Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Argand Diagrams: Modulus, Argument and Polar Form: Ib HL Adrian Sparrow
Uploaded by
Paul Kideman0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views10 pagesOriginal Title
argand
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views10 pagesArgand Diagrams: Modulus, Argument and Polar Form: Ib HL Adrian Sparrow
Uploaded by
Paul KidemanCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 10
Argand diagrams: modulus,
argument and polar form
IB HL
www.ibmaths.com
Adrian Sparrow
Subscribe to www.ibmaths.com
and gain access to hundreds of
slideshows, worksheets, practice
tests and revision material.
Personal access is just $39 and
school access $99.
The Argand plane
The plane of complex numbers is known as the Argand plane.
The y-axis is the imaginary part and the x-axis is the real part.
Examples
z
1
= 3+ 2i
z
2
= 2 + i
z
1
+ z
2
=1+ 3i
2 z
2
( )
= 4 + 2i
z
1
( )
*
= 3 2i
z
1
z
2
z
1
+ z
2
2 z
2
( )
z
1
( )
*
Draw a sketch to show
each of these:
z
1
+ z
2
2z
2
z
1
( )
*
Modulus
Examples
The modulus, z, is the length the line z.
z
1
z
1
= 3+ 2i
z
2
= 2 + i
Find,
z
1
and z
2
Find,
z
1
+ z
2
2 z
2
( )
z
1
( )
*
z
1
= 3
2
+2
2
= 13
z
2
= 2
2
+1
2
= 5
2 5
13
z
2
10
Argument
The argument of a complex number is the angle, u, made between
the line and the positive axis.
Consider z
1
= 4 + 4i
u
tanu =
4
4
u =
t
4
argz
1
=
t
4
Note that: t su st
Consider z
2
= 3+ 3i
tanu =
3
3
u =
t
4
argz
2
= t
t
4
=
3t
4
u
Argument - examples 1
z
1
= 4
argz
1
=0
z
2
=5i
argz
2
=
t
2
z
3
= 3
argz
3
=t
z
4
=4i
argz
4
=
t
2
Argument - examples 2
1. Find the argument of the
complex number z = 3 + i.
2. Find the argument of the
complex number w=1 3i.
tanu =
1
3
or sinu =
1
2
argz =
t
6
tanu =
3
1
or cosu =
1
2
argw =
t
3
u
u
3
3
1
1
2
2
Polar and Euler form
Cartesian form: z =x+yi
Polar form: z = z cosu + isinu
( )
The modulus of
the complex
number.
The argument of the
complex number.
z = z cosu + i sinu
( )
can be z = z cisu
The Euler form of
z = z cisu is given as
z = z e
iu
We will derive the Euler form of
a complex number in a later
lessons.
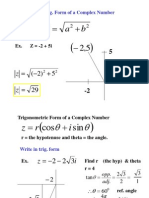
Cartesian to polar form
Write the complex number
z =3+i 3 in polar form.
Questions - write each of the
following in polar form.
Draw a sketch on your Argand
diagram
u
Make a right angled triangle and
find the hypotenuse, modulus, and
the angle, argument.
3
3
sinu =
3
2 3
=
1
2
|
\
|
.
|
u =
t
6
3
( )
2
+ 3
2
= 12 = 2 3
z = 2 3 cis
t
6
|
\
|
.
|
2 3
1. z = 2 2i
2. z = 2 + i 2 3
( )
3. z = 1 3i
4. z = 4 4i
z = 2 2cis
3t
4
|
\
|
.
|
z = 4cis
t
3
|
\
|
.
|
z = 2cis
2t
3
|
\
|
.
|
z = 4 2cis
t
4
|
\
|
.
|
Polar to cartesian form
Write the polar complex number
z =2cis -
t
6
|
\
|
.
|
in cartesian form.
Draw a sketch on your Argand
diagram.
t
6
2
sin
t
6
=
1
2
sin
opp
hyp
1
Work backward using the angle
t
6
.
opp =1, adj = 3
3
z = 3 i
Questions - write each of the
following in cartesian form.
z = 3+ i 3 3
( )
z = 5 2 i 5 2
( )
z = 2 3 2i
z = 8+ i 8 5
( )
1. z =6cis
t
3
2. z =10cis
t
4
|
\
|
.
|
3. z =4cis
5t
6
|
\
|
.
|
4. z =16cis
2t
3
|
\
|
.
|
You might also like
- LN Complex NumberDocument15 pagesLN Complex NumberWu ZhantaoNo ratings yet
- Course Notes On Complex Numbers Teachers NotesDocument60 pagesCourse Notes On Complex Numbers Teachers NotesKevin QuachNo ratings yet
- Complex SummaryDocument8 pagesComplex SummaryJiongHow SosadNo ratings yet
- Complex AlgebraDocument8 pagesComplex Algebramahek19579328100% (1)
- RN Complex NumbersDocument12 pagesRN Complex NumbersIsuruNo ratings yet
- Complex Numbers: N. N N NDocument4 pagesComplex Numbers: N. N N NHannan ZulfiqarNo ratings yet
- Complex Numbers: 1 The Arithmetic Form of A Complex NumberDocument25 pagesComplex Numbers: 1 The Arithmetic Form of A Complex Numberlhau_8No ratings yet
- Complex Numbers: Harvey Mudd College Math TutorialDocument4 pagesComplex Numbers: Harvey Mudd College Math TutorialArtist RecordingNo ratings yet
- Complex Analysis Problems With SolutionsDocument88 pagesComplex Analysis Problems With Solutions21260paco61No ratings yet
- Examples and SolutionsDocument22 pagesExamples and Solutionsflight2heaven1474No ratings yet
- Z Z Z Z Z Z: Summary of Complex Numbers Modulus and ArgumentDocument2 pagesZ Z Z Z Z Z: Summary of Complex Numbers Modulus and Argumentbdcyl1No ratings yet
- Complex PDFDocument34 pagesComplex PDFמוחמד טאהאNo ratings yet
- MT Chapter 04 STPM RevisionDocument3 pagesMT Chapter 04 STPM RevisionClaire LimNo ratings yet
- C - Fakepathc - fakepathALL LECTURES LA and AGDocument113 pagesC - Fakepathc - fakepathALL LECTURES LA and AGOrxan MirzəzadəNo ratings yet
- Complex Variables Lecture NotesDocument11 pagesComplex Variables Lecture NotesShan_ShripadNo ratings yet
- 08Document3 pages08brendannnNo ratings yet
- Kompleksni Brojevi SkriptaDocument52 pagesKompleksni Brojevi Skriptabmale91No ratings yet
- Imaginary and Complex NumbersDocument28 pagesImaginary and Complex NumbersZenonissya Galwan BataraNo ratings yet
- Topic 1B. Complex Numbers - MatricesDocument60 pagesTopic 1B. Complex Numbers - MatricesJessicaNo ratings yet
- Rev Chapter 4 Complex NumbersDocument2 pagesRev Chapter 4 Complex NumbersKwongKHNo ratings yet
- MTE201 NotescomplexDocument39 pagesMTE201 NotescomplexKudaNo ratings yet
- 12C Basic Complex NumbersDocument48 pages12C Basic Complex Numbersyddap100% (1)
- Unit-1 - Complex Analysis-1 - e ContentDocument14 pagesUnit-1 - Complex Analysis-1 - e ContentSourav SharmaNo ratings yet
- Maths 2A Complex Numbers Important QuestionsDocument17 pagesMaths 2A Complex Numbers Important Questionssimhadri.sridharNo ratings yet
- m211f2012 Slides AppA HandoutDocument39 pagesm211f2012 Slides AppA HandoutcmculhamNo ratings yet
- 2010 MA6102 Test 1Document8 pages2010 MA6102 Test 1Stuart TangNo ratings yet
- Examples 5: Complex Numbers 1Document1 pageExamples 5: Complex Numbers 1Mathaneshan RajagopalNo ratings yet
- Complex Numbers TheoremsDocument22 pagesComplex Numbers TheoremsChristine RasimoNo ratings yet
- Complex NumbersDocument32 pagesComplex NumbersNicolaus MdemuNo ratings yet
- Maths PPT 1-1Document24 pagesMaths PPT 1-1RoshanNo ratings yet
- Complex Numbers 1Document14 pagesComplex Numbers 1vijayalakshmi muraliNo ratings yet
- JEE MAIN MathematicsDocument301 pagesJEE MAIN MathematicsAnandhi Chidambaram100% (1)
- NCERT Exemplar Solutions For Class 11 Maths Chapter 5 Complex Numbers and Quadratic Equations PDFDocument12 pagesNCERT Exemplar Solutions For Class 11 Maths Chapter 5 Complex Numbers and Quadratic Equations PDFanonymousalwayzz1234No ratings yet
- Plex NumberDocument25 pagesPlex NumberBattleBeex rabinoNo ratings yet
- Complex Numbers & Quadratic Equations - Class 11 JEEDocument7 pagesComplex Numbers & Quadratic Equations - Class 11 JEEPrince Roy MondalNo ratings yet
- Complex NumberDocument44 pagesComplex NumberSonya MillerNo ratings yet
- Engineering MathDocument102 pagesEngineering MathIslam TokoevNo ratings yet
- PPTDocument12 pagesPPTChandan V ChanduNo ratings yet
- Wqd10202 Technicalmathii Complex NumberDocument33 pagesWqd10202 Technicalmathii Complex NumberAdrian BagayanNo ratings yet
- © Ncert Not To Be Republished: 3 1 3 1 2 2 2 3 1 2 4 2 4 4 3 1 3 1 Cos, Sin 2 2 2 2 5 4 6 12Document2 pages© Ncert Not To Be Republished: 3 1 3 1 2 2 2 3 1 2 4 2 4 4 3 1 3 1 Cos, Sin 2 2 2 2 5 4 6 12sameercoldplayNo ratings yet
- Complex No. ArihantDocument21 pagesComplex No. Arihantrahul0% (1)
- Complex No Slides-476Document103 pagesComplex No Slides-476Sanu RanjanNo ratings yet
- James Ruse 2005 4U at Div 1 & SolutionsDocument9 pagesJames Ruse 2005 4U at Div 1 & SolutionsLachlan SmithNo ratings yet
- CMPLX No. TtrialDocument10 pagesCMPLX No. TtrialHanif BahNo ratings yet
- Complex+Numbers++ +L3-Modulus+of+Complex+NumbersDocument62 pagesComplex+Numbers++ +L3-Modulus+of+Complex+NumbersGod is every whereNo ratings yet
- Ch04 Relations and Regions of The Complex PlaneDocument34 pagesCh04 Relations and Regions of The Complex PlaneLino100% (1)
- 2015 AJC Prelim Paper 1 QnsDocument7 pages2015 AJC Prelim Paper 1 QnsYing Ru ChuaNo ratings yet
- Complex Numbers (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandComplex Numbers (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- Test Bank for Precalculus: Functions & GraphsFrom EverandTest Bank for Precalculus: Functions & GraphsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Ten-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesFrom EverandTen-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesNo ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageFrom EverandAnalytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageNo ratings yet
- Factoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)From EverandFactoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)No ratings yet
- Mathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsFrom EverandMathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsNo ratings yet