100% found this document useful (1 vote)
463 views68 pagesUnderstanding Plant Tropisms
Here are the answers:
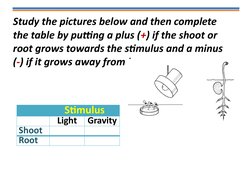
a) i) Stationary clinostat:
Shoot - Upwards
Root - Downwards
ii) Rotating clinostat:
Shoot - Horizontal
Root - Horizontal
b) Geotropism
c) To eliminate the effect of any other stimulus like light,
so that only the effect of gravity could be observed.
Uploaded by
Aghaanaa JaiganeshCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (1 vote)
463 views68 pagesUnderstanding Plant Tropisms
Here are the answers:
a) i) Stationary clinostat:
Shoot - Upwards
Root - Downwards
ii) Rotating clinostat:
Shoot - Horizontal
Root - Horizontal
b) Geotropism
c) To eliminate the effect of any other stimulus like light,
so that only the effect of gravity could be observed.
Uploaded by
Aghaanaa JaiganeshCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
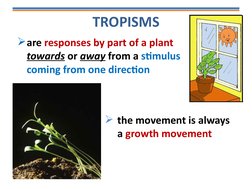
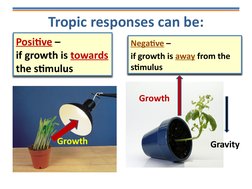
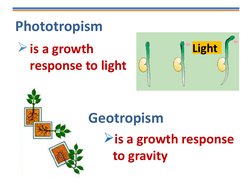
- Tropisms: Introduces tropisms, explaining plant responses to stimuli such as light and gravity through various illustrative examples.
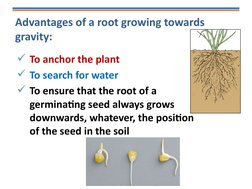
- Root Tropisms: Focuses on roots, detailing how they respond positively to gravity and negatively to light, explaining adaptive benefits.
- Experimental Questions and Activities: Includes exercises and experiments designed to help students explore plant growth responses to different environmental conditions.
- Auxins: Explains the role of auxins in plant growth, detailing cellular effects and experiments demonstrating their influence.
- Experimentation with Clinostats: Details experiments using clinostats to investigate tropisms, providing objectives, methods, and results.
- Seedling Responses: Discusses environmental influences on seedlings through various contextual experiments and diagrammatic questions.