100% found this document useful (3 votes)
9K views46 pagesProject Management Power Point Presentation PPT PDF Notes
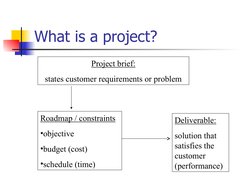
This document provides an introduction to project management. It defines what a project is, discusses the characteristics and attributes of projects, and explains what project management entails. It also outlines some of the key aspects of project management including the project life cycle, stakeholders, knowledge areas, tools and techniques, and certification. The document emphasizes that project management involves balancing scope, time, and cost constraints.
Uploaded by
Devesh ChauhanCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (3 votes)
9K views46 pagesProject Management Power Point Presentation PPT PDF Notes
This document provides an introduction to project management. It defines what a project is, discusses the characteristics and attributes of projects, and explains what project management entails. It also outlines some of the key aspects of project management including the project life cycle, stakeholders, knowledge areas, tools and techniques, and certification. The document emphasizes that project management involves balancing scope, time, and cost constraints.
Uploaded by
Devesh ChauhanCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd