0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views42 pagesTM 6 Control Activities & Bussiness Process
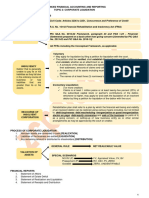
Control activities are specific actions established as policies and procedures to ensure that management's directives are carried out. They should address risks identified during risk assessments. Control activities exist at all levels of an organization and within business processes. The document discusses several types of important control activities, including proper authorization of transactions, separation of duties, project development controls, use of adequate documents/records, safeguarding of assets, and independent checks on performance. It emphasizes that control activities should be clearly documented and communicated.
Uploaded by
Yoannisa YoanCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views42 pagesTM 6 Control Activities & Bussiness Process
Control activities are specific actions established as policies and procedures to ensure that management's directives are carried out. They should address risks identified during risk assessments. Control activities exist at all levels of an organization and within business processes. The document discusses several types of important control activities, including proper authorization of transactions, separation of duties, project development controls, use of adequate documents/records, safeguarding of assets, and independent checks on performance. It emphasizes that control activities should be clearly documented and communicated.
Uploaded by
Yoannisa YoanCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd