Professional Documents
Culture Documents
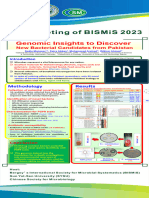
Poster - Acinetobacter Pakistanensis Strain NCCP-644
Uploaded by
iftikhar.ahmedOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Poster - Acinetobacter Pakistanensis Strain NCCP-644
Uploaded by
iftikhar.ahmedCopyright:
Available Formats
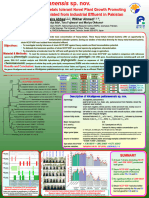
Acinetobacter pakistanensis sp. nov.
A Heavy-metals tolerant and Psychrotolerant Bacterium
Isolated from a Textile Dyeing Waste Water Treatment Pond
Saira Abbas 1, 2, 3
, Iftikhar Ahmed 1, 2, 3*
,
Takuji Kudo3, Toshiya Iida3, Toru Fujiwara2 and Moriya Ohkuma3
11
Institute of Microbial Culture Collection of Pakistan (IMCCP), National Agricultural Research Centre, Islamabad-45500, PAKISTAN.
22
Laboratory of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, Graduate School of Agricultural and Life Sciences, The University of Tokyo, Tokyo, Japan
33
Japan Collection of Microorganisms, RIKEN BioResource Center, Tsukuba, Ibaraki 305-0074, Japan
ABSTRACT
Introduction: Several microorganisms can tolerate toxic concentration of heavy-metals. These heavy-metals tolerant bacteria offer an opportunity to
exploit in the bioremediation of contaminated soil/water systems. During our studies of microbial diversity for heavy metal-tolerant bacteria, strain NCCP-644 TT
was isolated from a textile dyeing wastewater treatment pond, Kohnoor Mills, Islamabad.
Objective: To investigate the taxonomic position of the strain NCCP-644TT as a novel species by polyphasic characterisation.
Materials & Methods: To meet the minimum standards for delineation of any novel species, the strain NCCP-644 TT was studied in comparison with
references species by phenotypic (morphology of cells, physiology and biochemical studies), genotypic (16S rRNA gene, housekeeping genes
including gyrB, rpoB and atpD genes, DNA G+C content analysis and DNA-DNA hybridization), phylogenetic (based on sequences of 16S rRNA gene and
the housekeeping genes) and chemotaxonomic (analyses of cellular fatty acids, polar lipids, menaquinones) characterisation.
Results and Conclusion: Based on the results (mentioned in below Tables and Figures), it is concluded that the strain NCCP-644 TT represents a new
species of the genus Acinetobacter and named as Acinetobacter pakistanensis sp. nov.
82 Acinetobacter soli B1T (EU290155)
Acinetobacter baylyi DSM 14961T (APPT01000006) Analysis of Housekeeping gene(s) in
55
0.5% Acinetobacter boissieri SAP 284.1T (JQ771141) Acinetobacter pakistanensis strain NCCP-644T
Acinetobacter towneri DSM 14962T (APPY01000064) in comparison to the reference species and their accession numbers published in DNA database
Acinetobacter indicus A648T (HM047743)
Acinetobacter puyangensis BQ4-1T (JN664255)
Targeted Housekeeping Gene(s)
Acinetobacter baumannii ATCC 19606T (ACQB01000091) gyrB rpoB atpD infB rpoB rpoB rpoB
72 Acinetobacter junii CIP 64.5T (APPX01000010)
Primer pair for gyrB 01-F rpoB CM7- F atpD 01-F infB 01-F Ac696F Ac1055F Ac696F
70 Acinetobacter gerneri DSM 14967T (APPN01000041) amplification (forward) (forward) (forward) (forward) (forward) (forward) (forward)
Acinetobacter marinus SW-3T (AY633607) Ac1093R Ac1598R Ac1598R
gyrB 02-R rpoB CM31b-R atpD 02-R infB 02-R (reverse) (reverse) (reverse)
Acinetobacter rudis G30T (EF204258) (reverse) (reverse) (reverse) (reverse)
Acinetobacter guillouiae CIP 63.46T (APOS01000028) Expected
87 Acinetobacter bereziniae LMG 1003T (AIEI01000248) amplicon size 742 bp 558 bp 657 bp 615 bp 350 bp 450 bp 700 bp
Acinetobacter schindleri CIP 107287T (APPQ01000011)
Acinetobacter haemolyticus CIP 64.3T (APQQ01000002) Reference Coenye et al., 1999 La Scola et al., 2006
Negative control
Acinetobacter brisouii 5YN5-8T (DQ832256)
Marker (100 bp)
b - JCM118991
d - JCM118991
a - JCM118991
c - JCM118991
b – JCM18990
d – JCM18990
a – JCM18990
G - JCM17071
G - NCCP-644
b - JCM17071
d - JCM17071
E - JCM17071
16S rRNA gene
a - JCM17071
b - NCCP-644
c - JCM17071
d - NCCP-644
E - NCCP-644
F - JCM17071
a - NCCP-644
c - NCCP-644
c– JCM18990
Marker (1-kb)
Acinetobacter oleivorans DR1 (CP002080)
F- NCCP-644
T
78
Acinetobacter pittii CIP 70.29T (APQP01000001) sequence DNA- DNA
98
hybrid
Marker
Acinetobacter calcoaceticus DSM 30006T (AIEC01000170) similarity
84
Acinetobacter nosocomialis NIPH 2119 (APOP01000014)
T
94 Acinetobacter pakistanensis NCCP-644T (AB916465)
“Acinetobacter kyonggiensis” KSL5401-037T (FJ527818) 98.3 % 54.7%
Acinetobacter johnsonii CIP 64.6T (APON01000005) 97.5 % 20.6%
89 Acinetobacter oryzae B23T (GU954428)
Acinetobacter bouvetii DSM 14964T (APQD01000004) 97.5 % 10.3%
Acinetobacter gyllenbergii 1271T (AJ293694)
Acinetobacter tjernbergiae DSM 14971T (ARFU01000016)
81 Acinetobacter parvus DSM 16617T (AIEB01000124)
Acinetobacter kookii 11-0202T (JX137279)
Acinetobacter beijerinckii 58aT (AJ626712) 97.5 % 12.3%
Acinetobacter venetianus RAG-1T (AKIQ01000085) Strain Name Name of Number of Accession Closely related Similarity %age of Similarity %age
housekeeping nucleotides number of validly published housekeeping range of
Acinetobacter radioresistens DSM 6976T (BAGY01000082) Gene housekeeping housekeeping taxa as per gene sequence housekeeping gene
Acinetobacter harbinensis HITLi 7T (KC843488) 97.7 % 19.6% Gene Gene respective gene with closely sequence with all
sequence related species other species of
82 Prolinoborus fasciculus CIP 103579T (JN175353) the genus
similarity
100 Acinetobacter lwoffii NCTC 5866T (AIEL01000120)
Acinetobacter gyrB 876 AB924048 Acinetobacter 92.3 82.7 - 71.1
Acinetobacter ursingii DSM 16037T (AIEA01000080) pakistanensis kyonggiensis
Alkanindiges illinoisensis MVAB Hex1T (AF513979) NCCP-644T (AB924049)
Acinetobacter rpoB 873 AB938199 Acinetobacter 95.3 85.3 - 76.7
pakistanensis kyonggiensis
Neighbor-joining phylogenetic tree showing inter-relationship of strain NCCP-644 T NCCP-644T (AB938200 )
Acinetobacter atpD 756 AB924051 Acinetobacter 96.6 ---
with the closely related type species of genera Acinetobacter inferred from sequences of the 16S rRNA pakistanensis kyonggiensis
gene. Nodes indicated by empty circles were recovered by at least two algorithms, whereas nodes with NCCP-644T (AB924052)
solid circles were recovered by three algorithms.
Description of Acinetobacter pakistanensis sp. nov.
Major differentiating characteristics of strain NCCP-644T from the closely related species Etymology: Acinetobacter pakistanensis
(pak’is.tan’en.sis. N.L. masc. adj. pakistanensis from
Characteristics "A. A. A. A. A. A.
NCCP- kyonggiensis" harbinensis bouvetii beijerinckii johnsonii calcoaceticus Pakistan, where the organism was isolated).
644T JCM 17071T KCTC32411T JCM 18991T JCM 18990 T JCM 20194 T JCM 6842T Cell morphology: Gram-stain negative, cocci to short rod (coccobacillus),
Temperature (ºC) range, 3-37 5-30 2-35 5-37 5-40 10-33 5-37
(optimum) (20-25) (20-25) (8-20) † (20-30) (25-33) (20-30) (20-30) occur primarily in pairs and sometimes triplet form, which
pH range (optimum) 6-10 (7-8) 6-9 (7-8) 6-8.5 (7.2) † 6-9 (6-8) 6-10 (7-8) nd nd are non-motile and strictly aerobic.
NaCl range (%), (optimum) 0-3 (0-1) 0-3 (0) 0-4 (0)† 0-3 (0-2) 0-4 (0-2) 0-4 (1-2) 0-2 (0-1)
Tolerance to heavy metals: Colonies morphology: Moist, raised, off-white in colour with entire margins and are
Chromium (ppm) 2700 1200 nd 600 1800 300 300 1–2 mm in size after 1–2 days when grown on TSA (Difco)
Arsenic (ppm) 3000 2400 3000 3000 3000 900 1200 medium at 25°C.
Lead (ppm) 2100 900 900 1500 1500 300 900
Copper (ppm) 2700 1200 900 1200 2100 300 300 Cellular Fatty Acids: Summed feature 3 (iso-C15
15 :0
:0
2OH / C16
16 :1
:1
ω7c), followed by
Utilisation of citrate – – – – + – –
C18:1 ω9c, C16:0 , C12:0 3-OH, C12:0 and C10:0 .
Nitrate reduction to N2 + + – + + + + 18:1 16:0 12:0 12:0 10:0
Voges-Proskauer reaction + – + + + + + Major menaquinone: Q-9
Acid from N-acetyl glucosamine – + – – – – –
Assimilation of: G+C (mol%): 40.6 (analysed on HPLC)
Capric acid + – + + + + –
Adipic acid – – – – – – + Cell physiology: Tolerant to Heavy metals (Cr,
Malate + + – + + + + As, Pb, Cu)
Trisodium citrate – – – w+ + + –
Phenyl acetic acid – – – – – – w+ Major polar lipids: Phosphatidyl monomethyl ethanol (PME), phosphatidyl
Enzyme activity (API-Zym and Rapid 32 ID) inositol (PI), diphosphatidyl glycerol (DPG), phosphatidyl
Alkaline phosphatase +++ ++ – ++ w+ w+ +++
ethanolamine (PE), phosphatidyl serine (PS), phosphatidyl
Lipase (C 14) + + w+ ++ +++ ++ w+
Cysteine arylamidase + + w+ + + + w+
glycerol (PG) and one unknown phospholipid.
Acid phosphatase + w+ + ++ ++ + +++ Source of isolation: Textile dyeing wastewater treatment pond, Kohnoor
Napthol-As-BI-phosphohydrolase +++ – w+ + ++ + ++
Proline arylamidase + + + – + + + Mills, Islamabad, Pakistan
+ – – – + – +
Glutamyl glutamic acid arylamidase
Type strain NCCP-644TT = JCM18977TT = LMG 28467TT = KCTC 42081TT
Symbols: +++, Very strongly positive; ++, strongly positive; +, Positive; w+, weakly positive; –, negative;
Species validated: Validation List No. 161 (2015). IJSEM 65(1): 1-4
You might also like
- Package Insert - 048437-01 - en - 422243Document22 pagesPackage Insert - 048437-01 - en - 422243HadiNo ratings yet
- Assignment CHAP NO 1.... Computer Fundamentals by PK SinhaDocument7 pagesAssignment CHAP NO 1.... Computer Fundamentals by PK SinhaThreating King100% (2)
- Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy-2014-Iovieno-5626.fullDocument3 pagesAntimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy-2014-Iovieno-5626.fullNurul JannahNo ratings yet
- SMB 1Document7 pagesSMB 1Subhecchha BaidyaNo ratings yet
- 1155 Ijsem003285Document7 pages1155 Ijsem0032850237Đặng Quốc CườngNo ratings yet
- List of BacteriaDocument180 pagesList of BacteriaveeramaniNo ratings yet
- Isolation and Cross-Species Amplification of MicrosatelliteDocument3 pagesIsolation and Cross-Species Amplification of MicrosatelliteymoalicNo ratings yet
- Aminotransferase: Characterization Aspartate From Rhizobium MelilotiDocument11 pagesAminotransferase: Characterization Aspartate From Rhizobium MelilotiAndi MusdalifahNo ratings yet
- AAB Cleenwerck 2022Document8 pagesAAB Cleenwerck 2022nurrijawatiNo ratings yet
- Binder Et Al 2005 SupplDocument21 pagesBinder Et Al 2005 Supplkhalid HafazallahNo ratings yet
- BISMIS Poster-Sadia (15-10-2023)Document1 pageBISMIS Poster-Sadia (15-10-2023)iftikhar.ahmedNo ratings yet
- GuidanceCOVID19SurrogateSel April242020Document3 pagesGuidanceCOVID19SurrogateSel April242020eagles9777No ratings yet
- Identification of The Aquaporin Gene Family in Cannabis Sativa A - 2019 - PlantDocument9 pagesIdentification of The Aquaporin Gene Family in Cannabis Sativa A - 2019 - PlantArlen GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Export Wild Uit Suriname 2016 CITES Database 2Document1 pageExport Wild Uit Suriname 2016 CITES Database 2Suriname MirrorNo ratings yet
- Doc-20230326-Wa0015 230522 103617Document11 pagesDoc-20230326-Wa0015 230522 103617UMAR WIRANTO PUTRA DONAS Teknik IndustriNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Sismik 1Document3 pagesJurnal Sismik 1Surasta MitaNo ratings yet
- Catalogue of Microbial CulturesDocument78 pagesCatalogue of Microbial CulturesGowtham Selvaraj100% (1)
- Marine Natural Products - 2022 For 2020 Publications - ESI (001-126) PDFDocument126 pagesMarine Natural Products - 2022 For 2020 Publications - ESI (001-126) PDFDs Hoàng QuỳnhNo ratings yet
- Molecular Survey of Babesia Infection in Dogs in Okinawa, Japan 2004 Veterinary ParasitologyDocument6 pagesMolecular Survey of Babesia Infection in Dogs in Okinawa, Japan 2004 Veterinary ParasitologyGabriela Victoria MartinescuNo ratings yet
- Survelens Infeksi Daerah OperasiDocument2 pagesSurvelens Infeksi Daerah OperasiHajrah SaidNo ratings yet
- Benh VirusDocument7 pagesBenh VirusThu Hien NguyenNo ratings yet
- Novel Nitrogen-Fixing Acetobacter Nitrogenifigens Sp. Nov., Isolated From Kombucha Tea PDFDocument5 pagesNovel Nitrogen-Fixing Acetobacter Nitrogenifigens Sp. Nov., Isolated From Kombucha Tea PDFNayeli MartinezNo ratings yet
- 2005 - Lewinsohn, Freitas & Prado - Conservation InvertebratDocument6 pages2005 - Lewinsohn, Freitas & Prado - Conservation InvertebratKellyta RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Identification: of Gram-Negative Non-Fermenters and Oxidase-Positive Fermenters by The Oxi/Ferm TubeDocument8 pagesIdentification: of Gram-Negative Non-Fermenters and Oxidase-Positive Fermenters by The Oxi/Ferm TubeJack QuizonNo ratings yet
- 16S Phylogeny of The: StreptomycetaceaeDocument28 pages16S Phylogeny of The: StreptomycetaceaeArshad R ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Comparison Lamp Con OtrasDocument7 pagesComparison Lamp Con OtrasLuis Ernesto Mena ZapataNo ratings yet
- 1 BuruianaDocument3 pages1 BuruianaiqyuwidyaNo ratings yet
- Certificate of Analysis, Quality and Conformity: Certified: ISO 9001:2008, ISO 13485-2003 and WHO GMPDocument2 pagesCertificate of Analysis, Quality and Conformity: Certified: ISO 9001:2008, ISO 13485-2003 and WHO GMPsagor sagorNo ratings yet
- Characterization of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus Isolated From Retail Raw Chicken Meat in JapanDocument4 pagesCharacterization of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus Isolated From Retail Raw Chicken Meat in JapanIrham SupriajiNo ratings yet
- Ligation Sequencing gDNA V14 - Whole Genome Amplification (SQK-LSK114) - MinionDocument8 pagesLigation Sequencing gDNA V14 - Whole Genome Amplification (SQK-LSK114) - MinionDevansh PanwarNo ratings yet
- Provisional Lecture Timetable Semester 2 of 2021-2022 Academic Year Regular 1Document11 pagesProvisional Lecture Timetable Semester 2 of 2021-2022 Academic Year Regular 1Modest DarteyNo ratings yet
- 5 - PCR Primers To Identify and Detect Berkeleyomyces Rouxiae, A Causal Agent of Black Root Rot of LettuceDocument5 pages5 - PCR Primers To Identify and Detect Berkeleyomyces Rouxiae, A Causal Agent of Black Root Rot of LettuceValeriaNo ratings yet
- Dr. K C BansalDocument28 pagesDr. K C BansalVimuvimNo ratings yet
- 2019 nCoVmanual20200217 enDocument16 pages2019 nCoVmanual20200217 ensekharurlaNo ratings yet
- Eul 0495 188 00 nCoV-QS EN IFU v4Document18 pagesEul 0495 188 00 nCoV-QS EN IFU v4atpowrNo ratings yet
- Biomerieux BIOBALL Available Strains Iss 87 v6.pdf - CoredownloadDocument5 pagesBiomerieux BIOBALL Available Strains Iss 87 v6.pdf - CoredownloadAdeem Iqbal AnsariNo ratings yet
- Saccharomyces Cerevisiae: (Atcc 204508™)Document2 pagesSaccharomyces Cerevisiae: (Atcc 204508™)Trương Ngọc Xuân QuỳnhNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 10 Oct 2020Document1 pageAdobe Scan 10 Oct 2020Shyam Sundar JanaNo ratings yet
- TapanScan Dec 07, 2021Document10 pagesTapanScan Dec 07, 2021Anirban HaldarNo ratings yet
- Serendipita Indica (ATCC: Product SheetDocument2 pagesSerendipita Indica (ATCC: Product SheetknbiolabsNo ratings yet
- A Numerical Taxonomic Study of The Dominant Bacteria Isolated From Tilapia IntestinesDocument10 pagesA Numerical Taxonomic Study of The Dominant Bacteria Isolated From Tilapia IntestinesPutri ArisyaNo ratings yet
- Achromobacter Aloeverae Sp. Nov., Isolated From The Root of Aloe Vera (L.) Burm.fDocument5 pagesAchromobacter Aloeverae Sp. Nov., Isolated From The Root of Aloe Vera (L.) Burm.fNattakorn KuncharoenNo ratings yet
- KI67 Millipore - AB9260 - 2147027Document2 pagesKI67 Millipore - AB9260 - 2147027Samuel Madureira SilvaNo ratings yet
- BIOTECH Principal - E 20 MarchDocument28 pagesBIOTECH Principal - E 20 MarchRanjeet SinghNo ratings yet
- New Aminoglycoside-Modifying Enzymes APH (3 ) - VIII and APH (3 ) - IX in Acinetobacter Rudis and Acinetobacter GerneriDocument4 pagesNew Aminoglycoside-Modifying Enzymes APH (3 ) - VIII and APH (3 ) - IX in Acinetobacter Rudis and Acinetobacter Gerneriyanita rahmadhaniNo ratings yet
- Beauclerc Et Al-2018-Conservation Genetics ResourcesDocument5 pagesBeauclerc Et Al-2018-Conservation Genetics ResourcesDayanna CostaNo ratings yet
- Cundell Et Al PDA J Pharm Sci Tech March 2010 (Full Article) SfsDocument21 pagesCundell Et Al PDA J Pharm Sci Tech March 2010 (Full Article) SfsJessica González LaraNo ratings yet
- For Marketing PCR Catalog ProductDocument8 pagesFor Marketing PCR Catalog ProductwindaNo ratings yet
- Wang Et Al. - 2015 - Cloning and Iron Transportation of Nucleotide Binding Domain of Cryptosporidium Andersoni ATP-Binding Cassette (CaADocument6 pagesWang Et Al. - 2015 - Cloning and Iron Transportation of Nucleotide Binding Domain of Cryptosporidium Andersoni ATP-Binding Cassette (CaAWiwien HendrawanNo ratings yet
- Merck Rebrand - 105463 - 1906Document4 pagesMerck Rebrand - 105463 - 1906Peter NguyenNo ratings yet
- Synergistic Interaction Between Silver Nanoparticles and Membrane-Permeabilizing Antimicrobial PeptidesDocument3 pagesSynergistic Interaction Between Silver Nanoparticles and Membrane-Permeabilizing Antimicrobial PeptidesDiana RaieNo ratings yet
- UNIT 9 BIOTECH #ProjectClimaxDocument1 pageUNIT 9 BIOTECH #ProjectClimaxfdghdchNo ratings yet
- Silvestri 2007Document11 pagesSilvestri 2007Sheyla ANo ratings yet
- COA Buffered HimediaDocument2 pagesCOA Buffered HimediaCV HEXACINDO CHEMICALNo ratings yet
- Torres, 2020Document14 pagesTorres, 2020Andrés Mauricio PinzónNo ratings yet
- Kaempferia Galanga: Micropropagation of L - A Medicinal PlantDocument2 pagesKaempferia Galanga: Micropropagation of L - A Medicinal Plantrafiq supriadiNo ratings yet
- Week 1 RNA ExtractionDocument11 pagesWeek 1 RNA ExtractionArjun BujjiNo ratings yet
- Microsatellite Loci For The Weaver Ant Oecophylla SmaragdinaDocument4 pagesMicrosatellite Loci For The Weaver Ant Oecophylla SmaragdinaRifqi Fathul ArroisiNo ratings yet
- Ion Channel Factsbook: Extracellular Ligand-Gated ChannelsFrom EverandIon Channel Factsbook: Extracellular Ligand-Gated ChannelsNo ratings yet
- Economic Aspects: Fisheries and CultureFrom EverandEconomic Aspects: Fisheries and CultureAnthony Jr. ProvenzanoNo ratings yet
- POSTER NCCP ACM2013 MeetingDocument1 pagePOSTER NCCP ACM2013 Meetingiftikhar.ahmedNo ratings yet
- 2 - Poster NCCP-650 - (Aug 2017)Document1 page2 - Poster NCCP-650 - (Aug 2017)iftikhar.ahmedNo ratings yet
- BISMIS Poster-Sadia (15-10-2023)Document1 pageBISMIS Poster-Sadia (15-10-2023)iftikhar.ahmedNo ratings yet
- ICBES NUST, Feb 2017. Poster Presentation by Huma Bokhari and Yousaf RiazDocument1 pageICBES NUST, Feb 2017. Poster Presentation by Huma Bokhari and Yousaf Riaziftikhar.ahmedNo ratings yet
- 1 - POSTER NCCP Dec 2017 MeetingDocument1 page1 - POSTER NCCP Dec 2017 Meetingiftikhar.ahmedNo ratings yet
- Examination, June/July: ExplainDocument6 pagesExamination, June/July: ExplainSandesh KulalNo ratings yet
- 7 AcousticsDocument23 pages7 AcousticsSummer Yeoreumie100% (1)
- Latest CNC Cutting Design - Types, Materials and Installation - LivspaceDocument22 pagesLatest CNC Cutting Design - Types, Materials and Installation - Livspacesushil247No ratings yet
- Neals Token InstrumentDocument39 pagesNeals Token InstrumentVikas Srivastav100% (2)
- Class 8 Imo 5 Years e Book l2 2017 (PDF - Io)Document7 pagesClass 8 Imo 5 Years e Book l2 2017 (PDF - Io)JaySharan50% (2)
- Title: "The Effect of Flooding in The Tourism Industry in Dagupan City" Rationale and Background of The StudyDocument4 pagesTitle: "The Effect of Flooding in The Tourism Industry in Dagupan City" Rationale and Background of The StudyTaehyung KimNo ratings yet
- Magic HRC Scarf 1: by Assia BrillDocument6 pagesMagic HRC Scarf 1: by Assia BrillEmily HouNo ratings yet
- Sample Theory With Ques. - Organometallic Compounds (NET CH UNIT-3) PDFDocument26 pagesSample Theory With Ques. - Organometallic Compounds (NET CH UNIT-3) PDFPriyanshi VermaNo ratings yet
- An Open Letter To Annie Besant PDFDocument2 pagesAn Open Letter To Annie Besant PDFdeniseNo ratings yet
- Dyneema Vs SteelDocument5 pagesDyneema Vs SteelSaurabh KumarNo ratings yet
- Type VBPDF: Pilot Operated Check ValvesDocument3 pagesType VBPDF: Pilot Operated Check ValvesAslam ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Sulphur VapoursDocument12 pagesSulphur VapoursAnvay Choudhary100% (1)
- LogDocument8 pagesLogMaria SuyantiNo ratings yet
- Coumadin WarfarinDocument1 pageCoumadin WarfarinSheri490100% (1)
- Obturator / Orthodontic Courses by Indian Dental AcademyDocument97 pagesObturator / Orthodontic Courses by Indian Dental Academyindian dental academyNo ratings yet
- 2019 AnalysisDocument3 pages2019 AnalysisVedalam VetriNo ratings yet
- Affiliated Institutions Anna University, Chennai Regulations - 2009 Curriculum Ii To Iv Semesters (Full Time) M.E. Applied ElectronicsDocument21 pagesAffiliated Institutions Anna University, Chennai Regulations - 2009 Curriculum Ii To Iv Semesters (Full Time) M.E. Applied ElectronicsRamya VNo ratings yet
- Laporan Hasil Praktik Bahasa Inggris Dengan Tamu Asing Di Pantai KutaDocument12 pagesLaporan Hasil Praktik Bahasa Inggris Dengan Tamu Asing Di Pantai KutaEnal MegantaraNo ratings yet
- 2.2 - NDEP-C1574-5-6-7-8 - Rev.0 NDE Procedures Book PDFDocument59 pages2.2 - NDEP-C1574-5-6-7-8 - Rev.0 NDE Procedures Book PDFGeorge JhonsonNo ratings yet
- Technical Specifications For LT/HT, XLPE Insulated Aluminium/Copper CablesDocument49 pagesTechnical Specifications For LT/HT, XLPE Insulated Aluminium/Copper CablesAjay KumarNo ratings yet
- Egg, Boiled: Nutrition FactsDocument5 pagesEgg, Boiled: Nutrition FactsbolajiNo ratings yet
- Essay Test 2021 (Practice Test)Document3 pagesEssay Test 2021 (Practice Test)Philani HadebeNo ratings yet
- Troubleshooting Pt6a27Document7 pagesTroubleshooting Pt6a27Okky Pangestoe WibowoNo ratings yet
- Spare Parts: LKH Centrifugal PumpDocument20 pagesSpare Parts: LKH Centrifugal PumpService CTANo ratings yet
- Zener Diodes and Transient Voltage Suppressors Quarter 3, 1998 SG274 - D Rev 16Document8 pagesZener Diodes and Transient Voltage Suppressors Quarter 3, 1998 SG274 - D Rev 16Imraan RamdjanNo ratings yet
- Vo 1263 AaDocument8 pagesVo 1263 Aa801400No ratings yet
- Penetapan Kadar Sakarin, Asam Benzoat, Asam Sorbat, Kofeina, Dan Aspartam Di Dalam Beberapa Minuman Ringan Bersoda Secara Kro...Document13 pagesPenetapan Kadar Sakarin, Asam Benzoat, Asam Sorbat, Kofeina, Dan Aspartam Di Dalam Beberapa Minuman Ringan Bersoda Secara Kro...Wisnu WardhanaNo ratings yet
- SDLP in Science July 18 2019Document5 pagesSDLP in Science July 18 2019Pinky MarieNo ratings yet
- Aqa CHM4 W QP Jun09Document20 pagesAqa CHM4 W QP Jun09dharmik47No ratings yet