0% found this document useful (0 votes)
565 views9 pagesArray Operations in Data Structures
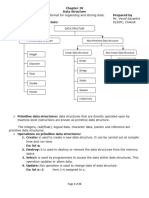
The document discusses various operations on array data structures. It describes how arrays are represented in memory, including the base address and computation of element addresses. It also discusses traversing a linear array, inserting and deleting elements from a linear array, and sorting a linear array using bubble sort. The key operations covered are traversing, inserting, deleting, and sorting of elements in linear arrays.
Uploaded by
YashCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
565 views9 pagesArray Operations in Data Structures
The document discusses various operations on array data structures. It describes how arrays are represented in memory, including the base address and computation of element addresses. It also discusses traversing a linear array, inserting and deleting elements from a linear array, and sorting a linear array using bubble sort. The key operations covered are traversing, inserting, deleting, and sorting of elements in linear arrays.
Uploaded by
YashCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd