Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lesson 3 The Peripheral Nervous System
Uploaded by
julio diazOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lesson 3 The Peripheral Nervous System
Uploaded by
julio diazCopyright:
Available Formats
LESSON 3
THE PERIPHERAL NERVOUS
SYSTEM
Docente: Mag. Carolina E. Zapana Rosado
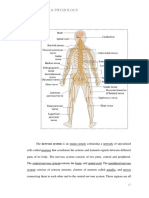
Peripheral Nervous System : PNS: Sistema Nervioso PeriféricoThe peripheral nervous
system consists of the nerves that branch out from the brain and spinal cord. These nerves form the
communication network between the CNS and the body parts. The peripheral nervous system is
further subdivided into the somatic nervous system and the autonomic nervous system.:
AUTONOMIC SYSTEM : sympathetic división & parasympathetic division :
The sympathetic nervous system is involved in preparing the body for stress-related activities; the
parasympathetic nervous system is associated with returning the body to routine, day-to-day
operations. The two systems have complementary functions, operating in tandem to maintain the
body's homeostasis.
Somatic nervous system: The somatic nervous system is a component of the peripheral nervous
system associated with the voluntary control of the body movements via the use of skeletal
muscles.
Autonomic nervous system: The autonomic nervous system is the part of the nervous system that
supplies the internal organs, including the blood vessels (vasos sanguineos), stomach, intestine, liver,
kidneys ( riñones), bladder,(vegija) genitals, lungs, pupils, heart, and sweat, salivary, and digestive glands.
The autonomic nervous system has two main divisions:
Medula oblengata: (medula oblonga) the continuation of the spinal cord within the skull
(craneo) forming the lowest part of the brainstem (tronco encefalico)and containing control centers for
the heart and lungs.
Constricts bronchi: Bronchoconstriction is the constriction of the airways in the lungs due to the
tightening of surrounding smooth muscle, with consequent coughing, wheezing, and shortness of
breath.
Vagus nerve: (nervio Vago ): El nervio vago (del lat. nervus vagus) o nervio neumogástrico es el
décimo de los doce pares craneales (nervios craneales).
Contracts bladder: (contracción de vegija)
Glycogen: (glucógeno) :It’s made and storage primarily in the cells of the liver and skeletal
muscle. It’s multibranched polysaccharide of glucose that srves as a form of energy storage in animals,
fungi, and bacteri.
Glucosa: La glucosa es la clave para mantener los mecanismos del cuerpo funcionando de manera
óptima. Cuando tus niveles de glucosa son óptimos, con frecuencia no lo notas. Sin embargo, cuando se
desvían de los límites recomendados, notarás el efecto no saludable que tiene en el funcionamiento
normal del cuerpo.
You might also like
- Anaphy Lesson 12Document14 pagesAnaphy Lesson 12Richee LunnayNo ratings yet
- 2autonomic Nervous SystemDocument28 pages2autonomic Nervous SystemSolomon H.No ratings yet
- Hlgjdkrthe Nervous SystemDocument8 pagesHlgjdkrthe Nervous SystemBernardo Villavicencio VanNo ratings yet
- Nervous System: Dr. Hendy Wijaya, M. BiomedDocument26 pagesNervous System: Dr. Hendy Wijaya, M. BiomedWndy 0903No ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument13 pagesNervous SystemAnn SerratoNo ratings yet
- Introduction and Organization of Nervous SystemDocument29 pagesIntroduction and Organization of Nervous Systemzaraali2405No ratings yet
- Biopsychology I - Anatomy of The Nervous System PDFDocument96 pagesBiopsychology I - Anatomy of The Nervous System PDFThomas Cheah100% (1)
- Nervous SystemDocument10 pagesNervous SystemAlicia ValverdeNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical Nursing PinoyDocument85 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing PinoyrosebaseNo ratings yet
- BCH 431. TISSUE BiochemistryDocument24 pagesBCH 431. TISSUE BiochemistryOkoro Janeth chisomNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 UNIT 1Document19 pagesChapter 2 UNIT 1Ayen LatosaNo ratings yet
- CH 7 The Nervous SystemDocument4 pagesCH 7 The Nervous Systemapi-267543553No ratings yet
- NervousSystem (6) &Document67 pagesNervousSystem (6) &Irfan Nur Fathur Rahman100% (1)
- Nervous System ReviewerDocument4 pagesNervous System ReviewerSophia CaisipNo ratings yet
- Biological Basis of BehaviourDocument29 pagesBiological Basis of Behaviourenoc4No ratings yet
- Nervous System ReportDocument24 pagesNervous System ReportChelo Jan GeronimoNo ratings yet
- UNIT 4 (Nervous System)Document14 pagesUNIT 4 (Nervous System)Workinesh Kaynabo KambaloNo ratings yet
- Lab 9 Nervous TissueDocument28 pagesLab 9 Nervous TissueSarwar JafarNo ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument3 pagesThe Nervous SystemOm TipsetwarNo ratings yet
- 2 NSDocument65 pages2 NSLilaNo ratings yet
- Motor Function - The Second Function Is The Response To The Stimuli That Causes Muscles To Contract orDocument2 pagesMotor Function - The Second Function Is The Response To The Stimuli That Causes Muscles To Contract orBea AdayoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Nervous SystemDocument5 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Nervous SystemnanatdaboyNo ratings yet
- Control and CoordinationDocument43 pagesControl and CoordinationDukhi InsaanNo ratings yet
- NEURO LECTURE Part 1 and 2 AutoRecoveredDocument32 pagesNEURO LECTURE Part 1 and 2 AutoRecoveredYusuf EspinaNo ratings yet
- V. Anatomy & PhysiologyDocument5 pagesV. Anatomy & PhysiologyAbigael Patricia GutierrezNo ratings yet
- The Central Nervous SystemDocument7 pagesThe Central Nervous Systemjoeywap29No ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument35 pagesNervous SystemRaven MayoNo ratings yet
- The Nervous System - Prepared by Group 3 1Document71 pagesThe Nervous System - Prepared by Group 3 1Shawn Henry CepedaNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemsDocument37 pagesNervous SystemsHannah CabritoNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 LecNotesDocument49 pagesUnit 1 LecNotesAnn NguyenNo ratings yet
- Important Definitions: Nervous SystemDocument4 pagesImportant Definitions: Nervous SystemValeri LopezNo ratings yet
- The Nervous System (BDS)Document27 pagesThe Nervous System (BDS)leeminhoangrybirdNo ratings yet
- The Nervous System (Edited)Document27 pagesThe Nervous System (Edited)Kiarana FleischerNo ratings yet
- Nervous System: Science 6 - Second QuarterDocument25 pagesNervous System: Science 6 - Second QuarterRegin BaguioNo ratings yet
- The Central Nervous System: BrainDocument12 pagesThe Central Nervous System: BrainsheinelleNo ratings yet
- LECTURE Nervous SystemDocument4 pagesLECTURE Nervous SystemanonymousNo ratings yet
- Nervous Anatomy Updated (PC)Document94 pagesNervous Anatomy Updated (PC)Yahya JuneydiNo ratings yet
- NeurologyDocument42 pagesNeurologybuzz Q100% (2)
- The Nervous System RECORDINGSDocument52 pagesThe Nervous System RECORDINGSKathy Angeli Bel-idaNo ratings yet
- 11 NsDocument29 pages11 NsWakanda ForeverNo ratings yet
- (Lecture - 4) Neuropsychology of Human BehaviorDocument58 pages(Lecture - 4) Neuropsychology of Human BehaviorN. W. FlannelNo ratings yet
- Concept of PsychobiologyDocument21 pagesConcept of Psychobiologydhivyaram100% (1)
- Nervous SystemDocument30 pagesNervous SystemkenNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument13 pagesNervous SystemRizkirmNo ratings yet
- Nervous System: Cranial NervesDocument1 pageNervous System: Cranial NervesEfynnie Rose EspararNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument9 pagesNervous SystemTahir AzizNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument9 pagesNervous SystemTahir AzizNo ratings yet
- Module 2: Physiological Basis of BehaviorDocument23 pagesModule 2: Physiological Basis of BehaviorRoxie May Theresse AbagatnanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument5 pagesAnatomy and Physiologyssairej06No ratings yet
- Z (H) IV Chordata SHDocument3 pagesZ (H) IV Chordata SHalshareefsaadalshareefNo ratings yet
- Nervous System - Summary NotesDocument9 pagesNervous System - Summary NotesHarshNo ratings yet
- Neurology - The Study of The Nervous SystemDocument3 pagesNeurology - The Study of The Nervous SystemMizchelle Angeles VilladorNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Nervous System: Division of The PNS and TheDocument3 pagesPeripheral Nervous System: Division of The PNS and Theawele lauraNo ratings yet
- Structure. The Basic Unit of The Nervous System Is A Cell Known AsDocument14 pagesStructure. The Basic Unit of The Nervous System Is A Cell Known AsSaraswathi GangadaranNo ratings yet
- 7 Nervous SystemDocument37 pages7 Nervous SystemAthar Habib ShahaniNo ratings yet
- HAPL 3 & 4 - The Nervous SystemDocument10 pagesHAPL 3 & 4 - The Nervous SystemwelpNo ratings yet
- 1 Sistema Autã NomoDocument10 pages1 Sistema Autã NomomonNo ratings yet
- Fisiologia Del Sistema Nervioso AutonomoDocument9 pagesFisiologia Del Sistema Nervioso AutonomoMaria CaicedoNo ratings yet
- Lec2 Sem2 Cnsweek1 20110630Document10 pagesLec2 Sem2 Cnsweek1 20110630arhamsalahuddinNo ratings yet
- Polyvagal Theory: A Self-Help Polyvagal Theory Guide to Reduce with Self Help Exercises Anxiety, Depression, Autism, Trauma and Improve Your Life.From EverandPolyvagal Theory: A Self-Help Polyvagal Theory Guide to Reduce with Self Help Exercises Anxiety, Depression, Autism, Trauma and Improve Your Life.Rating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Pterygopalatine FossaDocument20 pagesPterygopalatine FossaGeoffreyNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Nervous System & Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument28 pagesPeripheral Nervous System & Autonomic Nervous Systemobsgynunair januari18No ratings yet
- Term 2 Anaphy RatioDocument40 pagesTerm 2 Anaphy RatioAndrea Mae OdquierNo ratings yet
- General Anatomy NotesDocument15 pagesGeneral Anatomy NotesEmerald BunnyNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of The Sympathetic Nervous SystemDocument2 pagesStructure and Function of The Sympathetic Nervous SystemAnthony LopezNo ratings yet
- Cash Text Book of Chest and Vascular Disorders For PhysiotherapistsDocument702 pagesCash Text Book of Chest and Vascular Disorders For PhysiotherapistsVikas Jha86% (35)
- Adewumi ANS Case StudyDocument5 pagesAdewumi ANS Case StudyAbdulRahman AdewumiNo ratings yet
- Zen Intro To Buddhism & Practice of ZazenDocument33 pagesZen Intro To Buddhism & Practice of ZazendudcomeonNo ratings yet
- Nervous System ReviewerDocument4 pagesNervous System ReviewerSophia CaisipNo ratings yet
- اسئلة تشريحDocument20 pagesاسئلة تشريحابراهيم فلاح حسنNo ratings yet
- Biomedical InstrumentationDocument16 pagesBiomedical Instrumentationshaswatece100% (6)
- 412 Lab 6Document9 pages412 Lab 6Rock everydayNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Autonomic Nervous System: J J M Medical College, Davangere. Dept of AnesthesiaDocument117 pagesPhysiology of Autonomic Nervous System: J J M Medical College, Davangere. Dept of AnesthesiaKithminaNo ratings yet
- Nucleus Gracilis and CuneatusDocument52 pagesNucleus Gracilis and CuneatusBeryl MarshallNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5.doc AnsDocument8 pagesLecture 5.doc AnsElijah KamaniNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)Document11 pagesAutonomic Nervous System (ANS)Prathmesh vetalNo ratings yet
- Review - Pelvic Nerves - From Anatomy and Physiology To Clinical ApplicationsDocument17 pagesReview - Pelvic Nerves - From Anatomy and Physiology To Clinical ApplicationsNovi RobiyantiNo ratings yet
- TVP 2016 0102 OO AnisocoriaDocument7 pagesTVP 2016 0102 OO AnisocoriaRocioNo ratings yet
- Fisiologi Sistem Saraf TepiDocument19 pagesFisiologi Sistem Saraf TepiNata NayottamaNo ratings yet
- Bisc 305 Practice Questions PhysiologyDocument1 pageBisc 305 Practice Questions PhysiologyAman BassiNo ratings yet
- Regulation of BPDocument17 pagesRegulation of BPLemon CatbaganNo ratings yet
- Chap. 18 GuytonDocument4 pagesChap. 18 GuytonMarian Joyce Princess Yuque100% (2)
- Assignment 2 BIOL 235Document22 pagesAssignment 2 BIOL 235Kenah MwauraNo ratings yet
- Pex 06 02Document4 pagesPex 06 02Jihan FadillaNo ratings yet
- Polygraph HandoutDocument103 pagesPolygraph HandoutHEROWIN EDUARDO100% (1)
- Semester Reflection Paper-1Document7 pagesSemester Reflection Paper-1Nasir Ali RiazNo ratings yet
- Pelvis and Perineum Lecture NotesDocument12 pagesPelvis and Perineum Lecture NotesSolomon Seth SallforsNo ratings yet
- The Nervous System - NursingDocument59 pagesThe Nervous System - NursingDR Archana Agarwal100% (2)
- Reflexes That Control Cardiovascular FunctionDocument11 pagesReflexes That Control Cardiovascular FunctionRaam NaikNo ratings yet
- Petrosal NervesDocument12 pagesPetrosal NervesDeepika RathnaNo ratings yet