Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Photosynthesis
Uploaded by
Kim Bryan A. Galias0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views22 pages1. Photosynthesis is the process by which plants convert light energy from the sun into chemical energy stored in sugars.
2. Chlorophyll is the green pigment in plants that absorbs sunlight and allows plants to produce food from carbon dioxide and water through photosynthesis.
3. Stomata are openings on plant leaves that open and close to control gas exchange, with guard cells regulating their opening and closing.
Original Description:
Original Title
5. Photosynthesis
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1. Photosynthesis is the process by which plants convert light energy from the sun into chemical energy stored in sugars.
2. Chlorophyll is the green pigment in plants that absorbs sunlight and allows plants to produce food from carbon dioxide and water through photosynthesis.
3. Stomata are openings on plant leaves that open and close to control gas exchange, with guard cells regulating their opening and closing.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views22 pagesPhotosynthesis
Uploaded by
Kim Bryan A. Galias1. Photosynthesis is the process by which plants convert light energy from the sun into chemical energy stored in sugars.
2. Chlorophyll is the green pigment in plants that absorbs sunlight and allows plants to produce food from carbon dioxide and water through photosynthesis.
3. Stomata are openings on plant leaves that open and close to control gas exchange, with guard cells regulating their opening and closing.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 22
SCIENCE 9
Kim Bryan A. Galias
Fix Me I’m
Broken
EHHINOOPSSSTTY
is the process of converting light
energy into chemical energy
AEIINOPRRST
A light-dependent process in some
plants resulting in the oxidization
of glycolic acid and release carbon
dioxide under some environmental
conditions
YRPOOLLLHHC
A green substance in plants that
makes it possible for them to
make food from carbon dioxide
and water
ACDEG LLRU
One of the two crescent-shaped
epidermal cells that border and
control the opening and closing of
the stomata.
AAMOSTT
Opening in the epidermis of a
plant organ (as a leaf) through
which gaseous exchange takes
place
AGRSU
End product of photosynthesis
Photosynthesi
s
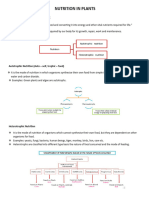
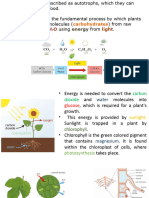
Photosynthesis
• an essential process because human
and animals depends on plant for
nourishment, shelter, and medicine.
• it comes from the Greek word phos,
which means light, and synthesis
which means putting together.
• Plants and other photosynthetic
organisms contains chlorophyll
that traps light energy from the sun
and converts is into chemical energy
stored in sugar (glucose) and other
organic molecules.
• Chlorophyll is a green pigment in
plants that is found in chloroplast.
• The chloroplast of plants use a
process called photosynthesis.
• Plants get the raw materials from
soil, the air and the sun.
• When it rains, water gets absorbed
into the ground. Plants take in water
along with minerals from soil
through its roots.
• Chlorophyll traps light from the sun
and carbon dioxide through the
stomata.
• It is in the leaves of the plant where
photosynthesis takes place.
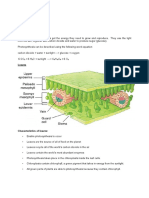
Internal Structure of Leaf
• Cuticle – this is a waxy substance
covering the upper epidermis and
protects the leaf
• from dehydration.
• Upper Epidermis – the outer layer
that protects the leaf.
• Palisade Mesophyll Cell – The cells
that contains chloroplasts
• Chloroplasts – cell organelle that
contains chlorophyll
• Xylem – Vascular tube carrying
water throughout the plant
• Phloem – Vascular tube carrying
dissolved sugar molecules
throughout the plant
• Guard cell – one of the two
crescent-shaped epidermal cells that
open and close a plant stomata
• Stomata – openings in the
epidermis of a plant where gas
exchange occurs
You might also like
- Chapter 6. PhotosynthesisDocument53 pagesChapter 6. Photosynthesisankurbiology100% (6)
- Biology Notes PDFDocument79 pagesBiology Notes PDFSaket GudimellaNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Notes - BiologyDocument8 pagesPhotosynthesis Notes - Biologythe lillyNo ratings yet
- c4 l1 Energy Flow in EcosystemDocument19 pagesc4 l1 Energy Flow in EcosystemShinesky GupongNo ratings yet
- Q2 L3 Science 9Document31 pagesQ2 L3 Science 9Raph tsuNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis and RespirationDocument46 pagesPhotosynthesis and RespirationCarmsNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis PDFDocument30 pagesPhotosynthesis PDFbobbyhaha05No ratings yet
- Plant Nutrition NoteDocument5 pagesPlant Nutrition NoteYolanda JesslinaNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1 (Photosynthesis)Document3 pagesGeneral Biology 1 (Photosynthesis)Jean Dacles100% (1)
- Biology Photosynthesis How Do Plants Get Their Energy?Document11 pagesBiology Photosynthesis How Do Plants Get Their Energy?rickyNo ratings yet
- Plant NutritionDocument10 pagesPlant Nutritiontazbeed rahmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 How Green Plants FeedDocument41 pagesChapter 5 How Green Plants FeedAnonymous s5veYTCyWHNo ratings yet
- All About PhotossynthesisDocument7 pagesAll About Photossynthesisapi-341032878No ratings yet
- Nutrition in PlantsDocument6 pagesNutrition in PlantsSarada KasyapNo ratings yet
- This Chapter Looks at PhotosynthesisDocument5 pagesThis Chapter Looks at PhotosynthesisGiuseppe CondelloNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in Plants 1 PDFDocument6 pagesNutrition in Plants 1 PDFNakshatra PaliwalNo ratings yet
- (Week 9) PhotosynthesisDocument13 pages(Week 9) PhotosynthesisNaiza AlamanNo ratings yet
- The Process of PhotosynthesisDocument2 pagesThe Process of Photosynthesisnelia mae laroyaNo ratings yet
- BotanicaDocument4 pagesBotanicacelineadziladzianNo ratings yet
- Fun Facts of PhotosynthesisDocument2 pagesFun Facts of PhotosynthesisPinkpink ChiuNo ratings yet
- NUTRITION - RegDocument35 pagesNUTRITION - Regwairimucarren77No ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document77 pagesChapter 7Joel CabañasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document4 pagesChapter 10Mahir ShahriyarNo ratings yet
- Pre-Labs 3: 1. What Are Autotrophs and Heterotrophs? Give Each One ExampleDocument4 pagesPre-Labs 3: 1. What Are Autotrophs and Heterotrophs? Give Each One ExampleGiao TranNo ratings yet
- 8 PhotosynthesisDocument8 pages8 PhotosynthesisRAVINDRA PRASADNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis 1 AmlDocument3 pagesPhotosynthesis 1 Amlapi-3731257No ratings yet
- Notes Grade 8 - Chapter 6Document7 pagesNotes Grade 8 - Chapter 6qasimzebest2010No ratings yet
- Photosynthesis in PlantasDocument4 pagesPhotosynthesis in PlantasAedeni MirandaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Plant ProcessesDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Plant ProcessesRajiv SinghNo ratings yet
- PlantsNotesDistanceLearning 1 PDFDocument3 pagesPlantsNotesDistanceLearning 1 PDFdesiNo ratings yet
- Biolab 2Document3 pagesBiolab 2diemtruc414No ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Plant NutritionDocument20 pagesChapter 6 - Plant Nutritionkiera angNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in PlantsDocument2 pagesNutrition in PlantsAhmed OmarNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis: Prepared By: Raz Jawhar 9-ADocument8 pagesPhotosynthesis: Prepared By: Raz Jawhar 9-ArjchkrksnzNo ratings yet
- Plant NutritionDocument9 pagesPlant Nutritionakshai.ar13No ratings yet
- Life ProcessesDocument36 pagesLife Processes2erwr100% (1)
- Year 8:biology Chapter 1: PlantsDocument7 pagesYear 8:biology Chapter 1: PlantsrickyNo ratings yet
- Concept Notes Concept Notes Concept NotesDocument2 pagesConcept Notes Concept Notes Concept NotesIsmaelAlongNo ratings yet
- Process of Plants/Crops Making Their Food and The Importance To Study The Mechanism For Plant PhysiologistsDocument17 pagesProcess of Plants/Crops Making Their Food and The Importance To Study The Mechanism For Plant PhysiologistsJos siNo ratings yet
- Labbio Sat DangPhuongQuynh Prelab3Document3 pagesLabbio Sat DangPhuongQuynh Prelab3Quynh Dang PhuongNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis #2Document1 pagePhotosynthesis #2Wally WestNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument86 pagesPhotosynthesisReinalyn Claire DizonNo ratings yet
- Bio Topic 4 Notes PDFDocument11 pagesBio Topic 4 Notes PDFdgfhjNo ratings yet
- Life of PlantsDocument8 pagesLife of PlantsKhlane R. LunaNo ratings yet
- PHOTOSYNTHESISDocument14 pagesPHOTOSYNTHESIStintin plataNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in PlantsDocument6 pagesNutrition in PlantsVikrant SharmaNo ratings yet
- Cell EnergyDocument29 pagesCell EnergyKimberly Anne T. RinNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Class 10Document14 pagesPhotosynthesis Class 10shreya morajkarNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes SummaryDocument12 pagesBiology Notes Summaryrobin.kipchumbaNo ratings yet
- Biology Preliminary Study NotesDocument23 pagesBiology Preliminary Study NotesNabiha SyedaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 ChloroplastDocument43 pagesChapter 5 Chloroplastapi-302118206No ratings yet
- PLB 101 - Excretion and Transportation Note, TypedDocument8 pagesPLB 101 - Excretion and Transportation Note, Typedabdulmaliqopeyemi04No ratings yet
- Kendriya Vidyalaya, Jalgaon Study Material - Class Vii Chapter-Nutrition in PlantsDocument5 pagesKendriya Vidyalaya, Jalgaon Study Material - Class Vii Chapter-Nutrition in PlantsMathew AbrahamNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument16 pagesPhotosynthesisDivine Mahrke RodrigoNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis?Document2 pagesPhotosynthesis?PrageethNo ratings yet
- Plants Food Chemical Carbon Dioxide Algae Protists Bacteria Earth ChemoautotrophsDocument1 pagePlants Food Chemical Carbon Dioxide Algae Protists Bacteria Earth Chemoautotrophsdarenven 1996No ratings yet
- 07 PlantPhysiology ReadingDocument4 pages07 PlantPhysiology ReadingMahaletchumyKavidasanNo ratings yet
- Write Ups Chapter 7Document12 pagesWrite Ups Chapter 7Joel CabañasNo ratings yet
- Understanding Photosynthesis with Max Axiom Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceFrom EverandUnderstanding Photosynthesis with Max Axiom Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceNo ratings yet