0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1K views17 pagesCoriolis Effect Presentation
The document discusses the Coriolis effect, which causes objects moving in rotating frames of reference to deflect from their intended path. Specifically:
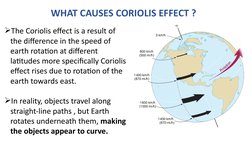
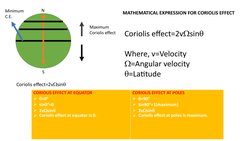
- The Coriolis effect is caused by the difference in rotation speeds of the Earth at different latitudes, making paths appear curved from a stationary viewpoint.
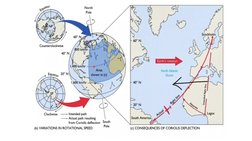
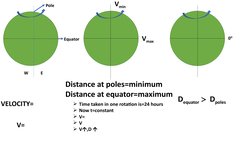
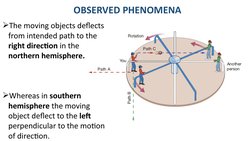
- It is maximum at the poles and zero at the equator. In the northern hemisphere, objects deflect to the right, and in the southern hemisphere they deflect to the left.
- Examples like ocean currents and atmospheric circulation demonstrate how the Coriolis effect significantly impacts large-scale motions on Earth over long time periods.
Uploaded by
Dillip KumarCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1K views17 pagesCoriolis Effect Presentation
The document discusses the Coriolis effect, which causes objects moving in rotating frames of reference to deflect from their intended path. Specifically:
- The Coriolis effect is caused by the difference in rotation speeds of the Earth at different latitudes, making paths appear curved from a stationary viewpoint.
- It is maximum at the poles and zero at the equator. In the northern hemisphere, objects deflect to the right, and in the southern hemisphere they deflect to the left.
- Examples like ocean currents and atmospheric circulation demonstrate how the Coriolis effect significantly impacts large-scale motions on Earth over long time periods.
Uploaded by
Dillip KumarCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Introduction to Coriolis Effect: Provides an introduction to the Coriolis Effect, outlining the key topics and the structure of the presentation.
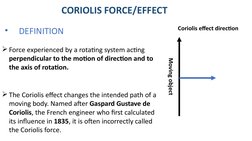
- Definition of Coriolis Force: Defines the Coriolis force and explains its origins and the direction of its influence on moving objects on Earth.
- Nature of Coriolis Force: Discusses whether the Coriolis force is a true force or an observational effect, detailing its impact on motion.
- Causes of the Coriolis Effect: Explains the causes behind the Coriolis effect, focusing on the influence of Earth’s rotation and speed variation with latitude.
- Facts About Coriolis Effect: Highlights important facts and common misconceptions about the Coriolis effect and its real-world implications.
- Mathematical Description: Presents the mathematical expression used to calculate the Coriolis effect, explaining the variables involved.
- Observed Phenomena: Discusses the observable phenomena resulting from the Coriolis effect, including deflections in the northern and southern hemispheres.
- Perception and Interpretation: Explores how perception affects the interpretation of the Coriolis effect, with explanations from different frames of reference.
- Conclusion: Summarizes the importance and applications of understanding the Coriolis effect in meteorology and oceanography.