Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bank Performance
Uploaded by
br bhandariCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bank Performance
Uploaded by
br bhandariCopyright:
Available Formats
1
Bank Performance
Ultimate measure of Performance –
Value of Common Shares
Maximization of shareholders wealth
Complex
Involves internal and external management
factors
Need to allocate scarce resources to
different performance dimensions
Health Assessment of Banks
2
Bank Performance
Internal Performance
Bank Planning
Objective, Budget and Strategy
Technology
Computer and Communication
Personal Development
Training and Incentives
Bank Condition
CAMELS
Health Assessment of Banks
3
Bank Performance
External Performance
Market Share
Equity / Earning, Technology
Regulatory Compliance
Capital, Lending, Other
Public Confidence
Deposit Insurance, Public Image
Health Assessment of Banks
4
Difference between financial institutions
and other business?
Health Assessment of Banks
5
Financial statements of a bank
More disclosure
Corporate Governance
Guided by
International Accounting Standards
Nepal Accounting Standards
Basel II Disclosure Requirements
NRB / Central Bank Directives
Tax Laws
Health Assessment of Banks
6
Balance Sheet
Capital
Paid up Capital
Reserve and Surplus
Liabilities
Debenture and Bond
Borrowings
Deposits
Income Tax Liability
Other Liabilities
Health Assessment of Banks
7
Assets
Cash and Bank Balance
Money at Call and Short Notice
Investments
Loan and Advances
Fixed Assets
Non Banking Assets
Other Assets
Health Assessment of Banks
8
Income Expense Statement
Normal P&L A/c
Turnover
Gross Profit (Turnover – COGS)
Operating Profit (GP – Operating Expenses)
PBIT (Operating – Depreciation /
Amortization)
Profit before Bonus and Tax
Net Income
Health Assessment of Banks
9
Income Expense Statement
Net Interest Income
Add Non Interest Income and FX Income
Total Operating Income
Less Operating / Staff Expense
Operating Profit before Provision
Less Provision for possible loss
Operating Profit
Add Non operating income and prov. write back
Profit from Regular Activities
Add Extra Ordinary Income
Profit before Bonus and Tax
Net Profit / Loss
Health Assessment of Banks
10
Income
Interest Income
Fees / Commission Income
Exchange Income
Expense
Interest Expense
Staff Expense
Operating Expense
Health Assessment of Banks
11
Contingent Liabilities
Letter of Credit
Bank Guarantee
Acceptance Payments
Delivery Orders
Health Assessment of Banks
12
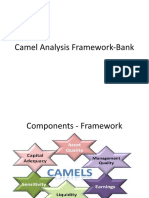
CAMELS Rating
Capital Adequacy
Asset Quality
Management
Earnings
Liquidity
Sensitivity to Market Risk
Health Assessment of Banks
13
Capital Adequacy
Capital = Total Assets – External Liability
Commercial Banks: NPR 2 Bio (Paid Up
Capital) by FY 2011/12
Leverage Ratio: Equity Capital / Average
Total Assets
Health Assessment of Banks
14
Minimum Capital
Requirements
The minimum capital requirement under
Basel II Framework:
Core Capital: 6% of Total RWE
Capital Fund: 10% of Total RWE
Health Assessment of Banks
15
Capital Adequacy Ratio
Core Capital + Supplementary Capital / RWE
Core Capital / Tier I Capital
Supplementary Capital / Tier II Capital
Risk Weighted Exposure:
Credit Risk
Market Risk
Operational Risk
Health Assessment of Banks
16
Asset Quality
Assets include Loans, Investment, Fixed
assets and others
Concentrated on Risk Assets
Health Assessment of Banks
17
Asset Quality
NPA (Non performing Loan to Total
Loan) – Expressed in percentage
Provisioning (Total LLP to Total NPL) –
Coverage Ratio
Sector Concentration
Group Concentration
Single Obligor Limit
Health Assessment of Banks
18
Loan Category
Performing Loans
Pass (1% Provisioning)
Non – Performing Loan
Sub-standard (25% Provisioning)
Doubtful (50% Provisioning)
Bad (100% Provisioning)
Restructured / Reschedules
(12.5% Provisioning)
Health Assessment of Banks
19
Ratios
Texas Ratio: Delinquent Loans + NPA / Capital
+ Loan Loss Reserve
Should be less than 100%; if higher than 50%, additional
capital could be required
Health Assessment of Banks
20
Concentration of Loans
Sectors Number Principal Interest
1. Agriculture
2 Mines
3 About Productions
4 Construction
5 Metal Productions, Machinery & Electrical Tools & fitting
6 Transportation Equipment Production & Fitting
7 Transportation, Communications & Public Services
8 Wholesaler & Retailers
9 Finance, Insurance & Fixed Assets
10 Service Industries
11 Consumable Loan
12 Local Government
13 Others
Total
Health Assessment of Banks
21
Management
Quality of Management
Management Stability
Subjective Analysis
Knowledge / Experience/ Effectiveness
Board Members
Senior Management Team
Operating Staffs
Health Assessment of Banks
22
Earning
Interest Income / Interest Spread
Spread through intermediation between
savers and users of funds.
Bank is a financial intermediary
Commission Income
Exchange Income
Health Assessment of Banks
23
Staff Cost
Other Operating Cost
Provisions
Health Assessment of Banks
24
Weighted Average Interest Spread
Rate %
Average Yield on Loans /Advances and Investment 8.6
Average Rate on Deposits & Borrowings 5.5
Net Interest Spread 3.1
Health Assessment of Banks
25
Profitability Ratios
Return on Equity (ROE)
Return on Assets (ROA)
Return on Earning Assets
Gross Yield: Interest Income / Average
Earning Assets
Net Interest Margin: NII / Average Earning
Assets
Health Assessment of Banks
26
Profitability Ratios
Cost to Income
NII to Total Income
Income per staff
Health Assessment of Banks
27
Profitability Ratios
Burden Ratio: Non interest Expense /
Non interest income
Overhead Ratio: Non interest Expense /
Total Average Assets
Efficiency Ratio: Non interest Expense /
Operating Income
Health Assessment of Banks
28
Liquidity
CRR – 5%
SLR - 15% (CRR+TB/GB+ Cash at Vault)
Liquid Assets / Total Deposits – Min 20%
CD Ratio
Asset Liability Management
FOREX Management (Manage Position
Risks)
Health Assessment of Banks
29
Liquid Assets
NRB Balances
Cash Balances
Gold / other liquid assets
Balances with other financial institutions
(local / foreign)
Investment in Treasury Bills / Short term
government securities
Inter-bank lending
Other short term investment
Health Assessment of Banks
30
Asset Liability Management
ALCO
Overall Fund Position (Long / Short)
Cost of Fund / Money Market Rate
(Treasury Bills / IB Rate)
Deposit Concentration
Deposit Mix
Maturity Profile
Liquidity Profile / Gap Analysis
Health Assessment of Banks
31
Health Assessment of Banks
32
Sensitivity
Not covered by Financial Statements
Banks are sensitive to Changes in
Market Scenarios
Will real estate price and share price affect health of
banks in Nepal?
What will be the effect of Global Financial Crisis in
Nepalese Bank’s Financial Health?
Will changes in government policies affect health of
banks?
Health Assessment of Banks
33
Ratio Analysis
Various ratios can be calculated to check
financial health of financial institutions
Ratios can check:
Strength in few of CAMELS broad areas like
Capital Adequacy, Asset Quality, Earnings
and Liquidity
Health Assessment of Banks
34
Financials of Nepali
Commercial Banks
Quarterly Results and Comparison
Annual Financial Statements
Health Assessment of Banks
You might also like
- Evaluating Bank PerformanceDocument39 pagesEvaluating Bank PerformancePrashamsa RijalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 06Document25 pagesChapter 06Farjana Hossain DharaNo ratings yet
- 06 Camel AnalysisDocument37 pages06 Camel Analysissachinp patilNo ratings yet
- BFS4 Bank Financial StatementsDocument20 pagesBFS4 Bank Financial Statementsroshan_agrawal0123No ratings yet
- NYIF Williams Credit Risk Analysis II 2018Document106 pagesNYIF Williams Credit Risk Analysis II 2018jojozie100% (1)
- NPA of Indian BanksDocument27 pagesNPA of Indian BanksShristi GuptaNo ratings yet
- Camel 1Document7 pagesCamel 1Papa PappaNo ratings yet
- BWBB2013 - Topic 4 Part 2Document11 pagesBWBB2013 - Topic 4 Part 2myteacheroht.managementNo ratings yet
- Final ProjectDocument90 pagesFinal ProjectdgpatNo ratings yet
- Bank Performance Measurement & Analysis & PCADocument46 pagesBank Performance Measurement & Analysis & PCAVenkatsubramanian R IyerNo ratings yet
- Measuring and Evaluating The Performance of Banks and Their Principal CompetitorsDocument46 pagesMeasuring and Evaluating The Performance of Banks and Their Principal CompetitorsyeehawwwwNo ratings yet
- Camel - Rating - Bank Management - MBA-FA20Document19 pagesCamel - Rating - Bank Management - MBA-FA20Sudheer VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- 3.0. Performance Measurement of Banking SectorDocument15 pages3.0. Performance Measurement of Banking SectorFarzana Akter 28No ratings yet
- Camels Model of Performance Evaluation of Banks: By, Tripura, Sishira.P, S.Neha, Mythili.MDocument30 pagesCamels Model of Performance Evaluation of Banks: By, Tripura, Sishira.P, S.Neha, Mythili.MMythili MadapatiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document22 pagesChapter 6Mahra AlMazroueiNo ratings yet
- Camel Analysis Framework-BankDocument27 pagesCamel Analysis Framework-BankAmnaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Banking SystemsDocument16 pagesIntroduction To Banking SystemsSagar AnsaryNo ratings yet
- Risk Management System in BanksDocument50 pagesRisk Management System in Banksersudhirthakur100% (1)
- Topic 4 Types of RisksDocument33 pagesTopic 4 Types of RisksSimaSergazinaNo ratings yet
- FM 1Document92 pagesFM 1Abdul MoinNo ratings yet
- Camels Ratings: USAID-Funded Economic Governance II ProjectDocument49 pagesCamels Ratings: USAID-Funded Economic Governance II ProjectNghi Dung HtNo ratings yet
- Research On Banking Sector by Witty AdvisoryDocument141 pagesResearch On Banking Sector by Witty AdvisoryAnkit GuptaNo ratings yet
- Bank Lending Abhishek KumarDocument16 pagesBank Lending Abhishek KumarShashi ThakurNo ratings yet
- Concept ChecksDocument8 pagesConcept ChecksAshraful AlamNo ratings yet
- Credit MGT TraineesDocument20 pagesCredit MGT TraineesTewodros2014No ratings yet
- P.K.Mitra General Manager Punjab National Bank Head Office, New DelhiDocument50 pagesP.K.Mitra General Manager Punjab National Bank Head Office, New DelhiashimathakurNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 (A182)Document42 pagesChapter 4 (A182)Aina ZalinaNo ratings yet
- Pillar 3 USB Disclosure 6-30-17Document33 pagesPillar 3 USB Disclosure 6-30-17Siva RenjithNo ratings yet
- Financial Analysis of A BankDocument7 pagesFinancial Analysis of A BankLourenz Mae AcainNo ratings yet
- شلبتر 6Document8 pagesشلبتر 6Ahmad RahhalNo ratings yet
- IBP - Lending-Products-Ops Risk Mgmnt-IBP Course-Day 4-2 4 12Document19 pagesIBP - Lending-Products-Ops Risk Mgmnt-IBP Course-Day 4-2 4 12Zehra RizviNo ratings yet
- Bank Management: Measuring and Evaluating Bank PerformanceDocument41 pagesBank Management: Measuring and Evaluating Bank PerformanceMuhaizam MusaNo ratings yet
- A222 BWBB3193 Topic 05 - Fin Ratio Part 2Document41 pagesA222 BWBB3193 Topic 05 - Fin Ratio Part 2NurFazalina AkbarNo ratings yet
- Important Ratios For Banks: Sumit Puri (56) Tamal Bhattacharya (47) Namit ManglaniDocument41 pagesImportant Ratios For Banks: Sumit Puri (56) Tamal Bhattacharya (47) Namit ManglaniPrachi AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Definition of NPADocument3 pagesDefinition of NPAsajilapkNo ratings yet
- Do Not Use Cut, Copy Paste Anywhere.: Need Based Financial Planning MR Anil GhaiDocument27 pagesDo Not Use Cut, Copy Paste Anywhere.: Need Based Financial Planning MR Anil GhaiAmit SheoranNo ratings yet
- Risk Management & Basel IIIDocument31 pagesRisk Management & Basel IIIsatishNo ratings yet
- Thesis UpdateDocument42 pagesThesis UpdateNo B TaNo ratings yet
- By:-Shraddha Dharmadhikari Mba-IiDocument19 pagesBy:-Shraddha Dharmadhikari Mba-IiRaj HuqeNo ratings yet
- Write UpDocument2 pagesWrite Upnehaaa78No ratings yet
- Basel Capital Accord & Risk Management in BanksDocument75 pagesBasel Capital Accord & Risk Management in Banksrahulg0710No ratings yet
- Chap 5Document23 pagesChap 5selva0% (1)
- Class Notes Financial Risk M: F PGDMDocument11 pagesClass Notes Financial Risk M: F PGDMprat05No ratings yet
- Credit Risk PDFDocument28 pagesCredit Risk PDFAnubhav SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Aashi Gupta (FE1702) - Prakhar Sikka (FE1730)Document12 pagesAashi Gupta (FE1702) - Prakhar Sikka (FE1730)Suprabha GambhirNo ratings yet
- Risk Management in Banking SectorDocument31 pagesRisk Management in Banking SectorManish SethiNo ratings yet
- CamelsDocument4 pagesCamelsWaseem KhanNo ratings yet
- CAMELS and PEARLS Applied To Financial Management of Commercial Bank in VietnamDocument44 pagesCAMELS and PEARLS Applied To Financial Management of Commercial Bank in VietnamDan LinhNo ratings yet
- Healthcare Deal Multiples (Select Transactions) - Part 1Document10 pagesHealthcare Deal Multiples (Select Transactions) - Part 1Reevolv Advisory Services Private LimitedNo ratings yet
- International Convergence of Capital Measurement & Capital StandardsDocument57 pagesInternational Convergence of Capital Measurement & Capital StandardsDaniel VincentNo ratings yet
- Basel - Foreing Exchange-2022Document32 pagesBasel - Foreing Exchange-2022Salman AhmedNo ratings yet
- BM Introduction To BankingDocument36 pagesBM Introduction To BankingNatasha OliviaNo ratings yet
- Board Memo - For CRG (2020)Document8 pagesBoard Memo - For CRG (2020)Md Ibna Fahad ShibluNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Asset Liability and Risk MGMTDocument147 pagesIntroduction To Asset Liability and Risk MGMTMani ManandharNo ratings yet
- Bank Accounting Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesBank Accounting Cheat Sheetlorismaillard0No ratings yet
- Bank Fundamentals: Class 3-Chapter 7Document19 pagesBank Fundamentals: Class 3-Chapter 7amberNo ratings yet
- Bank RiskPrudential NormsDocument35 pagesBank RiskPrudential Normsdivanshu aroraNo ratings yet
- Outperform with Expectations-Based Management: A State-of-the-Art Approach to Creating and Enhancing Shareholder ValueFrom EverandOutperform with Expectations-Based Management: A State-of-the-Art Approach to Creating and Enhancing Shareholder ValueNo ratings yet
- C S4FTR 2020 1669389459Document63 pagesC S4FTR 2020 1669389459Thirumalai ShanmugamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Interest Rates FuturesDocument24 pagesChapter 6 - Interest Rates FuturesNatasha GhazaliNo ratings yet
- DTC Eligibility Q & ADocument18 pagesDTC Eligibility Q & AjeremyNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Debt Equity Ratio, Return On Assets and Net Profit Margin On Price Book Value in The Food and BeverageDocument5 pagesThe Effect of Debt Equity Ratio, Return On Assets and Net Profit Margin On Price Book Value in The Food and BeverageThe IjbmtNo ratings yet
- Paper 1 Practice Questions 2023Document1 pagePaper 1 Practice Questions 2023Krrishna Rajesh TOKARAWATNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Indian Financial SystemDocument73 pagesUnit 1 - Indian Financial SystemHasrat AliNo ratings yet
- MPP Specker NoteDocument34 pagesMPP Specker NoteJ.J priyaNo ratings yet
- Vision Ias SeptDocument27 pagesVision Ias SeptAkash SarkarNo ratings yet
- StartupDocument18 pagesStartup401-030 B. Harika bcom regNo ratings yet
- Bullet Notes 9 - Other Percentage TaxDocument4 pagesBullet Notes 9 - Other Percentage TaxFlores Renato Jr. S.No ratings yet
- Mock Test 3Document10 pagesMock Test 3Shubham GuptaNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument29 pagesUntitledKrrishnachaithanya bukka ThantriswamyNo ratings yet
- 12th Accountancy EM Important Questions To Half Yearly Exam Englishl Medium PDF DownloadDocument3 pages12th Accountancy EM Important Questions To Half Yearly Exam Englishl Medium PDF Downloadqueensmiling495No ratings yet
- Finman Multiple Choice Reviewer - CompressDocument9 pagesFinman Multiple Choice Reviewer - CompressAerwyna AfarinNo ratings yet
- Fiac Epi-: Oa-Jul-2022Document1 pageFiac Epi-: Oa-Jul-2022zamanasifNo ratings yet
- Traders in FuturesDocument10 pagesTraders in FuturesmymadhavaNo ratings yet
- Eyelab OpticalDocument12 pagesEyelab OpticalHartono EffendiNo ratings yet
- SIP InterimDocument12 pagesSIP InterimSai KiranNo ratings yet
- A Dozen Lessons On Investing From Ed ThorpDocument54 pagesA Dozen Lessons On Investing From Ed ThorptoniNo ratings yet
- PRICE DISCRIMINATION - LuongLeThuHang - D0K0PVDocument13 pagesPRICE DISCRIMINATION - LuongLeThuHang - D0K0PVHuyn NNo ratings yet
- GST 2024 BatchDocument16 pagesGST 2024 BatchHarjeet Playz100% (1)
- Pricelist Meden Meadow Shared Ownership Legal and General Affordable Homes Week 42 Oct 2023Document1 pagePricelist Meden Meadow Shared Ownership Legal and General Affordable Homes Week 42 Oct 2023pachterNo ratings yet
- Tesla FSAPDocument20 pagesTesla FSAPSihongYanNo ratings yet
- 2018 10 Exam FM Sample QuestionsDocument137 pages2018 10 Exam FM Sample QuestionsRuoyuNo ratings yet
- Cera Sanitaryware Limited 1Document58 pagesCera Sanitaryware Limited 1Parul KatiyarNo ratings yet
- Understanding Asian Kill Zone, London Manipulation, Optimum TradingDocument35 pagesUnderstanding Asian Kill Zone, London Manipulation, Optimum TradingKevin Mwaura100% (1)
- Saksham Project ReportDocument60 pagesSaksham Project Reporttanish22yNo ratings yet
- Aaryan - IIT Bombay - CVDocument1 pageAaryan - IIT Bombay - CVAaryan GuptaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 MCQDocument6 pagesChapter 7 MCQArun KumarNo ratings yet
- Africa Macro - Credit Outlook - TLG-Future Africa Venture DebtDocument18 pagesAfrica Macro - Credit Outlook - TLG-Future Africa Venture DebtAyomikun OgunkanmiNo ratings yet