Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Gas Chromatography
Uploaded by
Gunner Stoner0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views8 pagesGas chromatography is a technique used to separate volatile or vaporizable compounds. It works by carrying a gas mobile phase, like helium or nitrogen, through a narrow column coated with a non-volatile liquid stationary phase. Samples are injected and swept through the column, with more volatile compounds moving faster. Compounds exit the column at different retention times and are detected, producing a chromatogram that identifies the compounds and indicates their concentrations. Gas chromatography is commonly used in clinical labs to analyze compounds like lipids that withstand high temperatures.
Original Description:
Original Title
Gas chromatography
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentGas chromatography is a technique used to separate volatile or vaporizable compounds. It works by carrying a gas mobile phase, like helium or nitrogen, through a narrow column coated with a non-volatile liquid stationary phase. Samples are injected and swept through the column, with more volatile compounds moving faster. Compounds exit the column at different retention times and are detected, producing a chromatogram that identifies the compounds and indicates their concentrations. Gas chromatography is commonly used in clinical labs to analyze compounds like lipids that withstand high temperatures.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views8 pagesGas Chromatography
Uploaded by
Gunner StonerGas chromatography is a technique used to separate volatile or vaporizable compounds. It works by carrying a gas mobile phase, like helium or nitrogen, through a narrow column coated with a non-volatile liquid stationary phase. Samples are injected and swept through the column, with more volatile compounds moving faster. Compounds exit the column at different retention times and are detected, producing a chromatogram that identifies the compounds and indicates their concentrations. Gas chromatography is commonly used in clinical labs to analyze compounds like lipids that withstand high temperatures.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 8
Gas Chromatography
BY : ASHISH THAPA MAGAR
Introduction
Gas chromatography is also known as vapour-
phase chromatography .
It is used to separate compounds that are volatile
or can be made volatile
It can be gas-solid chromatography (GSC) with a
solid stationary phase or gas-liquid
chromatography (GLC)with a non-volatile liquid
stationary phase .
GLC is commonly used in clinical laboratories.
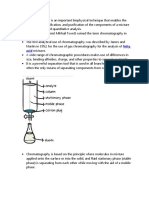
Gas liquid chromatography
In GLC the stationary phase is liquid and the
mobile phase is gas.
The mobile phase (gas ) can be helium, nitrogen or
argon.
The stationary phase(liquid) is supported by a
column of inert materials such as silica in a long
narrow column.
The instrument can be operated in constant
temperature or programmed to run in different
temperature (sample with different votalities).
GLC
Cont.
The sample to be injected must be gas or made
volatile by high temperature.
Sample vapour is swept through the column
partially as gas and partially dissolved in the liquid
phase.
Volatile compounds the are present mainly is gas
phase will have low boiling point and move quickly
through the column.
Compounds with higher boiling point will move
slowly through the column.
Cont.
The elute that passes through the detector produces
an electric signal in proportion to the conc. of the
volatile components.
The chromatogram is used both to identify the
compounds by their retention time and conc.
This is more suitable for compounds (e.g. lipids )
which resist degradation at high temperature.
Reference :
Textbook of Biochemistry for Medical Students , DM
Vasdevan
Biochemistry , Dr. U. Satyanarayana , Dr. U.
Chakrapani
THANK YOU
You might also like
- High-Pressure Fluid Phase Equilibria: Phenomenology and ComputationFrom EverandHigh-Pressure Fluid Phase Equilibria: Phenomenology and ComputationNo ratings yet
- A System of Instruction in the Practical Use of the Blowpipe Being A Graduated Course Of Analysis For The Use Of Students And All Those Engaged In The Examination Of Metallic CombinationsFrom EverandA System of Instruction in the Practical Use of the Blowpipe Being A Graduated Course Of Analysis For The Use Of Students And All Those Engaged In The Examination Of Metallic CombinationsNo ratings yet
- Gas ChromatographyDocument38 pagesGas ChromatographyManoj SigdelNo ratings yet
- Gas Chromatography - WikipediaDocument13 pagesGas Chromatography - WikipediaMuhammed BatureNo ratings yet
- Gas ChromatographyDocument11 pagesGas Chromatographysumit sharmaNo ratings yet
- Gas ChromatographyDocument70 pagesGas ChromatographypraveenNo ratings yet
- Gas Chromatography (GC), Is A Common Type of Chromatography Used in Analytic Chemistry For Separating andDocument2 pagesGas Chromatography (GC), Is A Common Type of Chromatography Used in Analytic Chemistry For Separating andhemu99898No ratings yet
- CHROMATOGRAPHYDocument9 pagesCHROMATOGRAPHYKarthi Keyan KanagarajNo ratings yet
- Analaytical Assignment Group-3Document10 pagesAnalaytical Assignment Group-3yilma wendayehuNo ratings yet
- Gas Liquid ChromotographyDocument29 pagesGas Liquid Chromotographyscicws1133No ratings yet
- Gas Chromatography - Chemistry LibreTextsDocument22 pagesGas Chromatography - Chemistry LibreTextsMohammad NadimNo ratings yet
- IMA Unit 4Document30 pagesIMA Unit 4vinushakaveripakam26No ratings yet
- Gas ChromatographyDocument12 pagesGas ChromatographyYaman Adnan QabajaNo ratings yet
- GC PDFDocument27 pagesGC PDFViper ThroughNo ratings yet
- Food PresentationDocument18 pagesFood PresentationEducationNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Analytical SeparationDocument75 pagesIntroduction To Analytical SeparationVincentius EkyNo ratings yet
- مكامن كورس ثاني 2Document9 pagesمكامن كورس ثاني 2سجاد كريم هاشم سماويNo ratings yet
- Chromatographic Biochemistry Analytical ChemistryDocument8 pagesChromatographic Biochemistry Analytical ChemistryDeepanshi BansalNo ratings yet
- Gas ChromatographyDocument22 pagesGas ChromatographyYoussef AliNo ratings yet
- How Does Gas Chromatography Work?Document1 pageHow Does Gas Chromatography Work?Vijay KumarNo ratings yet
- Chromatography BOOKDocument9 pagesChromatography BOOKDeepak PradhanNo ratings yet
- Unit 4, Instrumental Methods of Analysis, B Pharmacy 7th Sem, Carewell PharmaDocument27 pagesUnit 4, Instrumental Methods of Analysis, B Pharmacy 7th Sem, Carewell Pharmaayush pathakNo ratings yet
- GCDocument15 pagesGCMalik DaniyalNo ratings yet
- Gas ChromatographyDocument25 pagesGas ChromatographyPrabneeshNo ratings yet
- Chromatography, Classification, Principle of Working and Selected TechniquesDocument13 pagesChromatography, Classification, Principle of Working and Selected TechniquesS.Umair Jarwar70% (10)
- InTech Stationary PhasesDocument25 pagesInTech Stationary PhasesqncargbNo ratings yet
- 4 - Gas ChromatographyDocument49 pages4 - Gas Chromatographyamany mohamedNo ratings yet
- Working Principle of GCDocument4 pagesWorking Principle of GCAmnaKamranNo ratings yet
- General Description of ChromatographyDocument5 pagesGeneral Description of ChromatographySrima DasNo ratings yet
- Chromatography NotesDocument19 pagesChromatography Noteswama ojhaNo ratings yet
- Gas Chromatography - A Brief Review: July 2018Document8 pagesGas Chromatography - A Brief Review: July 2018hàNo ratings yet
- Research Paper On Gas ChromatographyDocument6 pagesResearch Paper On Gas Chromatographyc9rbzcr0100% (1)
- Gas Chromatography - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument10 pagesGas Chromatography - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaMarco García HernándezNo ratings yet
- Gas ChromatographyDocument56 pagesGas Chromatographyshruti shahNo ratings yet
- Gas Chromatograhy (G.C) : Schematic Diagram For Gas ChromatographyDocument10 pagesGas Chromatograhy (G.C) : Schematic Diagram For Gas ChromatographySunday IstifanusNo ratings yet
- ChomatographyDocument5 pagesChomatographyAlaeldeen EltayebNo ratings yet
- Gas Liquid Chromatography (GLC)Document10 pagesGas Liquid Chromatography (GLC)Gopinathan MNo ratings yet
- Atomic Absorption SpectrosDocument2 pagesAtomic Absorption SpectrosSirTonz100% (1)
- GCDocument5 pagesGCstarsubhashNo ratings yet
- Gas ChromatographyDocument5 pagesGas ChromatographyassertivailNo ratings yet
- Gas ChromatographyDocument13 pagesGas Chromatographyajay696No ratings yet
- Gas ChromatographyDocument9 pagesGas ChromatographyharshiniNo ratings yet
- Packed Bed AbsorptionDocument4 pagesPacked Bed AbsorptionSenthilNathanNo ratings yet
- 45 GC PDFDocument2 pages45 GC PDFFaizal ThelordImmortalNo ratings yet
- Sni 7119-2-2017Document20 pagesSni 7119-2-2017alexander adi PratamaNo ratings yet
- GC Connections: A Compendium of GC Terms and TechniquesDocument5 pagesGC Connections: A Compendium of GC Terms and TechniquesClaudia GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Gas ChromatographyDocument77 pagesGas Chromatography1 2No ratings yet
- Experiment of Gas ChromatographyDocument11 pagesExperiment of Gas ChromatographyMohd Sukri DaudNo ratings yet
- Separation TechniquesDocument9 pagesSeparation TechniquesBobbo KabirNo ratings yet
- Gas Chromatography Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS)Document45 pagesGas Chromatography Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS)Ganesh Parsewar93% (15)
- Che 413 1Document5 pagesChe 413 1Looking forwardNo ratings yet
- Review of Gas ChromatographyDocument38 pagesReview of Gas Chromatographyabhijit612No ratings yet
- Gas Liquid ChromatographyDocument3 pagesGas Liquid ChromatographyDennis MuneneNo ratings yet
- Carrying Out Gas-Liquid ChromatographyDocument9 pagesCarrying Out Gas-Liquid ChromatographymahtabsirNo ratings yet
- Gas Liquid ChromatographyDocument8 pagesGas Liquid Chromatographyindra_f04No ratings yet
- Unit 4 Chromatography-IIDocument18 pagesUnit 4 Chromatography-IIAli SheikhNo ratings yet
- Cognosy Lab PresentationDocument16 pagesCognosy Lab PresentationAhsham AliNo ratings yet
- Chromatography NotesDocument8 pagesChromatography Notesaryan86yaNo ratings yet
- JW GC and HPLC (Notes On Othe Chromatographic Techinques Are Absent)Document21 pagesJW GC and HPLC (Notes On Othe Chromatographic Techinques Are Absent)Greatness AgwazeNo ratings yet
- Answer To The Question No. 1 (A)Document5 pagesAnswer To The Question No. 1 (A)Mohona JesicaNo ratings yet