Professional Documents
Culture Documents
To Assemble A Household Circuit Comprising Three Bulbs, Three (On/off) Switches A Fuse and A Power Source.
Uploaded by
Study Material100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
977 views4 pagesActivity file
Original Title
To assemble a household circuit comprising three bulbs, three (on/off) switches a fuse and a power source.
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentActivity file
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
977 views4 pagesTo Assemble A Household Circuit Comprising Three Bulbs, Three (On/off) Switches A Fuse and A Power Source.
Uploaded by
Study MaterialActivity file
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
ACTIVITIES:1
Aim: To assemble a household circuit comprising three bulbs,
three (on/ off) switches a fuse and a power source.
Apparatus: Three blubs (6 V, 1 W) each, fuse of 0.6A,
main switch a power supply (battery eliminator), three (on/off)
switches flexible connecting wire with red and black plastic
covering, a fuse wire.
Theory: Electricity supplied to us for domestic purposes is
220 A.C. and 50 Hz. The household circuit, all appliances are
connected in 8parallel9 with mains. The switches are
connected in series with each appliances in live wire.5A
switches are required for heavy load appliances like refrigerator,
air conditioner, geyser, hot plates etc. All appliances must have
three wires called live, neutral and the earth. Total power
consumption 8P9 at a time
P = P1 + P2 +P3 +………………
Where P1, P2 , P3 are the powers drawn by appliances.
To protect the appliances from damage when unduly high
currents are drawn fuse of little higher rating, 10 to 20 higher
than the current normally drawn by all appliances. For further
safety, a suitable value MAINS FUSE like rating 32A is
connected in series and supply source.
• Procedure:
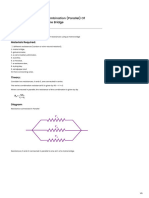
• 1. Connect the components as per the Wheatstone bridge circuit: battery, galvanometer, jockey, and a one-ohm standard resistor in series.
• 2. Attach the meter bridge wire in parallel with the galvanometer, and connect the unknown resistor in one gap and the known resistor in the
opposite gap.
• 3. Adjust the jockey along the meter bridge wire to find the null point (zero deflection) on the galvanometer.
• 4. Record the lengths L1 and L2 on either side of the null point.
• 5. Calculate the unknown resistance (R2) using the formula \( R1/R2 = L1/L2 \).
• 6. Repeat the experiment for series combination by connecting R2 in series with R1 and calculate the equivalent resistance (( R_eq = R1 +
R2 )).
• 7. Repeat for parallel combination by connecting R2 in parallel with R1 and calculate the equivalent resistance ( 1/R_eq = 1/R1 + 1/R2 )
• .8. Compare the experimental results with the theoretical predictions .
Conclusion: Creating this circuit helps understand the concept of a series circuit where the current flows through one
path. It also demonstrates the functionality of switches in controlling the flow of electricity to individual components
(bulbs, in this case).
The fuse acts as a safety measure, breaking the circuit if there's an excessive flow of current. Overall, it's a simple but
effective setup to grasp the basics of a household electrical circuit.
Precaution:
1.Ensure all wires are properly insulated and free from damage or wear.
2.Using electrical tape or wire nuts to cover exposed wires helps prevent accidental contact and potential hazards.
ACTIVITY :2
• AIM: To assemble the components of a given electrical circuit.
• MATERIAL REQUIRED: Resistor, ammeter, (0-1.5A) voltmeter (0-5V ), battery, one way key, rheostat,
sand paper, connecting wires.
• PROCEDURE:
• 1. Connect the components as shown in Figure.
• 2. After closing the key K, check that the voltmeter and ammeter show deflections on the right hand side.
• 3. Check the continuity of the assembled circuit using a multimeter .
• RESULT: The components of the electrical circuit were assembled
• PRECAUTIONS:
• 1. The positive terminal of the battery should be connected to the positive terminal of ammeter and positive terminal
of the voltmeter.
• 2. The ammeter should be connected in series with the resistor and the voltmeter should be connected in parallel with
the resistor.
• 3. Sand paper should be used to clean the ends of connecting wires and leads of the component terminals.
• Grease/oil or oxide on their surfaces is insulating in nature and needs to be removed. However, do not clean the plugs
and keys with sand paper. Excessive use of sand paper in such a case will make the plug unfit to be used with the key.
Activity :3
Aim :
To draw the diagram of a given open circuit comprising at least a battery, resistor/rheostat,
key, ammeter and voltmeter. Mark the components that are not connected in proper order
and correct the circuit and also the circuit diagram.
• Apparatus and material :
A battery eliminator or a battery (0 to 6 V), rheostat, resistance box (0 to 100 £2), two or one way key. D.C.
ammeter (0-3) A and a D.C. voltmeter (0-3) V.
• Theory:
An open circuit is the combination of primary components of electric circuit in a such a manner that on
closing the circuit no current is drawn from the battery.
Procedure
Ammeter: It should be connected in series, with the battery eliminator.
Voltmeter: It should be connected in parallel to the resistor.
Rheostat: It should be connected in series (in place of resistance coil) with the battery eliminator.
Resistance coil: It should be connected in parallel (in place of rheostat).
One way key: It should be connected in series to the battery eliminator.
You might also like
- Physics Activity FileDocument16 pagesPhysics Activity FileAyush Raj100% (1)
- Activity Notes BookDocument12 pagesActivity Notes Bookkaran singh class 11 aNo ratings yet
- Boat Maintenance Companions: Electrics & Diesel Companions at SeaFrom EverandBoat Maintenance Companions: Electrics & Diesel Companions at SeaNo ratings yet
- Activity Activity Activity Activity Activity: ActivitiesDocument2 pagesActivity Activity Activity Activity Activity: ActivitiesHarsh ShahNo ratings yet
- Focal Length of Convex Lens by Plotting The Graph Between U and VDocument7 pagesFocal Length of Convex Lens by Plotting The Graph Between U and VSwapnil Khora100% (1)
- Focal Length of Convex Lens by Plotting GraphsDocument2 pagesFocal Length of Convex Lens by Plotting GraphshNo ratings yet
- Phy FileDocument14 pagesPhy FileNasreen FatimaNo ratings yet
- Frequency of AC Mains Using SonometerDocument2 pagesFrequency of AC Mains Using Sonometerharsh33% (3)
- Physicsinvestigatoryproject 170908150740Document20 pagesPhysicsinvestigatoryproject 170908150740Nx GamingYTNo ratings yet
- To Study The Factors On Which The Internal Resistance of A Cell DeoendsDocument17 pagesTo Study The Factors On Which The Internal Resistance of A Cell DeoendsSakshi GodaraNo ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory ProjectDocument11 pagesPhysics Investigatory ProjectRavi zalaNo ratings yet
- Physics Activity 2Document4 pagesPhysics Activity 2Ankit PanigrahiNo ratings yet
- Effect of light intensity on LDRDocument3 pagesEffect of light intensity on LDRAlura100% (1)
- Class 12th Physics Lab Manual Activity 6Document5 pagesClass 12th Physics Lab Manual Activity 6CoolBoyNo ratings yet
- AC SonometerDocument2 pagesAC Sonometerkirti100% (1)
- Metre Bridge ResistanceDocument2 pagesMetre Bridge ResistanceKrish Jain100% (3)
- Factors Affecting Internal Resistance of a CellDocument18 pagesFactors Affecting Internal Resistance of a CellPrajesh Biswas100% (1)
- Experiment 2 PhysicsDocument5 pagesExperiment 2 Physicsansh BeniwalNo ratings yet
- Sotyo Proko Blic School: TopicDocument15 pagesSotyo Proko Blic School: TopicYahyouknowme100% (1)
- Half Deflection of GalvanometerDocument3 pagesHalf Deflection of GalvanometerTamanna NayakNo ratings yet
- To Study Various Factors On Which The Internal Resistance Emf of A Cell DependsDocument17 pagesTo Study Various Factors On Which The Internal Resistance Emf of A Cell Dependsprashik vigheNo ratings yet
- FINAL2 MergedDocument17 pagesFINAL2 MergedDev Barot100% (1)
- Physics Investigatory ProjectDocument8 pagesPhysics Investigatory Projectharry potter33% (3)
- Experiment 3 - Meterbridge ParallelDocument7 pagesExperiment 3 - Meterbridge Parallelayushmanjee1303No ratings yet
- Activity - 2 - To Assemble The Component of An Electric CircuitDocument1 pageActivity - 2 - To Assemble The Component of An Electric CircuitAtul Kumar Mishra100% (1)
- Activity 3Document3 pagesActivity 3KUNo ratings yet
- Study the change in E.m.f of a Daniel cellDocument20 pagesStudy the change in E.m.f of a Daniel cellrahuhlNo ratings yet
- Phy ActivityDocument13 pagesPhy Activityrohit100% (1)
- Tangent Galvanometer Project FileDocument14 pagesTangent Galvanometer Project Filegaurav ramrakhiyaniNo ratings yet
- PHYsics Class12 Project Report Cbse 2020 2021 On Topic Ac GeneratorDocument11 pagesPHYsics Class12 Project Report Cbse 2020 2021 On Topic Ac GeneratorParth SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Measuring Resistance of a WireDocument14 pagesMeasuring Resistance of a WireSATYAM X-C100% (2)
- PHYSICS - FACTORS AFFECTING CELL RESISTANCEDocument5 pagesPHYSICS - FACTORS AFFECTING CELL RESISTANCEAaryan Shroff100% (2)
- Physics Investigatory ProjectDocument23 pagesPhysics Investigatory ProjectChampa Deepa PalialNo ratings yet
- Determine Galvanometer Resistance & Figure of MeritDocument4 pagesDetermine Galvanometer Resistance & Figure of MeritPriyanshu Kumar100% (4)
- To Verify The Laws of The Parallel Combination of ResistancesDocument3 pagesTo Verify The Laws of The Parallel Combination of Resistancesanamika7005865200No ratings yet
- PHYSICS Project Class 12Document16 pagesPHYSICS Project Class 12mihir khabiya100% (1)
- Factors Self Inductance Coil DependDocument23 pagesFactors Self Inductance Coil DependUpendra Mandal100% (1)
- Jasleen Kaur's full wave rectifier projectDocument17 pagesJasleen Kaur's full wave rectifier projectDaily Meme DOSENo ratings yet
- Meter Bridge ResistanceDocument3 pagesMeter Bridge ResistancekirtiNo ratings yet
- To use a multimeter to (a) identify base of a multimeter (b) distinguish between non and pop type transistors (c) see the unidirectional flow of current in case of a diode and an LED (d) check whether a given electronic component (ex- diode, transistor, or IC) is in working orderDocument5 pagesTo use a multimeter to (a) identify base of a multimeter (b) distinguish between non and pop type transistors (c) see the unidirectional flow of current in case of a diode and an LED (d) check whether a given electronic component (ex- diode, transistor, or IC) is in working orderAurora Aurealis50% (2)
- Full Wave Rectifier ProjectDocument20 pagesFull Wave Rectifier ProjectKhushi ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Integrated Project PhysicsDocument20 pagesIntegrated Project PhysicsRΛJIBUL ISLΛMNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 2 Meter BridgeDocument5 pagesExperiment No. 2 Meter Bridgepeniwal magicsNo ratings yet
- Observe Light Diffraction Thin SlitDocument3 pagesObserve Light Diffraction Thin SlitABHISHEK TIWARI100% (1)
- Factors On Which Self Inductance of CoilDocument7 pagesFactors On Which Self Inductance of CoilShikhar BajpaiNo ratings yet
- Increasing and Decreasing Math FunctionsDocument2 pagesIncreasing and Decreasing Math FunctionsAniruddha Kadam50% (2)
- PHYsics Class12 Project Report Cbse 2020 2021 On Topic Ac GeneratorDocument16 pagesPHYsics Class12 Project Report Cbse 2020 2021 On Topic Ac Generatorsufiyan haqueNo ratings yet
- XII Physics Investigatory Project To Study The Factor On Which The Self-Inductance of A Coil Depends (2) FinalDocument15 pagesXII Physics Investigatory Project To Study The Factor On Which The Self-Inductance of A Coil Depends (2) FinalMehul Ananthakumar100% (3)
- Physics Practical 22-23Document25 pagesPhysics Practical 22-23Arnav100% (1)
- Class Xii Physics Practical Lab Manual NewDocument28 pagesClass Xii Physics Practical Lab Manual NewAditya jainNo ratings yet
- Angle of Minimum Deviation for a PrismDocument2 pagesAngle of Minimum Deviation for a PrismMijazuddin Mansoori100% (1)
- Physics ProjectDocument9 pagesPhysics ProjectSoumya RamaiyaNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument12 pagesChemistrySouptik Pal100% (1)
- To Assemble The Components of A Given Electrical CircuitDocument2 pagesTo Assemble The Components of A Given Electrical Circuitarpit375rajputNo ratings yet
- How to assemble a basic household circuitDocument11 pagesHow to assemble a basic household circuitKrishnashis DasNo ratings yet
- Six Activities Class 12Document16 pagesSix Activities Class 12Priyanshu jhaNo ratings yet
- Pparatus and Material RequiredDocument4 pagesPparatus and Material RequiredANAND TALARINo ratings yet
- List of ActivitiesDocument15 pagesList of Activitieskaustubhkushagra9No ratings yet
- Postmodern EthicsDocument1 pagePostmodern Ethicsgeorge elerickNo ratings yet
- 2008 Infosys Model QuestionsDocument23 pages2008 Infosys Model Questionsapi-3824713No ratings yet
- Tooth Development, Eruption & Applied Aspects: Saurabh Roy 09.03.2016Document95 pagesTooth Development, Eruption & Applied Aspects: Saurabh Roy 09.03.2016reema aslamNo ratings yet
- A Grammar of Anong Language Death Under Intense ContactDocument409 pagesA Grammar of Anong Language Death Under Intense ContacthaoyichuanNo ratings yet
- List of Students Allotted in Open Elective Subjects (B. Tech and M. Tech (Dual Degree) Integrated MSc. - 4th Semester - Regular - 2018 - 19) - 2 PDFDocument26 pagesList of Students Allotted in Open Elective Subjects (B. Tech and M. Tech (Dual Degree) Integrated MSc. - 4th Semester - Regular - 2018 - 19) - 2 PDFArpan JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Construction Site PremisesDocument78 pagesConstruction Site PremisesDrew B Mrtnz67% (6)
- NPT Pipe Thread Sizes and TapersDocument1 pageNPT Pipe Thread Sizes and TapersRajesh J BharadwajNo ratings yet
- Let Us Discover: Hairdressing-Grade 11Document5 pagesLet Us Discover: Hairdressing-Grade 11cherry d.bandolaNo ratings yet
- Bentley Bentayga BrochureDocument9 pagesBentley Bentayga BrochureGerry CalàNo ratings yet
- The Future - G&VDocument6 pagesThe Future - G&VManuelHerreraMontoyaNo ratings yet
- Proximity Sensing and Warning Technology For Heavy Construction Equipment OperationDocument10 pagesProximity Sensing and Warning Technology For Heavy Construction Equipment OperationAnand ReddyNo ratings yet
- Errata Introduction To Quantum Mechanics, David Griffiths, 2nd Ed.Document3 pagesErrata Introduction To Quantum Mechanics, David Griffiths, 2nd Ed.Marcel BezerraNo ratings yet
- CHS-WWW - Polsteel. TUBOS METALICOS PDFDocument3 pagesCHS-WWW - Polsteel. TUBOS METALICOS PDFEduardo TorreNo ratings yet
- 11 - FORAGERS by Sam BoyerDocument106 pages11 - FORAGERS by Sam BoyerMurtaza HussainNo ratings yet
- Simulation of bitumen upgrading processes modelling and optimisationDocument6 pagesSimulation of bitumen upgrading processes modelling and optimisationDonato MontroneNo ratings yet
- 0610 m16 QP 62Document12 pages0610 m16 QP 62faryal khanNo ratings yet
- Hydromechanical Piercing Perforation: Oil Service Innovation TechnologiesDocument8 pagesHydromechanical Piercing Perforation: Oil Service Innovation TechnologiesЕлена ПаниотNo ratings yet
- Animal cell organelle and plant cell structure quizDocument20 pagesAnimal cell organelle and plant cell structure quizSITI ZAHILA ARYANIE BINTI ABD RAHIM KPM-GuruNo ratings yet
- My Version of Meatlaof Project DraftDocument3 pagesMy Version of Meatlaof Project DraftCloue Faye I. BasalloNo ratings yet
- CaseStudy AmtrakDocument14 pagesCaseStudy Amtraksnob_kNo ratings yet
- SFM Issue Repor 15-4-2023Document3 pagesSFM Issue Repor 15-4-2023Esdras Fransua CisnerosNo ratings yet
- MidtermDocument3 pagesMidtermTrisha MondonedoNo ratings yet
- Sponge BobDocument4 pagesSponge BobchabriesNo ratings yet
- Eutelsat 12 West A Satellite FootprintDocument2 pagesEutelsat 12 West A Satellite FootprintSkybrokersNo ratings yet
- 07 IRIS NV PCB OtherDocument15 pages07 IRIS NV PCB OtherArnaldo cordovaNo ratings yet
- Sampling and Field Testing at Wastewater Treatment FacilitiesDocument11 pagesSampling and Field Testing at Wastewater Treatment FacilitiesSundarapandiyan SundaramoorthyNo ratings yet
- Foreign Body Airway ObstructionDocument6 pagesForeign Body Airway ObstructionReeja RajeshNo ratings yet
- 4 Floral ClockDocument4 pages4 Floral ClockmiguelibasterNo ratings yet
- yudaturana,+Manajer+Jurnal,+dr +nelson+rev+2+ (162-172)Document12 pagesyudaturana,+Manajer+Jurnal,+dr +nelson+rev+2+ (162-172)Fath TiaraNo ratings yet