagesSeparating Mixtures PDFDenise Adriene ParanNo ratings yet
- Notes - Separating and Purifying SubstancesDocument2 pagesNotes - Separating and Purifying SubstancesJayasutha Raman100% (1)
- Seperation of MixturesDocument24 pagesSeperation of MixturesShehbaaz SinghNo ratings yet
- Separation of MixturesDocument25 pagesSeparation of MixturesYumie YamazukiNo ratings yet
- Separating MixturesDocument4 pagesSeparating MixturesRoxette RoseteNo ratings yet
- Surface ChemistryDocument63 pagesSurface ChemistryChikchikchat ChatNo ratings yet
- Separating Mixtures: Techniques and Applications: Evaporation, Distillation and FiltrationDocument4 pagesSeparating Mixtures: Techniques and Applications: Evaporation, Distillation and FiltrationAndrea SobredillaNo ratings yet
- Let's Discuss Some of The Separation TechniquesDocument6 pagesLet's Discuss Some of The Separation Techniquesmay ann dimaanoNo ratings yet
- Separation TechniquesDocument17 pagesSeparation Techniquesdenise adrieneNo ratings yet
- Filtration, EvaporationDocument3 pagesFiltration, EvaporationH.Mohammad JohanyNo ratings yet
- Different Ways of Separating Mixtures: ChromatographyDocument2 pagesDifferent Ways of Separating Mixtures: ChromatographyClark Hailie Wayne EstrellaNo ratings yet
- Life As A Scientist: 1. States of MatterDocument5 pagesLife As A Scientist: 1. States of MatterManisha ManishaNo ratings yet
- Methods of Purifying Organic Compounds 2024Document11 pagesMethods of Purifying Organic Compounds 2024speechless720No ratings yet
- Chem RevisionDocument5 pagesChem RevisionajeesharulkumaranNo ratings yet
- Study Guide Japan Part 1Document73 pagesStudy Guide Japan Part 1Janzu SalazarNo ratings yet
- 3.drying (Summer Semester)Document62 pages3.drying (Summer Semester)mohammmadNo ratings yet
- Deli Que ScentDocument10 pagesDeli Que ScentJoyce RevitaNo ratings yet
- Handout 3Document8 pagesHandout 3Naomi JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Note On Separating TechniquesDocument8 pagesGrade 7 Note On Separating TechniquesBadass PolapainNo ratings yet
- Our Objective: How Is A Homogeneous Mixture Different From A Heterogeneous Mixture?Document10 pagesOur Objective: How Is A Homogeneous Mixture Different From A Heterogeneous Mixture?Erick Ello RodelNo ratings yet
- Chemical Earth NotesDocument15 pagesChemical Earth NotesLuluNo ratings yet
- 2.1 C6 Separation Techniques - Teacher (27 July 2011)Document27 pages2.1 C6 Separation Techniques - Teacher (27 July 2011)ronnie_gohNo ratings yet
- G07-Chemistry-Notes For Second TermDocument9 pagesG07-Chemistry-Notes For Second TermSkeltten MinecraftNo ratings yet
- Csec Chemistry Chapter 2 - Separations and MixturesDocument14 pagesCsec Chemistry Chapter 2 - Separations and Mixtureschelsea AlexandriaNo ratings yet
- C. Unit 2 Separating Techniques PowerpointDocument17 pagesC. Unit 2 Separating Techniques Powerpointbibjin4No ratings yet
- 2.3 Water and Solutions: Unit 2: Chemistry of LifeDocument27 pages2.3 Water and Solutions: Unit 2: Chemistry of Lifeapi-520057338100% (1)
- Water & SolutionDocument27 pagesWater & SolutionleeNo ratings yet
- Water: 9 Chemistry (Unit 3)Document30 pagesWater: 9 Chemistry (Unit 3)SK GADDAMNo ratings yet
- Purification MethodsDocument10 pagesPurification MethodsamyNo ratings yet
- Notes of "Is Matter Around Us Pure?"Document20 pagesNotes of "Is Matter Around Us Pure?"SKULL XT GAMINGNo ratings yet
- Miscellaneous ProcessesDocument103 pagesMiscellaneous ProcessesAhmed Imran75% (4)
- General Chemistry 1: Greizl Czandreen A. Secjadas 11-STEM AbalosDocument18 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1: Greizl Czandreen A. Secjadas 11-STEM AbalosMark Heinrich B. ParasNo ratings yet
- The Hydrosphere: Industrial Seperation ProcessesDocument1 pageThe Hydrosphere: Industrial Seperation ProcessesAmanda LeNo ratings yet
- DecantationDocument7 pagesDecantationMUHAMMAD AKRAMNo ratings yet
- CHM 120 Purifications of Organic CompoundsDocument21 pagesCHM 120 Purifications of Organic Compoundsgilguilen001No ratings yet
- Separation TechniquesDocument30 pagesSeparation TechniquesSindhu SanthoshNo ratings yet
- FALLSEM2014 15 CP1384 11 Jul 2014 RM01 Structure and Properties of WaterDocument136 pagesFALLSEM2014 15 CP1384 11 Jul 2014 RM01 Structure and Properties of WaterNavaneetha LakshmanNo ratings yet
- Process of Water Treatment SystemDocument33 pagesProcess of Water Treatment Systemروسيده بت محمد سعدNo ratings yet
- 6 (D) Miscellaneous ProcessesDocument59 pages6 (D) Miscellaneous ProcessesYashfa YasinNo ratings yet
- 8 Mixtures and Solutions (Revised)Document44 pages8 Mixtures and Solutions (Revised)Janna May ManliguezNo ratings yet
- Method of PurificationDocument18 pagesMethod of PurificationPratyush KumarNo ratings yet
- SP 1a Adsorption-Part1Document45 pagesSP 1a Adsorption-Part1geevitha raoNo ratings yet
- CHM121 Purification 1A PDFDocument29 pagesCHM121 Purification 1A PDFOyem DavidNo ratings yet
- Chromatography Is Used To Separate Mixtures of Substances Into Their ComponentsDocument8 pagesChromatography Is Used To Separate Mixtures of Substances Into Their ComponentsAyrea Riclye Sanaes'yumealoverNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 and 7 Wastwater TreatmentDocument51 pagesChapter 6 and 7 Wastwater Treatmentgebremeskel.gang24No ratings yet
- Chemistry 5Document18 pagesChemistry 5ShailendraNo ratings yet
- Matter: By: Sir Rylle Andrian P.Barona, LPTDocument40 pagesMatter: By: Sir Rylle Andrian P.Barona, LPTBea Bianca Chavez-AlladoNo ratings yet
- Mixtures and Their Characteristics: GED101-Uu Prepared By: Asgar, Raifa CDocument5 pagesMixtures and Their Characteristics: GED101-Uu Prepared By: Asgar, Raifa CRaifa C. AsgarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13Document36 pagesChapter 13Arlane M. AbenojaNo ratings yet
- Centrifugation, Desiccation and LevigationDocument16 pagesCentrifugation, Desiccation and Levigationengr587No ratings yet
- Oil and Water Won't Mix and Other Mixture Separation Techniques - Chemistry Book for Kids 8-10 | Children's Chemistry BooksFrom EverandOil and Water Won't Mix and Other Mixture Separation Techniques - Chemistry Book for Kids 8-10 | Children's Chemistry BooksNo ratings yet