0% found this document useful (0 votes)
589 views33 pagesUnderstanding Astigmatism and Its Treatment
This document provides an overview of four topics related to visual optics:
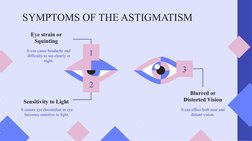
1) Astigmatism - An eye condition caused by an irregularly shaped cornea or lens that results in blurred vision. It can be corrected with glasses, contact lenses, or refractive surgery.
2) Aberrations - Imperfections in optical systems like the eye that cause light to spread out rather than focus to a point, blurring vision. Common types are chromatic, spherical, and peripheral aberration.
3) Aphakia - The absence of the eye's lens, usually due to cataract surgery. It causes blurred vision that can be corrected with glasses or contact lenses.
4) Pseudoph
Uploaded by
Simra WaheedCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
589 views33 pagesUnderstanding Astigmatism and Its Treatment
This document provides an overview of four topics related to visual optics:
1) Astigmatism - An eye condition caused by an irregularly shaped cornea or lens that results in blurred vision. It can be corrected with glasses, contact lenses, or refractive surgery.
2) Aberrations - Imperfections in optical systems like the eye that cause light to spread out rather than focus to a point, blurring vision. Common types are chromatic, spherical, and peripheral aberration.
3) Aphakia - The absence of the eye's lens, usually due to cataract surgery. It causes blurred vision that can be corrected with glasses or contact lenses.
4) Pseudoph
Uploaded by
Simra WaheedCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Astigmatism
- Aberrations
- Aphakia
- Pseudophakia