Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1.7 Video Slides Posted
Uploaded by
Rachel Anne0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views8 pagesOriginal Title
1.7_video_slides_posted.pptx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views8 pages1.7 Video Slides Posted
Uploaded by
Rachel AnneCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 8
Introduction COMPSCI 453 Computer Networks
Professor Jim Kurose
College of Information and Computer Sciences
University of Massachusetts
Overview. What is the Internet? What is
a protocol?
Network edge Class textbook:
Computer Networking: A Top-
Network core Down Approach (8th ed.)
J.F. Kurose, K.W. Ross
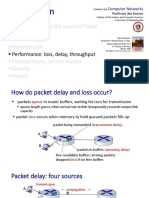
Performance: loss, delay, throughput Pearson, 2020
http://gaia.cs.umass.edu/kurose_ross
Layering, encapsulation, service models
Networks under attack
History
Internet history
1961-1972: Early packet-switching principles
1961: Kleinrock - queueing 1972:
theory shows effectiveness of • ARPAnet public demo
packet-switching • NCP (Network Control Protocol)
1964: Baran - packet-switching first host-host protocol
in military nets • first e-mail program
1967: ARPAnet conceived by • ARPAnet has 15 nodes
Advanced Research Projects
Agency
1969: first ARPAnet node
operational
Internet history
1972-1980: Internetworking, new and proprietary networks
1970: ALOHAnet satellite
Cerf and Kahn’s internetworking
network in Hawaii principles:
1974: Cerf and Kahn - minimalism, autonomy - no
architecture for interconnecting internal changes required to
networks interconnect networks
best-effort service model
1976: Ethernet at Xerox PARC
stateless routing
late70’s: proprietary decentralized control
architectures: DECnet, SNA, XNA define today’s Internet architecture
1979: ARPAnet has 200 nodes
Internet history
1980-1990: new protocols, a proliferation of networks
1983: deployment of TCP/IP new national networks: CSnet,
1982: smtp e-mail protocol BITnet, NSFnet, Minitel
defined 100,000 hosts connected to
1983: DNS defined for name- confederation of networks
to-IP-address translation
1985: ftp protocol defined
1988: TCP congestion control
Internet history
1990, 2000s: commercialization, the Web, new applications
early 1990s: ARPAnet late 1990s – 2000s:
decommissioned more killer apps: instant
1991: NSF lifts restrictions on messaging, P2P file sharing
commercial use of NSFnet network security to forefront
(decommissioned, 1995)
est. 50 million host, 100 million+
early 1990s: Web users
• hypertext [Bush 1945, Nelson 1960’s]
• HTML, HTTP: Berners-Lee
backbone links running at Gbps
• 1994: Mosaic, later Netscape
• late 1990s: commercialization of the
Web
Internet history
2005-present: scale, SDN, mobility, cloud
aggressive deployment of broadband home access (10-100’s Mbps)
2008: software-defined networking (SDN)
increasing ubiquity of high-speed wireless access: 4G/5G, WiFi
service providers (Google, FB, Microsoft) create their own networks
• bypass commercial Internet to connect “close” to end user, providing
“instantaneous” access to social media, search, video content, …
enterprises run their services in “cloud” (e.g., Amazon Web Services,
Microsoft Azure)
rise of smartphones: more mobile than fixed devices on Internet (2017)
~18B devices attached to Internet (2017)
Chapter 1: summary
We’ve covered a “ton” of material! You now have:
Internet overview context, overview,
what’s a protocol? vocabulary, “feel”
network edge, access network, core of networking
• packet-switching versus circuit- more depth, detail,
switching
• Internet structure and fun to follow!
performance: loss, delay, throughput
layering, service , encapsulation
networks under attack
history
Introduction COMPSCI 453 Computer Networks
Professor Jim Kurose
College of Information and Computer Sciences
University of Massachusetts
Overview. What is the Internet? What is
a protocol?
Network edge Class textbook:
Computer Networking: A Top-
Network core Down Approach (8th ed.)
J.F. Kurose, K.W. Ross
Performance: loss, delay, throughput Pearson, 2020
http://gaia.cs.umass.edu/kurose_ross
Layering, encapsulation, service models
Networks under attack
History
Video: 2020, J.F. Kurose, All Rights Reserved
Powerpoint: 1996-2020, J.F. Kurose, K.W. Ross, All Rights Reserved
You might also like
- EW160 AlarmsDocument12 pagesEW160 AlarmsIgor MaricNo ratings yet
- ATLAS HONDA Internship ReportDocument83 pagesATLAS HONDA Internship ReportAhmed Aitsam93% (14)
- Speed of Light Communications and the Internet Protocol (IP)From EverandSpeed of Light Communications and the Internet Protocol (IP)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- SH210 5 SERVCE CD PDF Pages 1 33Document33 pagesSH210 5 SERVCE CD PDF Pages 1 33Em sulistio87% (23)
- EC2 406006 001 EFE 0121 - Controgen Generator Excitation System Description - Rev - ADocument29 pagesEC2 406006 001 EFE 0121 - Controgen Generator Excitation System Description - Rev - AAnonymous bSpP1m8j0n50% (2)
- 1.6 - Network SecurityDocument7 pages1.6 - Network Securityakash123qwNo ratings yet
- Textual Learning Material - Module 1Document44 pagesTextual Learning Material - Module 1SaurabhChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Computer NetworksDocument59 pagesComputer Networksتسنيم الفراصيNo ratings yet
- Ioanu@eed - Usv.ro CAP I - Recapitulare: Titular Curs: Ioan UngureanDocument271 pagesIoanu@eed - Usv.ro CAP I - Recapitulare: Titular Curs: Ioan UngureanCosminNo ratings yet
- Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach: 6 Edition Jim Kurose, Keith Ross Addison-WesleyDocument52 pagesComputer Networking: A Top Down Approach: 6 Edition Jim Kurose, Keith Ross Addison-WesleyMuhammad FaisalNo ratings yet
- Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach: 6 Edition Jim Kurose, Keith Ross Addison-WesleyDocument52 pagesComputer Networking: A Top Down Approach: 6 Edition Jim Kurose, Keith Ross Addison-WesleyMuhammad FaisalNo ratings yet
- Gaitan@eed - Usv.ro CAP I - Recapitulare: Titular Curs: Prof. Dr. Ing. Vasile GĂITANDocument271 pagesGaitan@eed - Usv.ro CAP I - Recapitulare: Titular Curs: Prof. Dr. Ing. Vasile GĂITANsleviciNo ratings yet
- Sunshine, C. A. (1989) - A Brief History of Computer Networking.Document4 pagesSunshine, C. A. (1989) - A Brief History of Computer Networking.Naroa AretxabalaNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Merged PDFDocument141 pagesWeek 1 Merged PDFRaunak PatilNo ratings yet
- Lecture-1 History of Networking (11 Files Merged) (1) (1) (3 Files Merged) (1) (9 Files Merged) (12 Files Merged) (5 Files Merged) (7 Files Merged)Document1,146 pagesLecture-1 History of Networking (11 Files Merged) (1) (1) (3 Files Merged) (1) (9 Files Merged) (12 Files Merged) (5 Files Merged) (7 Files Merged)Nikhil GaddamNo ratings yet
- Presentation Computer Networks 1486029094 257582Document15 pagesPresentation Computer Networks 1486029094 257582sanskar guptaNo ratings yet
- 1 SKG Network Intro PDFDocument29 pages1 SKG Network Intro PDFVed BharathNo ratings yet
- Materi 1 - Latar BelakangDocument30 pagesMateri 1 - Latar Belakangrasyidi arazzNo ratings yet
- NetworkingDocument40 pagesNetworkingBINS THOMASNo ratings yet
- BooksDocument68 pagesBooksAnkur AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Transition To Widespread InfrastructureDocument3 pagesTransition To Widespread Infrastructurematt092No ratings yet
- COE332 Ch01dDocument71 pagesCOE332 Ch01dMem MemNo ratings yet
- Computer NetworkDocument34 pagesComputer NetworkVargheseMartinNo ratings yet
- DF - UNIT-2 NotesDocument40 pagesDF - UNIT-2 NotesMANJUNATHA SNo ratings yet
- 1855osi TCPDocument50 pages1855osi TCPChinmoy GhoshNo ratings yet
- NetworkingDocument41 pagesNetworkingBINS THOMASNo ratings yet
- (TENG 307), Section 1 Project: Wireless CommunicationDocument7 pages(TENG 307), Section 1 Project: Wireless CommunicationWidimongar W. JarqueNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document29 pagesLecture 1Phạm Sơn BìnhNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 1 - Lecture 1 & 2Document74 pagesChapter - 1 - Lecture 1 & 2Junaid SarwarNo ratings yet
- Networking Basics: Carlo FondaDocument61 pagesNetworking Basics: Carlo FondapriankushNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 1-NewversionDocument15 pagesChapter 1 1-NewversionAgent NawabNo ratings yet
- Computer NetworksDocument4 pagesComputer NetworksArun KumarNo ratings yet
- CIR 209 (Lecture 4d) - OSI and TCP-IP ModelDocument22 pagesCIR 209 (Lecture 4d) - OSI and TCP-IP Modeldancanongori9No ratings yet
- Intro To Internet and EmailsDocument32 pagesIntro To Internet and Emailszakayo nyakungaNo ratings yet
- Solutions Manual of Intro To Linear Algebra Gilbert Strang 3rdeditionDocument35 pagesSolutions Manual of Intro To Linear Algebra Gilbert Strang 3rdeditionRahul sharmaNo ratings yet
- Comp 327035225Document4 pagesComp 327035225amritpalmrockNo ratings yet
- Local Area Network: Computer Networks LabDocument7 pagesLocal Area Network: Computer Networks LabljjbNo ratings yet
- Seminar Report On Internet: Submitted in Partial Fulfillement For The Degree of Masters of Business AdministrationDocument24 pagesSeminar Report On Internet: Submitted in Partial Fulfillement For The Degree of Masters of Business AdministrationVikash BhanwalaNo ratings yet
- CMP 474.3 Computer Networks-SyllabusDocument2 pagesCMP 474.3 Computer Networks-SyllabusDaya Ram Budhathoki100% (1)
- Computer Networks: Instructor: Kalyan Sasidhar P S Associate Professor, FB 2109 Kalyan - Sasidhar@daiict - Ac.inDocument28 pagesComputer Networks: Instructor: Kalyan Sasidhar P S Associate Professor, FB 2109 Kalyan - Sasidhar@daiict - Ac.inHeet MistryNo ratings yet
- 19ce013 Aman CN Practical FileDocument87 pages19ce013 Aman CN Practical FileAman SinghNo ratings yet
- 01+ +Internet+History+and+Network+EdgeDocument25 pages01+ +Internet+History+and+Network+Edgedbrianv1No ratings yet
- Ccna Project ReportDocument48 pagesCcna Project ReportISHAN CHAUDHARY89% (36)
- IntroductionDocument2 pagesIntroductiongelaeeNo ratings yet
- Transparencias Introducción - Aplicación - Transporte - v1Document59 pagesTransparencias Introducción - Aplicación - Transporte - v1vobes53358No ratings yet
- AmSci 1989 6 ArpanetDocument6 pagesAmSci 1989 6 Arpanetciudadano ciudadanoNo ratings yet
- Top 100 Networking Interview Questions & AnswersDocument23 pagesTop 100 Networking Interview Questions & Answersrakesh ranjanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Intro To Computer NetworksDocument72 pagesLecture 1 - Intro To Computer NetworksBatool SajidaNo ratings yet
- Local Area NetworkDocument4 pagesLocal Area Networkajaydashora14No ratings yet
- Internet History and Architectural Principles: Advanced Computer NetworksDocument34 pagesInternet History and Architectural Principles: Advanced Computer NetworksPankaj P Raibagkar JainNo ratings yet
- Unit 2-Computer Network FundamentalsDocument43 pagesUnit 2-Computer Network FundamentalsJez LarNo ratings yet
- Computer NetworkDocument25 pagesComputer Networkpaulohe972No ratings yet
- A Term Paper On: Department of Business Administration University of LucknowDocument20 pagesA Term Paper On: Department of Business Administration University of LucknowPawanLUMBANo ratings yet
- CN SyllabusDocument1 pageCN SyllabussachinNo ratings yet
- Internet TechnologyDocument8 pagesInternet TechnologySupta DebNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf MergedDocument9 pagesIlovepdf Mergedade ApriliaNo ratings yet
- Computer Networking: A Survey: September 2015Document6 pagesComputer Networking: A Survey: September 2015VaradNo ratings yet
- Chapter1 5th April2009Document92 pagesChapter1 5th April2009ThirtysevenDessertcafe QuicklyusaAutomallNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document23 pagesLecture 1Vikas DhimanNo ratings yet
- Network Recovery: Protection and Restoration of Optical, SONET-SDH, IP, and MPLSFrom EverandNetwork Recovery: Protection and Restoration of Optical, SONET-SDH, IP, and MPLSRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Internet Multimedia Communications Using SIP: A Modern Approach Including Java® PracticeFrom EverandInternet Multimedia Communications Using SIP: A Modern Approach Including Java® PracticeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- ch1 Supplemental Video Slides PostedDocument38 pagesch1 Supplemental Video Slides PostedRachel AnneNo ratings yet
- 1.4 Video Slides PostedDocument14 pages1.4 Video Slides PostedRachel AnneNo ratings yet
- ch1 Supplemental Video Slides PostedDocument38 pagesch1 Supplemental Video Slides PostedRachel AnneNo ratings yet
- 2.7 Video PostedDocument14 pages2.7 Video PostedRachel AnneNo ratings yet
- 2.3 Video PostedDocument14 pages2.3 Video PostedRachel AnneNo ratings yet
- Brochure Action GuideDocument2 pagesBrochure Action GuideRachel AnneNo ratings yet
- A Novel Monte Carlo Simulation Procedure For Modelling COVID 19 Spread Over TimeDocument9 pagesA Novel Monte Carlo Simulation Procedure For Modelling COVID 19 Spread Over TimeRachel AnneNo ratings yet
- Related Rates, A Conical TankDocument4 pagesRelated Rates, A Conical TankRachel AnneNo ratings yet
- Name: Section:: MATH 121 FINAL EXAM FALL 2010-2011 December 6, 2010Document16 pagesName: Section:: MATH 121 FINAL EXAM FALL 2010-2011 December 6, 2010Rachel AnneNo ratings yet
- MCDocument33 pagesMCRachel AnneNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Powerapps and Microsoft Flow Licensing Guide: July 2019Document17 pagesMicrosoft Powerapps and Microsoft Flow Licensing Guide: July 2019Rachel AnneNo ratings yet
- Bonding Models For Methane, CH - Models Are NOT Reality. Each Has Its Own Strengths and LimitationsDocument12 pagesBonding Models For Methane, CH - Models Are NOT Reality. Each Has Its Own Strengths and LimitationsRachel AnneNo ratings yet
- Warwick Fox's Transpersonal EcologyDocument5 pagesWarwick Fox's Transpersonal EcologyRachel Anne100% (1)
- Barry Commoner's Four Laws of EcologyDocument5 pagesBarry Commoner's Four Laws of EcologyRachel AnneNo ratings yet
- Preventive Maintenance - HematologyDocument5 pagesPreventive Maintenance - HematologyBem GarciaNo ratings yet
- Pthread TutorialDocument26 pagesPthread Tutorialapi-3754827No ratings yet
- Intelligent Smoke & Heat Detectors: Open, Digital Protocol Addressed by The Patented XPERT Card Electronics Free BaseDocument4 pagesIntelligent Smoke & Heat Detectors: Open, Digital Protocol Addressed by The Patented XPERT Card Electronics Free BaseBabali MedNo ratings yet
- Quantum Hopfield NetworksDocument83 pagesQuantum Hopfield NetworksSiddharth SharmaNo ratings yet
- Shopnil Tower 45KVA EicherDocument4 pagesShopnil Tower 45KVA EicherBrown builderNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument2 pagesReviewerAra Mae Pandez HugoNo ratings yet
- Rs 422Document1 pageRs 422rezakaihaniNo ratings yet
- Ficha Tecnica 320D3 GCDocument12 pagesFicha Tecnica 320D3 GCanahdezj88No ratings yet
- Legal Ethics HW 5Document7 pagesLegal Ethics HW 5Julius Robert JuicoNo ratings yet
- Automatic Stair Climbing Wheelchair: Professional Trends in Industrial and Systems Engineering (PTISE)Document7 pagesAutomatic Stair Climbing Wheelchair: Professional Trends in Industrial and Systems Engineering (PTISE)Abdelrahman MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Reference: Digital Image Processing Rafael C. Gonzalez Richard E. WoodsDocument43 pagesReference: Digital Image Processing Rafael C. Gonzalez Richard E. WoodsNisha JosephNo ratings yet
- Mpi Model QuestionsDocument4 pagesMpi Model QuestionshemanthnagNo ratings yet
- Product Guide TrioDocument32 pagesProduct Guide Triomarcosandia1974No ratings yet
- Emergency and Safety ProceduresDocument22 pagesEmergency and Safety Procedurespaupastrana94% (17)
- Chapter Two Complexity AnalysisDocument40 pagesChapter Two Complexity AnalysisSoressa HassenNo ratings yet
- ECO 101 Assignment - Introduction To EconomicsDocument5 pagesECO 101 Assignment - Introduction To EconomicsTabitha WatsaiNo ratings yet
- Tindara Addabbo, Edoardo Ales, Ylenia Curzi, Tommaso Fabbri, Olga Rymkevich, Iacopo Senatori - Performance Appraisal in Modern Employment Relations_ An Interdisciplinary Approach-Springer Internationa.pdfDocument278 pagesTindara Addabbo, Edoardo Ales, Ylenia Curzi, Tommaso Fabbri, Olga Rymkevich, Iacopo Senatori - Performance Appraisal in Modern Employment Relations_ An Interdisciplinary Approach-Springer Internationa.pdfMario ChristopherNo ratings yet
- Tenancy Law ReviewerDocument19 pagesTenancy Law ReviewerSef KimNo ratings yet
- Te 1569 Web PDFDocument272 pagesTe 1569 Web PDFdavid19890109No ratings yet
- Donation Drive List of Donations and BlocksDocument3 pagesDonation Drive List of Donations and BlocksElijah PunzalanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 A Guide To Using UnixDocument53 pagesChapter 2 A Guide To Using UnixAntwon KellyNo ratings yet
- DT2 (80 82)Document18 pagesDT2 (80 82)Anonymous jbeHFUNo ratings yet
- 87 - Case Study On Multicomponent Distillation and Distillation Column SequencingDocument15 pages87 - Case Study On Multicomponent Distillation and Distillation Column SequencingFranklin Santiago Suclla Podesta50% (2)
- Staircase and Lintel As-03Document1 pageStaircase and Lintel As-03Divith B SannakkiNo ratings yet
- Research Proposal IntroductionDocument8 pagesResearch Proposal IntroductionIsaac OmwengaNo ratings yet
- Gis Tabels 2014 15Document24 pagesGis Tabels 2014 15seprwglNo ratings yet