Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Robotics
Uploaded by
glpsurdu kodibag0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views19 pagesPpt
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentPpt
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views19 pagesRobotics
Uploaded by
glpsurdu kodibagPpt
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 19
Computer Network Architecture
• The design and setup of a computer network is called Computer Network Architecture. It is the
organization and arrangement of different network devices (i.e., the clients such as PCs, desktops,
laptops, mobiles etc.) at both physical and logical levels in order to fulfil the needs of the end
user/customer.
• The two most well-known Computer Network Architectures are:
09/07/2023 Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, NMAMIT,NITTE 1
Peer-to-Peer
• The peers referred to here are the individual
devices linked together directly, having equal
responsibilities and equal powers without the
presence of any central authority.
• Due to the absence of a central device in
charge of tasks, this architecture is also known
as decentralized architecture.
• Each computer has special rights for resource
sharing, however this might cause issues if the
computer with the resource is unavailable.
• Useful in smaller environments with less
number of computers.
09/07/2023 Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, NMAMIT,NITTE 2
Advantages of Peer to Peer Network
• No particular device is a client or a server, the
tasks and responsibilities of servers are
distributed among all the devices, which also
act as clients.
• Very inexpensive to set up, as there is no
requirement of a centralized server, and this
also ensures that in case of any failure in the
network, all unaffected devices continue to
operate normally.
• It’s simple to set up and maintain because
each computer runs independently.
09/07/2023 Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, NMAMIT,NITTE 3
Disadvantages of Peer to Peer Network
• No centralized system, thus difficult to keep a
backup of the data in case of any fault.
• It has a security flaw because the computers
are self-managed.
• With a growth in the number of machines on
this network, performance, security, and
access may all become big issues
09/07/2023 Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, NMAMIT,NITTE 4
Client-Server Architecture
• This is also known as centralized architecture,
as one powerful central computer is in charge
of serving all the requests from the client
computers. This central computer is a server.
• The client computers connect to the server as
and when they require the use of shared
resources or shared data. All of the shared data
is stored solely in the server, and not on any
other computer.
• A server handles all of the key tasks, such as
security and network administration.
• All of the clients interact with one another via
a server.
09/07/2023 Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, NMAMIT,NITTE 5
Advantages of Client-Server Architecture
• This type of architecture is much easier to
scale since it is much more convenient to add
more server computers than configure the
network on each and every computer (as is the
case in peer-to-peer architecture).
• Much faster network speeds.
• Because a single server manages the shared
resources in a Client/Server network, there is
improvement in security.
• Backing up data is easy because of the
centralized system.
• The server provides a customized Network
Operating System (NOS) to offer resources to
a large number of users that want them.
09/07/2023 Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, NMAMIT,NITTE 6
Disadvantages of Client-Server Architecture
• More prone to downtime because if the server
fails, none of the client machines are able to
get their requests served.
• Requirement of a dedicated network
administrator to handle all of the resources.
• It is far more expensive than P2P. This is due
to the requirement for a server with more
RAM, as well as the necessity for several
networking devices such as hubs, routers,
switches, and so on
09/07/2023 Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, NMAMIT,NITTE 7
There are some more lesser-known computer
architectures
09/07/2023 Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, NMAMIT,NITTE 8
Centralized Computing Architecture
One powerful computer is utilized to service one or more
low-powered computers in centralized computing
architecture. The nodes under the centralized architecture are
not linked; they are only connected to the server.
The centralized computing architecture includes the
following components:
• The primary, mainframe computer which handles all
processing.
• Terminals are connected to a central computer and function
as input/output devices.
• Linking of at least two mainframe computers together via
networks. Terminals communicate solely with the
mainframe and never with one another.
09/07/2023 Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, NMAMIT,NITTE 9
Distributed Computing Architecture
A distributed architecture connects one or more nodes, which are
personal computers. It supports a variety of functions, including
file sharing, hardware sharing, and network sharing. The nodes
in the distributed architecture can manage their own data and
rely on the network for administration rather than data
processing.
The following components are found in distributed computing
architecture:
• Different computers are effective at performing independently.
• Completion of tasks on multiple computers locally.
• Networks enable computers to exchange data and services, but
they do not offer processing help.
09/07/2023 Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, NMAMIT,NITTE 10
Collaborative Computing Architecture
The collaborative computing architecture is a hybrid of
centralized and decentralized computing. Individual
members of a network can process their users’
fundamental needs under the collaborative model.
A database server, such as an MSSQL server or an
ORACLE server, for example, observes or manages all
database-related operations on all network nodes. The
model will, however, execute requests that are not from
the database
09/07/2023 Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, NMAMIT,NITTE 11
Summary
• we have discussed the different types of architecture of computer network, such as peer to peer
architecture and client-server architecture, along with the advantages and disadvantages of each.
We have also discussed some architecture models such as: centralized computing, distributed
computing, collaborative computing.
09/07/2023 Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, NMAMIT,NITTE 12
09/07/2023 Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, NMAMIT,NITTE 13
OSI Model
• OSI stands for Open System Interconnection is a reference model that describes how information
from a software application in one computer moves through a physical medium to the software
application in another computer.
• OSI consists of seven layers, and each layer performs a particular network function.
• OSI model was developed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) in 1984,
and it is now considered as an architectural model for the inter-computer communications.
• OSI model divides the whole task into seven smaller and manageable tasks. Each layer is assigned
a particular task.
• Each layer is self-contained, so that tas.k assigned to each layer can be performed independently
09/07/2023 Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, NMAMIT,NITTE 14
Characteristics of OSI Model
• The OSI model is divided into two layers: upper layers and
lower layers.
• The upper layer of the OSI model mainly deals with the
application related issues, and they are implemented only in
the software. The application layer is closest to the end user.
Both the end user and the application layer interact with the
software applications. An upper layer refers to the layer just
above another layer.
• The lower layer of the OSI model deals with the data
transport issues. The data link layer and the physical layer
are implemented in hardware and software. The physical
layer is the lowest layer of the OSI model and is closest to
the physical medium. The physical layer is mainly
responsible for placing the information on the physical
medium.
09/07/2023 Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, NMAMIT,NITTE 15
Functions of the OSI Layers
There are the seven OSI layers. Each layer has different
functions. A list of seven layers are given below:
1. Physical Layer
2. Data-Link Layer
3. Network Layer
4. Transport Layer
5. Session Layer
6. Presentation Layer
7. Application Layer
09/07/2023 Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, NMAMIT,NITTE 16
09/07/2023 Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, NMAMIT,NITTE 17
Human–machine interfaces
A human–machine interface is built on either a microprocessor
or an FPGA chipset, which requires its software to include at
least an application program and an operating system.
The human–machine interface (HMI) software enables
operators to manage industrial and process control machinery
via a computer-based graphical user interface (GUI). There are
two basic types of HMI software: supervisory level and
machine level. The supervisory level is designed for control
room environment and used for system control and data
acquisition (SCADA) a process control application which
collects data from sensors on the shop floor and sends the
information to a central computer for processing.
09/07/2023 Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, NMAMIT,NITTE 18
The cutting area is an important section in the float glass production
line, which includes many productions control equipment, such as
longitudinal cutting, transverse cutting, conveying roller table, etc. The
main control part of the whole system is PLC, and the monitoring will
be undertaken by HMI. Is it required to use both HMI and PLC, As
opposed to just a PLC in this Production line? Justify your statement.
09/07/2023 Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, NMAMIT,NITTE 19
You might also like
- Fundamentals of Modern Computer Architecture: From Logic Gates to Parallel ProcessingFrom EverandFundamentals of Modern Computer Architecture: From Logic Gates to Parallel ProcessingNo ratings yet
- B D C & N: Usiness ATA Ommunications EtworkingDocument41 pagesB D C & N: Usiness ATA Ommunications EtworkingMoe KhalilNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Made Simple: Navigating the Cloud: A Practical Guide to Cloud ComputingFrom EverandCloud Computing Made Simple: Navigating the Cloud: A Practical Guide to Cloud ComputingNo ratings yet
- Unit - 1: Cloud Architecture and ModelDocument9 pagesUnit - 1: Cloud Architecture and ModelRitu SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Group No 13Document15 pagesGroup No 13Waleed Abdullah2k19 EE603No ratings yet
- Designing System Architecture Finalising Design SpecificationsDocument69 pagesDesigning System Architecture Finalising Design SpecificationskhususgwNo ratings yet
- Component Based Invisible Computing: Alessandro Forin, MSRDocument7 pagesComponent Based Invisible Computing: Alessandro Forin, MSRNithyananthan KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Project Report On Network Operating System: Strength To Client/Server ArchitectureDocument23 pagesProject Report On Network Operating System: Strength To Client/Server ArchitectureKavita KarkiNo ratings yet
- What Is A Network Operating SystemDocument5 pagesWhat Is A Network Operating Systemvolaa100% (1)
- Group No 13-1Document15 pagesGroup No 13-1Waleed Abdullah2k19 EE603No ratings yet
- 5.study Experiment On NOS and DOSDocument9 pages5.study Experiment On NOS and DOSShashank GosaviNo ratings yet
- TopologyiesDocument18 pagesTopologyieslahiruaioitNo ratings yet
- A) (I) A Distributed Computer System Consists of Multiple Software Components That Are OnDocument14 pagesA) (I) A Distributed Computer System Consists of Multiple Software Components That Are OnRoebarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction To System and Network AdministrationDocument50 pagesChapter 1 Introduction To System and Network AdministrationUkasha Mohammednur100% (1)
- Handout Cloud, Iot, IpDocument141 pagesHandout Cloud, Iot, IpGetnete degemuNo ratings yet
- Topic 3.3 - Network ArchitectureDocument4 pagesTopic 3.3 - Network ArchitectureKevin NdyabandihoNo ratings yet
- 01 - TopologyDocument26 pages01 - TopologySherif AhmedNo ratings yet
- 8Document3 pages8bernard_elleveraNo ratings yet
- Research and Realization of Reflective Memory Network: 1. AbstractDocument56 pagesResearch and Realization of Reflective Memory Network: 1. AbstractAtul KumbharNo ratings yet
- Processes: Hongfei Yan School of EECS, Peking University 3/16/2011Document69 pagesProcesses: Hongfei Yan School of EECS, Peking University 3/16/2011pbjoshiNo ratings yet
- Grid Computing ProjectDocument24 pagesGrid Computing ProjectSujith KmsNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document33 pagesLecture 3OmidNo ratings yet
- NetworksDocument6 pagesNetworksscribdNo ratings yet
- UNIT I - CS8791 - Cloud ComputingDocument21 pagesUNIT I - CS8791 - Cloud ComputingabiNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Is Changing How We Communicate: By-Ravi Ranjan (1NH06CS084)Document32 pagesCloud Computing Is Changing How We Communicate: By-Ravi Ranjan (1NH06CS084)ranjan_ravi04No ratings yet
- Parallel Computing - Unit IVDocument40 pagesParallel Computing - Unit IVshraddhaNo ratings yet
- EmbeddedDocument10 pagesEmbeddedSarthak BhattacharjeeNo ratings yet
- Let1 WKUDocument142 pagesLet1 WKUGetnete degemuNo ratings yet
- Networking - 2019Document19 pagesNetworking - 2019John SherchanNo ratings yet
- Seminar Presented By: Sehar Sultan M.SC (CS) 4 Semester UAFDocument33 pagesSeminar Presented By: Sehar Sultan M.SC (CS) 4 Semester UAFSahar SultanNo ratings yet
- Module1 1642682811816Document46 pagesModule1 1642682811816bhat.prateek97No ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument6 pagesAssignmentTayyaba RiazNo ratings yet
- System Architecture: Presented By: Sushant Mishra 11BM91R03 VgsomDocument18 pagesSystem Architecture: Presented By: Sushant Mishra 11BM91R03 Vgsomsushantmishra85No ratings yet
- Cloud Technologies: Grid ComputingDocument13 pagesCloud Technologies: Grid ComputingNarmatha ThiyagarajanNo ratings yet
- Traditional Network Architecture and SDNDocument9 pagesTraditional Network Architecture and SDNAqeel ZaffarNo ratings yet
- Seamless NetworkingDocument18 pagesSeamless NetworkingStanleyNo ratings yet
- Network ComputingDocument21 pagesNetwork ComputingbhengavilaNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing2-1Document29 pagesCloud Computing2-1Bangkok DudeNo ratings yet
- Designing Campus and Data Center NetworkDocument33 pagesDesigning Campus and Data Center NetworkBerihun Tenaye AliNo ratings yet
- The Distributed Computing Model Based On The Capabilities of The InternetDocument6 pagesThe Distributed Computing Model Based On The Capabilities of The InternetmanjulakinnalNo ratings yet
- IoT - Questions - With AnswersDocument4 pagesIoT - Questions - With AnswersDebashish MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Slide 3 (Seminar)Document19 pagesSlide 3 (Seminar)Tesfa MinuyeletNo ratings yet
- Operating StructureDocument7 pagesOperating StructureVaibhav PearsonNo ratings yet
- Ijrdet 0714 34Document5 pagesIjrdet 0714 34prem420No ratings yet
- A Seminar Sysnopsis ON Grid ComputingDocument4 pagesA Seminar Sysnopsis ON Grid ComputingSweetie PieNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes Unit-1 (Network Operating System) : Session: 2021-22Document21 pagesLecture Notes Unit-1 (Network Operating System) : Session: 2021-22Pradeep BediNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Introduction To Cloud Computing: StructureDocument17 pagesUnit 1 Introduction To Cloud Computing: StructureRaj SinghNo ratings yet
- CCS375 Web Technologies Lecture Notes 1Document454 pagesCCS375 Web Technologies Lecture Notes 1SindhuNo ratings yet
- Cloud TechnologiesDocument56 pagesCloud TechnologiesNarmatha ThiyagarajanNo ratings yet
- Itbm Networking ArchitectireDocument27 pagesItbm Networking ArchitectireDivyekant GuptaNo ratings yet
- 69 - Developing Middleware For Hybrid Cloud Computing ArchitecturesDocument3 pages69 - Developing Middleware For Hybrid Cloud Computing ArchitecturesLARS Projetos & Soluções em Engenharia ElétricaNo ratings yet
- CCunit 1Document69 pagesCCunit 1aman kumarNo ratings yet
- Digital Contents Computer-NetworksDocument57 pagesDigital Contents Computer-Networksnk1982632No ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document15 pagesLecture 2Sulojan VipulNo ratings yet
- CCunit 1Document57 pagesCCunit 1Manish RoyNo ratings yet
- Grid Computing As Virtual Supercomputing: Paper Presented byDocument6 pagesGrid Computing As Virtual Supercomputing: Paper Presented bysunny_deshmukh_3No ratings yet
- Distributed Systems System Models Unit-IiDocument43 pagesDistributed Systems System Models Unit-IiAvni SinghNo ratings yet
- New Trends in Mobile Computing ArchitectureDocument8 pagesNew Trends in Mobile Computing ArchitectureBibinMathewNo ratings yet
- 10 Most Common Software Architectural Patterns - NIX UnitedDocument15 pages10 Most Common Software Architectural Patterns - NIX UnitedrodribravoNo ratings yet
- Application of Real Time Operating System in The Internet of ThingsDocument6 pagesApplication of Real Time Operating System in The Internet of Thingspatelhiren3385No ratings yet
- Avg Serial KeysDocument2 pagesAvg Serial KeysKishore Viriyala0% (2)
- The 2 Dimensions of Audit InformationDocument4 pagesThe 2 Dimensions of Audit InformationAdolfNo ratings yet
- Explain What Is Virus? Give Some Types of Virus?Document5 pagesExplain What Is Virus? Give Some Types of Virus?JOHN ANDRE GICALENo ratings yet
- 51 Point Aws Security Configuration Checklist PDFDocument7 pages51 Point Aws Security Configuration Checklist PDFSarita GuptaNo ratings yet
- sp2 PaperDocument5 pagessp2 PaperPrincess BermundoNo ratings yet
- Retail SDK DocumentationDocument2 pagesRetail SDK DocumentationAli SananNo ratings yet
- Administrator ReferenceDocument745 pagesAdministrator Referenceinogomezpy5435No ratings yet
- Planning CiscoDocument34 pagesPlanning CiscoCornel IordacheNo ratings yet
- Pro Sup Adm Nor 013.3.00 PDFDocument59 pagesPro Sup Adm Nor 013.3.00 PDFsherin PMNo ratings yet
- CISSP Baseline Exam V5.5Document22 pagesCISSP Baseline Exam V5.5bonzecurve100% (2)
- CSC 466 Assignment 2Document11 pagesCSC 466 Assignment 2Mndzebele SipheleleNo ratings yet
- ECE 545-Digital System Design With VHDL: Memories (RAM/ROM) 11/11/08Document68 pagesECE 545-Digital System Design With VHDL: Memories (RAM/ROM) 11/11/08Animesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Info Cube: Venkata ManoharDocument20 pagesInfo Cube: Venkata ManoharManohar GoudNo ratings yet
- Week 5Document35 pagesWeek 5AKANKSHA RAJNo ratings yet
- Database Security and Audting: Application Data AuditingDocument9 pagesDatabase Security and Audting: Application Data AuditingYasir ShakilNo ratings yet
- Operating System Vtu Question Bank 2017schemeDocument3 pagesOperating System Vtu Question Bank 2017schemeJhansi NNo ratings yet
- Security+ SY0-501 Exam ObjectivesDocument20 pagesSecurity+ SY0-501 Exam ObjectiveskasimNo ratings yet
- Yealink IP Phones Configuration Guide For User Access Level V81 70Document220 pagesYealink IP Phones Configuration Guide For User Access Level V81 70Silvano F. RochaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14Document13 pagesChapter 14hnoor6No ratings yet
- g10 Ict Module 1stDocument27 pagesg10 Ict Module 1stnaygelaNo ratings yet
- Unit - 5 SadDocument17 pagesUnit - 5 SadAslam NizamiNo ratings yet
- GuardII Platform User ManualDocument54 pagesGuardII Platform User ManualEléctrica EBYNo ratings yet
- Bachelor of Science Information Technology MinDocument2 pagesBachelor of Science Information Technology MinYoyo ManuNo ratings yet
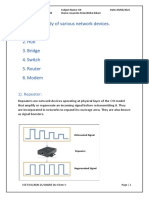
- Practical 1: Study of Various Network Devices. 1. Repeater 2. Hub 3. Bridge 4. Switch 5. Router 6. ModemDocument13 pagesPractical 1: Study of Various Network Devices. 1. Repeater 2. Hub 3. Bridge 4. Switch 5. Router 6. ModemKikani JayanshuNo ratings yet
- Enable The MRS Proxy Endpoint For Remote Moves in Exchange ServerDocument7 pagesEnable The MRS Proxy Endpoint For Remote Moves in Exchange Server743737469No ratings yet
- Introduction To SAS® Clinical Standards ToolkitDocument16 pagesIntroduction To SAS® Clinical Standards ToolkitSUMAN CHAUDHURINo ratings yet
- Guide To Data Governance Part2 People and Process WhitepaperDocument28 pagesGuide To Data Governance Part2 People and Process WhitepaperchurchillNo ratings yet
- OSS Citrix How ToV1Document7 pagesOSS Citrix How ToV1hjk6500No ratings yet
- Syllabus of Punjab State Co Operative Bank IT OfficerDocument3 pagesSyllabus of Punjab State Co Operative Bank IT OfficerSarbjit SinghNo ratings yet
- Summary HadoopDocument2 pagesSummary HadoopazamNo ratings yet