0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1K views30 pagesIcepak Tutorial
This document provides a tutorial for using Ansys Icepak to simulate electronic cooling solutions. It outlines the steps of preliminary settings, elements drawing, simulation setup, and reviewing simulation results. Icepak uses Ansys Fluent CFD to analyze thermal and fluid flow in ICs, packages, PCBs and electronics. Key steps include defining materials, geometry, mesh, boundary conditions, and analyzing the model to obtain thermal and velocity plots and data. Icepak can perform steady-state and transient simulations to estimate thermal performance over time.
Uploaded by
Atharva Joshi.Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1K views30 pagesIcepak Tutorial
This document provides a tutorial for using Ansys Icepak to simulate electronic cooling solutions. It outlines the steps of preliminary settings, elements drawing, simulation setup, and reviewing simulation results. Icepak uses Ansys Fluent CFD to analyze thermal and fluid flow in ICs, packages, PCBs and electronics. Key steps include defining materials, geometry, mesh, boundary conditions, and analyzing the model to obtain thermal and velocity plots and data. Icepak can perform steady-state and transient simulations to estimate thermal performance over time.
Uploaded by
Atharva Joshi.Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Icepac Introduction: Describes Ansys Icepak's role in electronic cooling solutions and provides examples of its applications.
- Preliminary Settings: Outlines the initial conditions necessary for running simulations in Ansys Icepak, focusing on solution types and temperature settings.
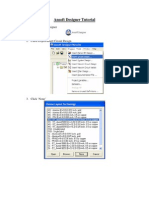
- Elements Drawing: Guides the user on configuring and creating elements in Icepak, including coordinate systems, trimming, and regions.
- Simulation Setup: Covers detailed setup processes for simulations such as material assignment, mesh configuration, and analysis setup.
- Simulation Result: Discusses how to interpret and display the results of simulations, with focus on plot fields and simulation data analysis.