Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Portfolio 3 Matthijs Lucas
Portfolio 3 Matthijs Lucas
Uploaded by
matthijsOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Portfolio 3 Matthijs Lucas
Portfolio 3 Matthijs Lucas
Uploaded by
matthijsCopyright:
Available Formats
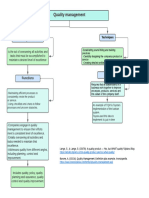
Production systems & Improvement programs
Improvement programs: Agile manufacturing.
Focuses on the change over from one product to
Benchmarking.
another. To increase the ability of producing a wider
Comparing with other companies, colleagues or other industries.
range of products in lower volumes than possible in the
Focussing on cost, quality, delivery time, NPD.
past.
Quality management.
Kaizen.
Helps meeting and exceeding customer expectations by features and
A structured and focused improvement project, where
zero defects. In order to do this, poor quality (waste) needs to be
the priority is action. So small incremental
identified. The following tools can be used: Cost of quality, plan-do-
improvements.
check-act cycle, statistical process control, house of quality, design of
experiments or process capability and six sigma. There are also
Re-engineering.
different models to help companies improving their quality systems,
Focuses on developing completely new ways of doing
such as ISO 9000. ISO 9000 is a series of standards, it represents in
things. To make huge improvements. This requires a
most industries the minimum / market qualifying level of quality.
significant amount of time and skilled and committed
resources.
Cycle time reduction.
Focuses on order process, design, purchasing, production and
distribution. It will reduce the delivery time, reduce costs and improve
quality.
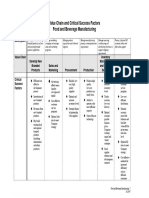
Levers Job shop Batch flow Operator pace line flow Equipment based line flow Continuous flow Just in time FlMS
Human resources • High skilled employees. • Employees assigned to cell. • Employees in teams, trained to • Employees assigned to • Unskilled operators monitor • Multi skilled operators & • Small number of operators,
(Not flexible) • Incentive pay schemes are work on more then one station. operate specific equipment. and track quality attributes. managers. teamwork across departments.
• Expert fees. (Wages) used. • Incentive programmes are used. • Procedures and standards • No incentive pay schemes. • Wages according to number • No incentive pay schemes.
exist for all activities. of skills.
Organisational • Flat by function. • Flat by function. • Often a profit centre running • Hierarchical, centralised and • Hierarchical, centralised and • Flat structure. • Line departments are small.
structure & • Staff is small. • Staff is small. autonomously. bureaucratic structure. bureaucratic structure. • Teams are used extensively. • Staff large.
controls • Labor intensive. • Quality is responsibility of • Management of materials is • Staff large. • Staff large. • KPI’s are mainly costumer- • Quality department
operators. prioritized. • Decisions are taken top- • Quality department focused. responsible for all aspects of
• Scheduling production is down. responsible for all aspects of quality in sc.
prioritized to ensure capacity. quality in SC.
Sourcing • Many suppliers. • Low level of vertical • Little integration, irregular orders, • Partnership relations an • Small number of suppliers, high • Small number of suppliers, • A little vertical integration,
• No / limited control of integration, many suppliers. medium suppliers. option, small number of level of integration. long term relations. many suppliers.
suppliers. • Small irregular orders. • Suppliers evaluated on quality and suppliers. • Evaluating suppliers on cost, • Partnerships, exchanging • Evaluating suppliers on quality,
fast reliable delivery. • Shared responsibility on quality and delivery reliability. information. cost and delivery time.
quality and continuous
improvement.
Production • Make-to-order. • Make-to-order, common • Make-to-order, common • Make-to-stock, forecast. • Make-to-stock, forecast. • Production according to pull • Make-to-order.
planning & control • Small RM & FG components made to stock. components made to stock. • Plans exist far in the future. • Large RM & FG inventories. signals. • Real time scheduling & control.
inventories, large work-in- • MRP is introduced. • Large RM inventory, small WIP & • Larger RM & FG inventories. • Plans available far in the • MRP sets capacity plan. • Small RM & FG inventories.
progress. • Small RM & FG inventories, FG. future. • Inventories are reduced in
large work-in-progress. • Scheduling is flexible. general to stress
improvements.
Process technology • General purpose • General purpose machines. • Following the technical • Very specialized machines, • Highly specialized & • Smaller equipment, shorter • Everything automated,
machines, technology • Set-up times are long, development, semi specialized. technology leader. automated, technology leader. set-up, lower speed. technology leader.
follower. frequency of set-ups is high. • Easy & quick set-up, frequency of • Set-up time reduction • Automated, expensive. • Less expensive • Automated, expensive.
• Set-up times are long. set-ups is high. programmes.
Facilities • Small general purpose. • Linkage between • Medium sized. • Large facilities. • Very large, economy of scale. • Medium sized. • New & tidy facilities.
• Small areas for RM & FG. departments are loose. • Medium speed in production, • Line speed is high and • Production rate is very high, no • Speed of system is steady. • Speed of system is medium but
• Capacity fluctuates, bottlenecks infrequent. synchronized. bottlenecks. smooth.
bottlenecks move.
Matthijs Lucas
Portfolio 3
You might also like
- Mathcad Design Studies Trade-Off AnalysesDocument7 pagesMathcad Design Studies Trade-Off Analysesculai13No ratings yet
- IISE 2021 - Systems OptimizationDocument35 pagesIISE 2021 - Systems OptimizationIntan Putri Maharani SinagaNo ratings yet
- Profile Summary Core Competencies: Santhosh NayakDocument4 pagesProfile Summary Core Competencies: Santhosh NayakVarinder Pal SinghNo ratings yet
- Implementation of A Quality Management SystemDocument20 pagesImplementation of A Quality Management SystemJESUS DANIEL CORRALES MENDOZA100% (1)
- Agile QuizDocument19 pagesAgile QuizGRAZIELE LIMA MIRANDA100% (1)
- Foundation Sample Questionsbyk ValueDocument6 pagesFoundation Sample Questionsbyk ValuesuhamadiNo ratings yet
- ? Functional CompetenciesDocument8 pages? Functional CompetenciesRamy MagdyNo ratings yet
- Full Comparison - Agile Vs Scrum Vs Waterfall Vs KanbanDocument21 pagesFull Comparison - Agile Vs Scrum Vs Waterfall Vs KanbanparadescartarNo ratings yet
- Apqp & Ppap PDFDocument52 pagesApqp & Ppap PDFAman Poonia100% (1)
- Improve Your Business Through Kaizen: Boost your results with continuous improvementFrom EverandImprove Your Business Through Kaizen: Boost your results with continuous improvementRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Chapter 6 Process ImprovementDocument52 pagesChapter 6 Process ImprovementArvin RajNo ratings yet
- Benefits of MRP II: Manufacturing Resource PlanningDocument2 pagesBenefits of MRP II: Manufacturing Resource PlanningFazli Aleem100% (2)
- Business Analyst - MurexDocument2 pagesBusiness Analyst - MurexBogdan DobrieNo ratings yet
- Quality Function DeploymentDocument39 pagesQuality Function Deploymentnanda yudhistiraNo ratings yet
- Fulfil OrderDocument28 pagesFulfil OrderRachmad AriefNo ratings yet
- Actividad 7 Tema 3 Manufactura EsbeltaDocument7 pagesActividad 7 Tema 3 Manufactura EsbeltaDaniel AlemánNo ratings yet
- SQM Assignment 1Document3 pagesSQM Assignment 12K20SE164YASHNo ratings yet
- Business & Management Mind Map - W4Document1 pageBusiness & Management Mind Map - W4Diva Tertia AlmiraNo ratings yet
- Advanced Product Quality Planning For New Product DevelopmentDocument1 pageAdvanced Product Quality Planning For New Product Developmentabdalballah1151No ratings yet
- Operation Management: CHAPTER 1: Introduction To Total Quality ManagementDocument24 pagesOperation Management: CHAPTER 1: Introduction To Total Quality ManagementRica CalderonNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document19 pagesLecture 3SanchuNo ratings yet
- StratmanDocument8 pagesStratmanblueviolet21No ratings yet
- 14 - Module1topic8Document5 pages14 - Module1topic8Annakay FaircloughNo ratings yet
- Quality - You Know It When You See It Fit For Purpose Meets The Customer's Requirements Delighting The CustomerDocument21 pagesQuality - You Know It When You See It Fit For Purpose Meets The Customer's Requirements Delighting The CustomerRama Shanker LalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 TQMDocument2 pagesChapter 5 TQMEugene PilotonNo ratings yet
- Activity A9. Cognitive Map. 192169Document1 pageActivity A9. Cognitive Map. 192169Joanna HerreraNo ratings yet
- Value Engineering WhitepaperDocument3 pagesValue Engineering WhitepaperPaulanthonyGeorgeNo ratings yet
- Managing Product Introduction ProjectsDocument6 pagesManaging Product Introduction ProjectsTGTrindadeNo ratings yet
- Target Operating Model Customer Service 16Document5 pagesTarget Operating Model Customer Service 16VINENNo ratings yet
- Stratman 1Document8 pagesStratman 1blueviolet21No ratings yet
- Presentation Deck For Paynet - LGDocument7 pagesPresentation Deck For Paynet - LGArveentheran DevarajanNo ratings yet
- Capacity Planning, Group 8, FPODocument11 pagesCapacity Planning, Group 8, FPOKalpesh TailorNo ratings yet
- Machine Learning Canvas: Background Solution Data Modeling FeedbackDocument1 pageMachine Learning Canvas: Background Solution Data Modeling FeedbackLeonard TVNo ratings yet
- Controlmapping Finalproject 03Document3 pagesControlmapping Finalproject 03siti zubaidah purwaning arumNo ratings yet
- Æ For The ICANDO Chemicals System (To The Original Table Are Added and As Stakeholders) : ÆDocument6 pagesÆ For The ICANDO Chemicals System (To The Original Table Are Added and As Stakeholders) : ÆElzbethyNo ratings yet
- Informmation System - Hindalco MisDocument3 pagesInformmation System - Hindalco MisPurushottam WankhedeNo ratings yet
- Operational Management ReviewerDocument5 pagesOperational Management ReviewerADRHEINE RENOVALLESNo ratings yet
- Quality in IT Projects Cheat Sheet: by ViaDocument2 pagesQuality in IT Projects Cheat Sheet: by ViadilaNo ratings yet
- Cbmec 2 Chap. 8Document8 pagesCbmec 2 Chap. 8Robert Adrian YambotNo ratings yet
- Homework Week 4Document3 pagesHomework Week 4esmeralda.cruz217751No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Managing QualityDocument21 pagesChapter 4 Managing QualityAndrew Pradana PutraNo ratings yet
- Agile NotesDocument10 pagesAgile Notesnavdeep kaurNo ratings yet
- Benchmarking StepsDocument28 pagesBenchmarking Stepsdni oduNo ratings yet
- CSFs F&BDocument2 pagesCSFs F&Btranlamtuyen1911No ratings yet
- Ebook - Information Technology Project Management-254-272Document19 pagesEbook - Information Technology Project Management-254-272Milleony TianaNo ratings yet
- TQM ReviewerDocument8 pagesTQM ReviewerLeslie SilverioNo ratings yet
- 1) Continuous Improvement: Chapter 6: Managing QualityDocument3 pages1) Continuous Improvement: Chapter 6: Managing QualityShyrine EjemNo ratings yet
- 1-49 MergedDocument49 pages1-49 Mergednesey76043No ratings yet
- 09 Quiz 1Document1 page09 Quiz 1Von Marvic PonceNo ratings yet
- Opman Chapter 45610Document20 pagesOpman Chapter 45610ABBY ROSE PERALTANo ratings yet
- Nestle-Chapter 06Document22 pagesNestle-Chapter 06Tahseen ArshadNo ratings yet
- Financial - Services - 6 Sigma - Program Overview G2 Consulting - GVS RAODocument2 pagesFinancial - Services - 6 Sigma - Program Overview G2 Consulting - GVS RAOGVS RaoNo ratings yet
- Business Process Management w5 PDFDocument8 pagesBusiness Process Management w5 PDFGerardo GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Product DesignDocument6 pagesProduct Designayushnk6No ratings yet
- Quality Assurance For A Stable Server OperationDocument7 pagesQuality Assurance For A Stable Server OperationJo-Sharon UdohNo ratings yet
- WCE2013 pp634-639 PDFDocument6 pagesWCE2013 pp634-639 PDFVishal KumarNo ratings yet
- Highlights PrelimsDocument3 pagesHighlights Prelimsedu.teacherchaNo ratings yet
- Continuous Improvement Under Modern Quality Systems and CgmpsDocument27 pagesContinuous Improvement Under Modern Quality Systems and CgmpsyusranarifNo ratings yet
- Competency Dictionary 75 ComDocument92 pagesCompetency Dictionary 75 Commohammedhosni911No ratings yet
- To Total Quality Management: Prepared By: PRINCESS DAE D. LIMDocument12 pagesTo Total Quality Management: Prepared By: PRINCESS DAE D. LIMCess Dae LimNo ratings yet
- A QFD Based Performance Measurement ToolDocument10 pagesA QFD Based Performance Measurement Toolpatortiz1980No ratings yet
- Cleaner ProduktionDocument78 pagesCleaner ProduktionVina YusniartiNo ratings yet
- Tiss 1-10 PrintDocument24 pagesTiss 1-10 PrintSNEHAL GARGNo ratings yet
- Case Study: Manufacturing Process Improvement: Demonstrated ExperienceDocument2 pagesCase Study: Manufacturing Process Improvement: Demonstrated ExperienceshailendraNo ratings yet
- CM Saini 04.01.2022 PM IntroductionDocument44 pagesCM Saini 04.01.2022 PM IntroductionManish GuptaNo ratings yet
- Oracle Product Lifecycle Management ENGDocument60 pagesOracle Product Lifecycle Management ENGRidwansyah HaryoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 11Document29 pagesLecture 11ahsan puriNo ratings yet
- Resume ParseDocument3 pagesResume ParseALI HAIDERNo ratings yet
- AI and IPDocument60 pagesAI and IPkripa shresthaNo ratings yet
- CNC Machining Control SystemsDocument14 pagesCNC Machining Control SystemsraviNo ratings yet
- 01Document7 pages01Patricia AmadorNo ratings yet
- BPM Conference Portugal 2013 - Ivo Velichkov "Reasoning With Taskless BPMN "Document42 pagesBPM Conference Portugal 2013 - Ivo Velichkov "Reasoning With Taskless BPMN "Escola de Estudos Avançados Grupo RumosNo ratings yet
- Smart CBM Brochure EnglishDocument4 pagesSmart CBM Brochure EnglishAlbeiro MolinaNo ratings yet
- Resume - Isuru Nipun Hewamanna - Business Analyst - 5yrsDocument2 pagesResume - Isuru Nipun Hewamanna - Business Analyst - 5yrsMoyeed MaXxNo ratings yet
- Specialized Process Models: Session - 4Document16 pagesSpecialized Process Models: Session - 4NanishivaNo ratings yet
- Artikel MMT Lisa Nilhuda 17002060Document6 pagesArtikel MMT Lisa Nilhuda 17002060khansNo ratings yet
- Environmental Sound Classificationwith Convolutional Neural NetworksDocument6 pagesEnvironmental Sound Classificationwith Convolutional Neural Networksamine hamdiNo ratings yet
- Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering Chaitanya Bharathi Institute of TechnologyDocument15 pagesDepartment of Electronics and Communication Engineering Chaitanya Bharathi Institute of TechnologyNAVEEN CHANDRANo ratings yet
- Top ISTQB Interview Questions and Answers Part 2Document13 pagesTop ISTQB Interview Questions and Answers Part 2sabbam s deekshithNo ratings yet
- Introduction To System Analysis and DesignDocument1 pageIntroduction To System Analysis and Designaust austNo ratings yet
- Software Engineering: Spring Term 2016 Marymount University School of Business Administration Professor SuydamDocument36 pagesSoftware Engineering: Spring Term 2016 Marymount University School of Business Administration Professor SuydamCaro Torres CarrilloNo ratings yet
- 00 OMII Outline Book CJ 15 Ed International PDFDocument3 pages00 OMII Outline Book CJ 15 Ed International PDFDeepanshuAgarwalNo ratings yet
- N Modular RedundancyDocument15 pagesN Modular RedundancyShambhu KhanalNo ratings yet
- ProfileDocument6 pagesProfileAmar DoshiNo ratings yet
- Unit - Ii: Process PlanningDocument24 pagesUnit - Ii: Process PlanningJackson ..No ratings yet
- Dbms Case ToolsDocument1 pageDbms Case ToolsVaibhav AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Business Process RedesignDocument8 pagesBusiness Process RedesignlogautamNo ratings yet
- Fault Tree Analysis GuideDocument6 pagesFault Tree Analysis GuideBong BongNo ratings yet
- ENGR 410 Process Instrumentation and ControlDocument2 pagesENGR 410 Process Instrumentation and ControlRajesh RoyNo ratings yet
- Y20cs027 InternshipDocument18 pagesY20cs027 InternshipSARATH CHANDRANo ratings yet