Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Trunk and Extremities
Uploaded by
prathimapesaru70 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views43 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views43 pagesTrunk and Extremities
Uploaded by
prathimapesaru7Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 43
Trunk and Extremities
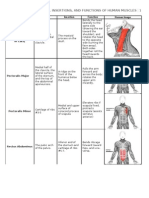
SOMATOMETRIC LANDMARKS ON HUMAN BODY
Standard hand hanging position
Acromion (a)
• It is the most lateral point on the lateral margin of the acromial
process at the scapula when the subject stands in normal position
with his arms hanging by the sides. It can be located by palpating the
scapular spine with the fingers.
Acropodion (ap)
• It is the most forwardly placed point of the toe cap, either on the first
or the second toe, if the foot is kept in normal position. As a matter of
fact, the Acropodion (ap) is a point at the tip of the longest toes.
• It is the most distally placed point on the tip of the longest toe (first or
second toe) when the foot is stretched to the maximum.
Dactylion (da)
• It is the lowest point on the anterior curved top of the middle finger,
provided me arm hangs sidewise.
• It is the most distally placed point on the anterior margin of the
middle finger when the subject is in standard arm hanging position.
Iliocristale (ic)
• It is the most laterally placed point on the iliac crest when the subject
stands in normal position. Iliocristale is located on the lateral border
at the upper margin of the iliac crest which can be found out by
palpating with the fingers from down to upwards along the margin of
the crest to see where it crosses over the upper margin.
• It is the most laterally placed point on the lateral border at the upper
margin of the iliac crest.
Iliospinale anterior (isa)
• It is a highest point on superior-anterior iliac spine. It can be located
by placing the fingers on the hips and letting the thumb to find out
the tip of the bone.
• It is the highest point on the superior anterior iliac spine.
Iliospinale posterior (isp)
• This is the most posteriorly placed point on superior posterior iliac
crest.
• It is the most posteriorly placed point on the superior posterior iliac
crest,
Metacarpale radiale (mr)
• It is the most medially placed point on the head of second metacarpal
bone, on the stretched palm.
• It is the most medially placed point on the tip of the second
metacarpal in a stretched hand.
Metacarpale ulnare (mu)
• It is the most laterally placed point on the head of the fifth
metacarpal bone, on the stretched palm.
• Metacarpale ulnare (mu): It is the most laterally placed point on the
tip of the fifth metacarpal in a stretched hand.
Metatarsal fibulare (mft)
• This is the most laterally placed point on the head of the fifth
metatarsal.
• Metatarsale fibulare (mft):It is the most laterally placed point on the
tip of the fifth metatarsal.
Mesosternale (mst)
• This point is located on the anterior border of the sternum where
mid- sagittal plane cuts the line joining the articular surface of the
fourth rib. The position of the ribs may be counted from the sides.
Metatarsale tibiale (mtt)
• This point is the most laterally placed point on the head of the first
metatarsal.
• It is the most laterally placed point on the tip of the first metatarsal.
Pternion (pte)
• It is the hind-most point of the heel when the foot is normally
posited.
• It is the most posteriorly placed point on the heel in mid-sagittal plane
of stretched foot.
Radiale (r)
• It is the highest point on the border of the radius bone i.e. the upper
margin of the radiale capitulum when the arm hangs downwardly.
This landmark can be determined accurately by pronating and
supinating the lower arm. The rotating head of the radius is clearly
distinguished from stationary condyle of the humerus.
• It is the highest point on the upper margin of the radiale capitulum
when the subject is oriented in standard arm hanging position. The
landmark is accurately determined by pronating and supinating the
lower arm.
Spherion (sph)
• It is a lowest point on the tip of the medial malleolus of tibia when
the subject stands erect. The point is to be identified at the tip of the
malleolus.
• It is the lowest point on the tip of the medial malleolus of tibia when
the subject is oriented in standard arm hanging position.
Stylion (sty)
• It is a deepest (lowest) point on the styloid process of the radius if the
arm hangs sidewise. For locating the exact point, one has to palpate
the entire lateral margin of the radius with the thumb-tip.
• It is the deepest point on the styloid process of radius when the
subject is oriented in standard arm hanging position.
Tibiale (ti)
• It is a highest point on the middle of the medial border, which
corresponds to the inner glenoidal margin of the head of tibia. The
point is very hard to locate when adiposity develops on the kneecap,
as found frequently among the females. However, the upper tibiale
margin can be located with first finger and thumb by bending the
knee. The articular surface of the tibia may be indicated by a
horizontal line.
• It is the highest point on the head of tibia.
Symphysion (sy)
• This point is found on the upper margin of the pubic bone in the mid-
sagittal plane. To find out this point, right hand with stretched fingers
will slide downwards till the fingers touch the hard bone and it lies on
the level of the junction of the genital area and abdomen when the
skin must not be folded.
• It is the point on the upper margin of the symphysis of pubic bone in
mid- sagittal plane.
Measurements
• Height vertex or stature: It measures the vertical distance from vertex
(v) to floor when the subject is in standard arm hanging position.
• Sitting height vertex:It measures the straight distance from vertex (v)
to sitting surface of the subject when the subject is oriented in
standard position with head oriented in eye-ear plane and
vertebral column stretched to the maximum.
• Body weight: Weight should be taken with standard weighing
machine with minimum number of clothes and subject should stand
erect and barefooted.
• Skinfold measurements: Skin fold measurements provide a mean of
estimating the amount of fat in the body. Biceps and triceps are well
known sites for these measurements.
• Maximum calf girth: It measures the circumference of the calf where
the calf muscles are well
developed.
• Minimum waist girth: It measures the minimum circumference
between the chest and hip or the narrowest part between the ribs
and intestine.
• Maximum upper arm girth: It measures the maximum circumference
of the upper arm where the biceps muscles are most developed.
Measurement was taken horizontally.
• Chest girth: It measures the circumference of the chest when the
subject was breathing normally. This measurement is also taken
during maximum inspiration and maximum expiration.
• Hand length (isty-daIII): It measures the straight distance between the
midpoint (interstylion-isty) of a line joining the two stylion to
dactylion (daIII) of the middle finger.
• Hand breadth (mr-mu): It measures the straight distance between
metacarpal radialis (mr) to metacarpal ulnare (mu).
• Total upper extremity length (a-daIII): It measures the straight
distance between acromion (a) to dactylion (daIII) of the middle
finger when the subject is in standard arm hanging
position.
Somatometric indices
• Relative sitting height index: It is calculated by dividing sitting height
vertex with height vertex and then multiplied by 100.
• Relative bi-acromial breadth index = [(Bi-acromial breadth
(a-a))/(Height vertex (v-floor)] x 100
• Relative Bicristal breadth index = [(Bi-cristal breadth (ic-ic))/(Height
vertex (v-floor ))] x 100
• Relative chest girth index = [(Chest girth (circumference of the
chest))/(Height vertex (v-floor ))] x 100
• Hand index = [(Hand breadth (mr-mu))/(Hand length (sty-da))] x 100
You might also like
- Surface Anatomy of The Upper LimbDocument23 pagesSurface Anatomy of The Upper LimbSherifaNo ratings yet
- Living Anatomy of The Limbs and Back (With Answers)Document15 pagesLiving Anatomy of The Limbs and Back (With Answers)Aaron Nameer Abrar RahmanNo ratings yet
- Palpation of Bony LandmarksDocument4 pagesPalpation of Bony LandmarksNur Ashriawati BurhanNo ratings yet
- Thoracic WallDocument100 pagesThoracic WallEman RiazNo ratings yet
- AnthropometryDocument17 pagesAnthropometrybasmalanasser004No ratings yet
- 02 Appendicular SkeletonDocument40 pages02 Appendicular SkeletonkalyanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The HandDocument28 pagesAnatomy of The HandJorge Soto100% (3)
- ISAK Antrophometric CourseDocument5 pagesISAK Antrophometric Coursekabut81No ratings yet
- Unit 1 Anthr Pometry: N OductionDocument13 pagesUnit 1 Anthr Pometry: N OductionShreeja JadhavNo ratings yet
- Muscles of The Hand & WristDocument43 pagesMuscles of The Hand & WristWasemBhatNo ratings yet
- Gross Anatomy of The ForearmDocument52 pagesGross Anatomy of The ForearmADELAJA SAMUELNo ratings yet
- Anthropometry: Assessment and Monitoring of GrowthDocument10 pagesAnthropometry: Assessment and Monitoring of GrowthAbhishek GirdharNo ratings yet
- The HandDocument19 pagesThe HandNadhrah MazelinNo ratings yet
- Practical 3 FAO CRANIOMETRYDocument5 pagesPractical 3 FAO CRANIOMETRYparas.sharmaNo ratings yet
- Ankleand FootDocument35 pagesAnkleand FootHeba Abo bakrNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Examination TechniquesDocument36 pagesCardiovascular Examination TechniquesRUTUJA HARISH KSHIRSAGAR100% (1)
- Physical Examination of The Knee: Oleh: Dr. Feby Deliana Pembimbing: Dr. Deta Tanuwidjadja.,SpkfrDocument25 pagesPhysical Examination of The Knee: Oleh: Dr. Feby Deliana Pembimbing: Dr. Deta Tanuwidjadja.,Spkfrsingle_ladyNo ratings yet
- GA Wrist and HandDocument83 pagesGA Wrist and Handart gayoNo ratings yet
- Cervical GoniometeryDocument39 pagesCervical GoniometerySimranjit KaurNo ratings yet
- ForearmDocument60 pagesForearmhamadNo ratings yet
- Mnemonics and Memory Tips For Skeletal System and Muscles-1Document7 pagesMnemonics and Memory Tips For Skeletal System and Muscles-1cirelnonesNo ratings yet
- Radiography of Shoulder and ArmDocument81 pagesRadiography of Shoulder and ArmKristina ShresthaNo ratings yet
- KneeDocument29 pagesKneedoctoradeeb18No ratings yet
- Surface Landmarks and Body PositionsDocument2 pagesSurface Landmarks and Body PositionsLesNo ratings yet
- Hand and WristDocument29 pagesHand and WristsherysheryyNo ratings yet
- Part A: Introduction To The Surface Anatomy of The Thoracic SpineDocument11 pagesPart A: Introduction To The Surface Anatomy of The Thoracic SpineHammad -ullahNo ratings yet
- Cranio Sacral The Upper Sides of The SkullDocument2 pagesCranio Sacral The Upper Sides of The Skullmuitasorte9No ratings yet
- Surface Anatomy of Upper LimbDocument19 pagesSurface Anatomy of Upper LimbAkomolede AbosedeNo ratings yet
- Physical Examination of The Knee: Oleh: Dr. Darsuna Mardhiah Pembimbing: Dr. Deta Tanuwidjaja, SP - KFRDocument36 pagesPhysical Examination of The Knee: Oleh: Dr. Darsuna Mardhiah Pembimbing: Dr. Deta Tanuwidjaja, SP - KFRsingle_ladyNo ratings yet
- 202003291621086351upsingh SOMATOMETRYDocument21 pages202003291621086351upsingh SOMATOMETRYsumit kumarNo ratings yet
- Part ADocument14 pagesPart AHammad -ullahNo ratings yet
- Synthesis PelvimetryDocument2 pagesSynthesis PelvimetryCaguitla, Angela MayNo ratings yet
- 2.08 KinanthrEometric AssesDocument30 pages2.08 KinanthrEometric AssesAndreas ZourdosNo ratings yet
- Kiut BMS 2.1 IntroDocument39 pagesKiut BMS 2.1 IntroAbdulyNo ratings yet
- L - Upper Extremity (Bones and Muscles)Document56 pagesL - Upper Extremity (Bones and Muscles)Riyadh Ali nasser Al.Sharekh 0252No ratings yet
- ForearmDocument63 pagesForearmolamidealapa2608No ratings yet
- 22-Surface Anatomy of The Upper and Lower LimbsDocument24 pages22-Surface Anatomy of The Upper and Lower LimbsMiahz Tv100% (1)
- General AnatomyDocument71 pagesGeneral Anatomyrohit190585No ratings yet
- The Human ThoraxDocument71 pagesThe Human Thoraxbayenn100% (2)
- Static Palpation of The Spine FINALDocument13 pagesStatic Palpation of The Spine FINALPrathap KumarNo ratings yet
- Terminologia AnatomicaDocument37 pagesTerminologia AnatomicaAntony CevallosNo ratings yet
- Thoracic Cage and Wall: Dr. Afdal, Spa, M. BiomedDocument62 pagesThoracic Cage and Wall: Dr. Afdal, Spa, M. Biomedadhima indriNo ratings yet
- Rectus Capitis AnteriorDocument6 pagesRectus Capitis AnteriorSitiRabiatulAdawiyahNo ratings yet
- Anthropometry: by G Hema MaliniDocument52 pagesAnthropometry: by G Hema MaliniHema MaliniNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The HandDocument27 pagesAnatomy of The Handdoos1No ratings yet
- Origins, Insertions, and Functions of Human MusclesDocument5 pagesOrigins, Insertions, and Functions of Human MusclesNikhil Narang100% (1)
- 5001: Focus On Upper and Lower Limbs and Chest:: ST ST THDocument3 pages5001: Focus On Upper and Lower Limbs and Chest:: ST ST TH'Emily MillsNo ratings yet
- 3-Surface Anatomy of Upper and Lower Limbs PDFDocument31 pages3-Surface Anatomy of Upper and Lower Limbs PDFHuda KhanNo ratings yet
- Anterior Compartment of The ForearmDocument55 pagesAnterior Compartment of The ForearmAuza Moses IbrahimNo ratings yet
- CraniometryDocument31 pagesCraniometryMahesh TripathyNo ratings yet
- Anatomy 1st AssignmentDocument11 pagesAnatomy 1st Assignmenthasnain ahmedNo ratings yet
- 01 Bones of The Upper Limb by DR Derek NgabiranoDocument31 pages01 Bones of The Upper Limb by DR Derek NgabiranoYIKI ISAACNo ratings yet
- Ulnar NerveDocument19 pagesUlnar Nervemedical- physio classesNo ratings yet
- Fifteen Principles of Violin Playing Principles of PostureDocument2 pagesFifteen Principles of Violin Playing Principles of PostureJosepgf17 GirbesNo ratings yet
- HandDocument47 pagesHandadamufatimamaajiNo ratings yet
- Gastro & Ortho RecordDocument24 pagesGastro & Ortho RecordKV18 KK5No ratings yet
- Ankle Power PointDocument36 pagesAnkle Power PointjermaineNo ratings yet
- Animal Welfare in Bangladesh and The Role of Obhoyaronno CaseDocument11 pagesAnimal Welfare in Bangladesh and The Role of Obhoyaronno CaseZarin Tanjim WoyshorjoNo ratings yet
- JD For Library Interns Sep 2023Document2 pagesJD For Library Interns Sep 2023Bharat AntilNo ratings yet
- Sample Behavioral Interview QuestionsDocument3 pagesSample Behavioral Interview QuestionssanthoshvNo ratings yet
- Churches That Have Left RCCG 0722 PDFDocument2 pagesChurches That Have Left RCCG 0722 PDFKadiri JohnNo ratings yet
- Gee 103 L3 Ay 22 23 PDFDocument34 pagesGee 103 L3 Ay 22 23 PDFlhyka nogalesNo ratings yet
- Government College of Engineering Jalgaon (M.S) : Examination Form (Approved)Document2 pagesGovernment College of Engineering Jalgaon (M.S) : Examination Form (Approved)Sachin Yadorao BisenNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE Business Studies 4th Edition © Hodder & Stoughton LTD 2013Document1 pageCambridge IGCSE Business Studies 4th Edition © Hodder & Stoughton LTD 2013RedrioxNo ratings yet
- Present Continuous WorkshopDocument5 pagesPresent Continuous WorkshopPaula Camila Castelblanco (Jenni y Paula)No ratings yet
- Motion and Time: Check Your Progress Factual QuestionsDocument27 pagesMotion and Time: Check Your Progress Factual QuestionsRahul RajNo ratings yet
- Abramson, Glenda (Ed.) - Oxford Book of Hebrew Short Stories (Oxford, 1996) PDFDocument424 pagesAbramson, Glenda (Ed.) - Oxford Book of Hebrew Short Stories (Oxford, 1996) PDFptalus100% (2)
- Hydraulics Experiment No 1 Specific Gravity of LiquidsDocument3 pagesHydraulics Experiment No 1 Specific Gravity of LiquidsIpan DibaynNo ratings yet
- RSA ChangeMakers - Identifying The Key People Driving Positive Change in Local AreasDocument29 pagesRSA ChangeMakers - Identifying The Key People Driving Positive Change in Local AreasThe RSANo ratings yet
- Introduction To Control SystemDocument9 pagesIntroduction To Control SystemAbdulhakam Abubakar YusufNo ratings yet
- Steel and Timber Design: Arch 415Document35 pagesSteel and Timber Design: Arch 415Glennson BalacanaoNo ratings yet
- DLP No. 10 - Literary and Academic WritingDocument2 pagesDLP No. 10 - Literary and Academic WritingPam Lordan83% (12)
- Lista Agentiilor de Turism Licentiate Actualizare 16.09.2022Document498 pagesLista Agentiilor de Turism Licentiate Actualizare 16.09.2022LucianNo ratings yet
- Aero - 2013q2 Apu On DemandDocument32 pagesAero - 2013q2 Apu On DemandIvan MilosevicNo ratings yet
- GemDocument135 pagesGemZelia GregoriouNo ratings yet
- Student Worksheet Task 1 - Long Reading: Fanny Blankers-KoenDocument2 pagesStudent Worksheet Task 1 - Long Reading: Fanny Blankers-KoenDANIELA SIMONELLINo ratings yet
- Industrial Visit Report Part 2Document41 pagesIndustrial Visit Report Part 2Navratan JagnadeNo ratings yet
- 37 Sample Resolutions Very Useful, Indian Companies Act, 1956Document38 pages37 Sample Resolutions Very Useful, Indian Companies Act, 1956CA Vaibhav Maheshwari70% (23)
- Economies of Scale in European Manufacturing Revisited: July 2001Document31 pagesEconomies of Scale in European Manufacturing Revisited: July 2001vladut_stan_5No ratings yet
- Alice (Alice's Adventures in Wonderland)Document11 pagesAlice (Alice's Adventures in Wonderland)Oğuz KarayemişNo ratings yet
- Roman Roads in Southeast Wales Year 3Document81 pagesRoman Roads in Southeast Wales Year 3The Glamorgan-Gwent Archaeological Trust LtdNo ratings yet
- StatisticsAllTopicsDocument315 pagesStatisticsAllTopicsHoda HosnyNo ratings yet
- Gastric Emptying PresentationDocument8 pagesGastric Emptying Presentationrahul2kNo ratings yet
- Xavier High SchoolDocument1 pageXavier High SchoolHelen BennettNo ratings yet
- Discrete Probability Distribution UpdatedDocument44 pagesDiscrete Probability Distribution UpdatedWaylonNo ratings yet
- 23 East 4Th Street NEW YORK, NY 10003 Orchard Enterprises Ny, IncDocument2 pages23 East 4Th Street NEW YORK, NY 10003 Orchard Enterprises Ny, IncPamelaNo ratings yet
- IndianJPsychiatry632179-396519 110051Document5 pagesIndianJPsychiatry632179-396519 110051gion.nandNo ratings yet