Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bacterial Staining
Bacterial Staining
Uploaded by
CABAÑAS, Azenyth Ken A.0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views32 pagesNegative staining is useful for determining bacterial cell morphology with less cell shrinkage and more accurate size determination, especially for spirochetes. Differential staining uses primary, mordant, decolorizer, and secondary stains to distinguish bacteria. Gram positive bacteria retain the primary stain while gram negative bacteria take up the counterstain. Acid fast bacteria take up the primary stain pink/red and non-acid fast take the blue counterstain.
Original Description:
Original Title
Bacterial-staining
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentNegative staining is useful for determining bacterial cell morphology with less cell shrinkage and more accurate size determination, especially for spirochetes. Differential staining uses primary, mordant, decolorizer, and secondary stains to distinguish bacteria. Gram positive bacteria retain the primary stain while gram negative bacteria take up the counterstain. Acid fast bacteria take up the primary stain pink/red and non-acid fast take the blue counterstain.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views32 pagesBacterial Staining
Bacterial Staining
Uploaded by
CABAÑAS, Azenyth Ken A.Negative staining is useful for determining bacterial cell morphology with less cell shrinkage and more accurate size determination, especially for spirochetes. Differential staining uses primary, mordant, decolorizer, and secondary stains to distinguish bacteria. Gram positive bacteria retain the primary stain while gram negative bacteria take up the counterstain. Acid fast bacteria take up the primary stain pink/red and non-acid fast take the blue counterstain.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 32
BACTERIAL STAINING
MARIA DYNAH T. PETILONA
RMT, EDD
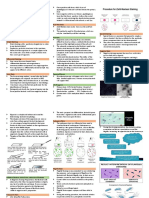
NEGATIVE
STAINING
Negative stain is also useful in determining bacterial
cell morphology.
Advantages:
Less shrinkage of the cells.
More accurate cell size dtermination.
Useful for spirochaetes
Leaving the orgnaisms transparent and visible in a
darkened field
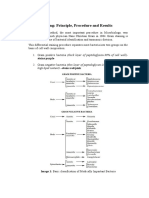
DIFFERENTIAL
STAINING
Differential staining reacts differently with
different kinds of bacteria and can be used to
distinguish them. Four types of reagents :
1. 1. Primary stain – initial stain applied to
bacterial smear.
2. 2. Mordant – increases the affinity of the
primary stain to the organisms.
3. 3. Decolorizer – washes off the primary stain.
4. 4. Secondary or counterstain – which gives
color to decolorized cell.
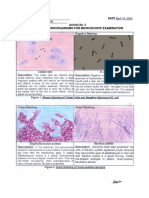
A bacterium is classified as Gram positive, if it
retains the color of the primary stain ( violet
or blue).
Gram positive cocci: Staphylococcus,
Streptococcus
Gram positive bacilli: Bacillus , Clostridium,
Corynebacterium, Lactobacillis, Listeria spp.
Gram negative if it decolorizes and takes up the color
of the counterstain (red or pink)
Gram negative cocci: Neisseria spp.
Gram negative bacilli: Escherichia, Pseudomonas,
Salmonella, Shigella, Haemophilus spp.
Acid fast organisms take up the color of the primary
stain (pink or red) while non acid fast take up the
counterstain (blue)
You might also like
- Microbiology: a QuickStudy Laminated 6-Page Reference GuideFrom EverandMicrobiology: a QuickStudy Laminated 6-Page Reference GuideNo ratings yet
- Gram StainingDocument6 pagesGram StainingSuci Yulia HartiNo ratings yet
- Staining TechniquesDocument10 pagesStaining TechniquesJohn Emmanuel TayagNo ratings yet
- Gram StainingDocument13 pagesGram Stainingzahra__100% (1)
- Gram Staining Clinical ExerciseDocument10 pagesGram Staining Clinical ExerciseHimani Aggarwal100% (1)
- Dyes and StainsDocument49 pagesDyes and StainsBilal Mumtaz AwanNo ratings yet
- Stainning 2019Document29 pagesStainning 2019Almoatazbellah AbdallahNo ratings yet
- Grpop 5-Gram StainingDocument8 pagesGrpop 5-Gram StainingMayaPopbozhikova100% (1)
- Gram StainingDocument37 pagesGram StainingdhanyaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Act. 8Document3 pagesWorksheet Act. 8ALDRISCHE TYRONNE TORIBIO JINGCONo ratings yet
- Gram StainingDocument72 pagesGram Stainingtummalapalli venkateswara rao100% (2)
- Staining TechniquesDocument13 pagesStaining TechniquesNichols Amy TarunNo ratings yet
- Lab CDocument3 pagesLab CEmmanNo ratings yet
- Simple Stain Differential StainDocument2 pagesSimple Stain Differential StainmomoNo ratings yet
- Lesson-02 COMMON STAINING TECHDocument13 pagesLesson-02 COMMON STAINING TECHno1dubakoorNo ratings yet
- Group 5 - Experiment No.9 - Preparation of Bacterial Smear and Gram StainingDocument10 pagesGroup 5 - Experiment No.9 - Preparation of Bacterial Smear and Gram StainingPMG BrightNo ratings yet
- Staining Techniques: Report By: Dimapinto Kulidtod Padayhag VelardeDocument21 pagesStaining Techniques: Report By: Dimapinto Kulidtod Padayhag VelardeconnievelardeNo ratings yet
- Gram StainDocument7 pagesGram StainYani ManuelNo ratings yet
- Differential StainingDocument8 pagesDifferential Stainingabdullah albayatiNo ratings yet
- Acivity 3 MicropharaDocument6 pagesAcivity 3 MicropharaDiane JaravataNo ratings yet
- Gram StainingDocument9 pagesGram StainingAnuNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Exercise 4Document6 pagesLaboratory Exercise 4Dane Ashley RubinoNo ratings yet
- Its Function Is To Impart Its: Differential StainingDocument7 pagesIts Function Is To Impart Its: Differential StainingAbdullah Muhammed khaleel HassanNo ratings yet
- Discuss The Various Theories On The Gram Stain.: Gram-Negative Bacteria Gram-Positive BacteriaDocument5 pagesDiscuss The Various Theories On The Gram Stain.: Gram-Negative Bacteria Gram-Positive BacteriaFiddo Waggay100% (3)
- Lab 4 DIFFERENTIAL & Special STAINDocument21 pagesLab 4 DIFFERENTIAL & Special STAINAAANo ratings yet
- Gram StainingDocument11 pagesGram StainingSri Ram Prasath TNo ratings yet
- Different Staing MethodDocument36 pagesDifferent Staing MethodAnik AlamNo ratings yet
- Observing Microorganism Through A Microscope: Basic Techniques Needed To Study BacteriaDocument6 pagesObserving Microorganism Through A Microscope: Basic Techniques Needed To Study BacteriaHNo ratings yet
- Post LabDocument3 pagesPost LabQueenie CalambaNo ratings yet
- Learn Microbiology Online Medical Microbiology Guide: News TickerDocument19 pagesLearn Microbiology Online Medical Microbiology Guide: News TickerCecilia MukototsiNo ratings yet
- Staining TechniquesDocument4 pagesStaining TechniquesAminat AdeolaNo ratings yet
- Gram Staining StainingDocument3 pagesGram Staining StainingSister RislyNo ratings yet
- Objective: Theory:: Differential StainingDocument5 pagesObjective: Theory:: Differential StainingPatricia Anne Nicole CuaresmaNo ratings yet
- Different Staing MethodDocument35 pagesDifferent Staing MethodAnik Alam100% (1)
- Cell Staining: The Simple StainDocument4 pagesCell Staining: The Simple StainAitlas KhanNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Staining: Departemen Mikrobiologi Program Studi Pendidikan Dokter Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas TanjungpuraDocument24 pagesBacterial Staining: Departemen Mikrobiologi Program Studi Pendidikan Dokter Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas TanjungpuraAdinda RANo ratings yet
- Lab Report MicrobiologyDocument8 pagesLab Report MicrobiologyOliaNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Principles in Microbiology 12.08.15Document50 pagesDiagnostic Principles in Microbiology 12.08.15Kurt ZepedaNo ratings yet
- Stains and Staining Lab3 and 4Document43 pagesStains and Staining Lab3 and 4Abdurraouf SaidNo ratings yet
- Bs Staining of Bacteria-1-1Document34 pagesBs Staining of Bacteria-1-1nchindalongchilewisNo ratings yet
- Moyes 2009, Tinción de GramDocument8 pagesMoyes 2009, Tinción de GramVale rumazNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9 Components of A BuildingDocument3 pagesLecture 9 Components of A BuildingAdam AhsanNo ratings yet
- Stainingbacteria 101004225924 Phpapp02Document63 pagesStainingbacteria 101004225924 Phpapp02pollux23No ratings yet
- Module 6 Gram Staining PreLabDocument24 pagesModule 6 Gram Staining PreLabcloudNo ratings yet
- Mikrobiologi - Pewarnaan GramDocument20 pagesMikrobiologi - Pewarnaan Gramanugrah syahrurramadhanNo ratings yet
- Lab Sheet - Gram StainingDocument4 pagesLab Sheet - Gram Stainingbliss polleyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document24 pagesChapter 3ettogameNo ratings yet
- Lab 3Document15 pagesLab 3maryamNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Classification, StainingDocument13 pagesBacterial Classification, Stainingapi-19969058No ratings yet
- Microbenotes Com Gram Stain Principle Reagents Procedure and Result InterpretationDocument5 pagesMicrobenotes Com Gram Stain Principle Reagents Procedure and Result Interpretationzoology qauNo ratings yet
- Lab Exercise 14,15,16 MicrobioDocument4 pagesLab Exercise 14,15,16 Microbiotaylorstack18No ratings yet
- 2-Bacterial StainingDocument17 pages2-Bacterial StainingreenaddeafNo ratings yet
- Micro. Lab 02Document11 pagesMicro. Lab 02susanNo ratings yet
- Exercise 7 Staining Techniques: Gram Stain For Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA)Document2 pagesExercise 7 Staining Techniques: Gram Stain For Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA)Jemimah Ruth GanoNo ratings yet
- Merhan, Kristine Mae M. (Lab Activity 5)Document5 pagesMerhan, Kristine Mae M. (Lab Activity 5)Kristine MerhanNo ratings yet
- 54 Staining TechniquesDocument6 pages54 Staining TechniquesPrajakta GawadeNo ratings yet
- Assignment Gram Stain.111Document6 pagesAssignment Gram Stain.111premium Shopping centreNo ratings yet
- Microbiology IntroductionDocument17 pagesMicrobiology IntroductionDiegoNo ratings yet
- StainingDocument49 pagesStainingShristi RanaNo ratings yet
- GramstainDocument3 pagesGramstainbasyalsumit555No ratings yet