Professional Documents
Culture Documents
4 Sinusoidal Wave
4 Sinusoidal Wave
Uploaded by
rahmana.henry0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views27 pagesThis document discusses sinusoidal wave analysis and impedance in AC circuits. It covers resistive elements, inductive reactance, capacitive reactance, impedance diagrams, admittance, conductance, and susceptance. Examples are provided to calculate current and voltage in circuits containing resistors, inductors and capacitors using complex algebra. The key concepts are that impedance is the opposition to current flow in AC circuits, admittance is the reciprocal of impedance, and inductors and capacitors contribute to susceptance which is the imaginary part of admittance.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses sinusoidal wave analysis and impedance in AC circuits. It covers resistive elements, inductive reactance, capacitive reactance, impedance diagrams, admittance, conductance, and susceptance. Examples are provided to calculate current and voltage in circuits containing resistors, inductors and capacitors using complex algebra. The key concepts are that impedance is the opposition to current flow in AC circuits, admittance is the reciprocal of impedance, and inductors and capacitors contribute to susceptance which is the imaginary part of admittance.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views27 pages4 Sinusoidal Wave
4 Sinusoidal Wave
Uploaded by
rahmana.henryThis document discusses sinusoidal wave analysis and impedance in AC circuits. It covers resistive elements, inductive reactance, capacitive reactance, impedance diagrams, admittance, conductance, and susceptance. Examples are provided to calculate current and voltage in circuits containing resistors, inductors and capacitors using complex algebra. The key concepts are that impedance is the opposition to current flow in AC circuits, admittance is the reciprocal of impedance, and inductors and capacitors contribute to susceptance which is the imaginary part of admittance.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 27
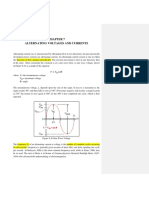
Sinusoidal wave analysis
Impedansi and Admittance
The Resistif element
Example 1
Using complex algebra, find the current for the circuit
below. Sketch the waveform of and .
Solution
Example 2
Using complex algebra, find the voltage for the circuit
below. Sketch the waveform of and .
Solution
Inductive Reactance
Example 1
Using complex algebra, find the current for the circuit
below. Sketch the and curves.
Solution
Example 2
Using complex algebra, find the voltage for the circuit
below. Sketch the and curve.
Solution
Capacitive reactance
Example 3
Using a complex algebra, find the current for the circuit
below. Sketch the and curves.
Solution
Example 4
Using complex algebra, find the voltage for the circuit
below. Sketch the and curves.
Solution
Impedance diagram
Admittance
In AC circuit, we define admittance () as being equal to .
The unit of measure for admittance as defined by system
is siemens, which has the symbol .
Admittance is a measure of how well an ac circuit will
admit, or allow, current to flow in the circuit.
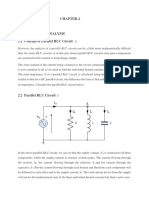
Parallel ac network
Conductance
Condustance is the reciprocal of resistance
Susceptance
The reciporal of reactance () is called susceptance and is a
measure of how susceptible an element is to passage of
current throught it.
Susceptance is also measured in siemens and is
represented by the capital letter
For the induktor
Note that for induktance, an increase in frequency or inductance will result
in a decrease in susceptance or correspondingly, in admttance
For the capasitor
For the capacitor, therefore, an increase in frequency or capacitance will
result in an increase in its susceptibility.
For parallel ac circuit, the admittance diagram is used with the three admittance,
represented as show in fig above.
The conductance (like resistance) is on the positive real axis, whereas inductive
and capacitive susceptance are in direct opposition on the imaginary axis
Terimakasih
You might also like
- AC CircuitsDocument30 pagesAC CircuitsAdzLinkBalaoang100% (2)
- Easy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2019-2023)From EverandEasy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2019-2023)No ratings yet
- SPLM #6 - Resonance and BandwidthDocument60 pagesSPLM #6 - Resonance and BandwidthSherwin Pagpaguitan100% (1)
- CHAPTER 9 Alternating CurrentDocument25 pagesCHAPTER 9 Alternating Currentmariamoi suarezNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 3Document15 pagesLab Report 3WaleedSubhan100% (1)
- Impedansi Dan AdmitansiDocument27 pagesImpedansi Dan AdmitansiArif Febriansyah JuwitoNo ratings yet
- Electrical ImpedanceDocument14 pagesElectrical ImpedanceAndey HemanthNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical by FarhanaDocument28 pagesBasic Electrical by FarhanaEr Rouf UlAlam BhatNo ratings yet
- Chap1 Lect3Document7 pagesChap1 Lect3Ibraheem MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Electrical Impedance: Electrical Impedance, or Simply Impedance, Is A Term Coined byDocument8 pagesElectrical Impedance: Electrical Impedance, or Simply Impedance, Is A Term Coined byidigitiNo ratings yet
- General Physics 2Document5 pagesGeneral Physics 2Nanzkie Andrei SamanNo ratings yet
- Topic 5 HandoutDocument11 pagesTopic 5 HandoutnattydreadfathelahNo ratings yet
- Parallel RLC Circuit and RLC Parallel Circuit AnalysisDocument24 pagesParallel RLC Circuit and RLC Parallel Circuit Analysisengrsana ullahNo ratings yet
- Module4 - AC Series and Parallel CircuitsDocument161 pagesModule4 - AC Series and Parallel CircuitsTatsumaki TornadoNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1 ElectDocument14 pagesCHAPTER 1 Electdavididosa40No ratings yet
- Electrical ReactanceDocument5 pagesElectrical ReactanceAndey HemanthNo ratings yet
- What Is Resonance?: An AC Circuit Containing A Resistor, A Capacitor and An InductorDocument4 pagesWhat Is Resonance?: An AC Circuit Containing A Resistor, A Capacitor and An InductorKaran SharmaNo ratings yet
- Capacitors Do Not Behave The Same As ResistorsDocument14 pagesCapacitors Do Not Behave The Same As Resistorsmtheo20No ratings yet
- 14 Alternating CurrentDocument39 pages14 Alternating CurrentWebby ZimbaNo ratings yet
- AC Capacitor CircuitDocument5 pagesAC Capacitor CircuitebasaytunoNo ratings yet
- Basics of ElectronicsDocument12 pagesBasics of ElectronicsSiddarth AkkiNo ratings yet
- Week 4 - Instructional Module - EE221 - EE222Document11 pagesWeek 4 - Instructional Module - EE221 - EE222AB CEDENo ratings yet
- Ac Through CapacitorsDocument5 pagesAc Through CapacitorsanandsupremeNo ratings yet
- Parallel TheoryDocument9 pagesParallel Theoryvaibhav singhNo ratings yet
- Topic 8. AC Bridges. C L MeasurementsDocument35 pagesTopic 8. AC Bridges. C L MeasurementsNeFe WeNo ratings yet
- Assignment CRKT 2Document3 pagesAssignment CRKT 2Strea RanarioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Steady State Single Phase AC Circuit Analysis Part 2 1Document19 pagesChapter 3 Steady State Single Phase AC Circuit Analysis Part 2 1temesgen adugnaNo ratings yet
- AC Power (Part Three) - AC Circuit Loads - Pumps & SystemsDocument7 pagesAC Power (Part Three) - AC Circuit Loads - Pumps & SystemschalaNo ratings yet
- 26Document69 pages26physicsdocs78% (9)
- Impedance and Reactance: "I Know That You Can Do All Things, and That No Purpose of Yours Can Be Thwarted". Job 42:2Document14 pagesImpedance and Reactance: "I Know That You Can Do All Things, and That No Purpose of Yours Can Be Thwarted". Job 42:2Prince JairoNo ratings yet
- Response of Capacitor and Inductor in AC and DC CircuitDocument8 pagesResponse of Capacitor and Inductor in AC and DC CircuitMd Chand AsiqueNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two Alternating Current and VoltageDocument21 pagesChapter Two Alternating Current and VoltageZiyad MohammedNo ratings yet
- Circuit Analysis ANALYSISDocument43 pagesCircuit Analysis ANALYSISAJIN RIBIA PNo ratings yet
- Parallel RLC Circuit and RLC Parallel Circuit AnalysisDocument7 pagesParallel RLC Circuit and RLC Parallel Circuit AnalysisProsenjit ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- AC-Circuits Stud PDFDocument22 pagesAC-Circuits Stud PDFPrince PersiaNo ratings yet
- ReactanceDocument2 pagesReactanceMary TankardNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 15 - Electric CircuitsDocument6 pagesCHAPTER 15 - Electric CircuitsGerry Lou QuilesNo ratings yet
- Communication Lab Assignment: Series and Parallel Resonance CircuitDocument21 pagesCommunication Lab Assignment: Series and Parallel Resonance CircuitUsama AkramNo ratings yet
- The Basic Elements & PhasorsDocument120 pagesThe Basic Elements & PhasorsShah ZamanNo ratings yet
- Discussion Lab 7Document1 pageDiscussion Lab 7Nazmi TutingNo ratings yet
- AC CircuitsDocument37 pagesAC Circuits50849No ratings yet
- Resistance Vs ReactanceDocument3 pagesResistance Vs ReactanceThomas SmithNo ratings yet
- CH 15-2 - Parallel Ac CircuitsDocument22 pagesCH 15-2 - Parallel Ac Circuitsعبدالله المعتقNo ratings yet
- Alternating CurrentDocument7 pagesAlternating CurrentSam LoveNo ratings yet
- Lab 2Document32 pagesLab 2AyeshaNo ratings yet
- LCA Lab Report 12Document12 pagesLCA Lab Report 12ayleeNo ratings yet
- Inductants and AC CircuitsDocument39 pagesInductants and AC CircuitsShinjiNo ratings yet
- Fundamental of AC Circuits: by byDocument28 pagesFundamental of AC Circuits: by byGURMEHAK MIGLANINo ratings yet
- Parallel ResonanceDocument4 pagesParallel ResonanceDevendra PatelNo ratings yet
- Purely Resistive Circuit - Purely Capacitive Circuit - RC Circuit - Purely Inductive Circuit - RL Circuit - RLC CircuitDocument28 pagesPurely Resistive Circuit - Purely Capacitive Circuit - RC Circuit - Purely Inductive Circuit - RL Circuit - RLC CircuitCogCoilNo ratings yet
- Alternating Current A.C.Document19 pagesAlternating Current A.C.Puran BistaNo ratings yet
- 3 AC Responses of Circuit ElementsDocument8 pages3 AC Responses of Circuit ElementstinymairaNo ratings yet
- NGFO70 BE1 Eh 6 Ibp Rwiv 7Document9 pagesNGFO70 BE1 Eh 6 Ibp Rwiv 7Aaditya manojNo ratings yet
- Lec 2 Ce333Document44 pagesLec 2 Ce333mdnitollamastem12hNo ratings yet
- 7 - Parallel ResonanceDocument14 pages7 - Parallel ResonanceSenjuti DeNo ratings yet
- Pure Inductive Circuit AND L R Circuit: Nimisha Lonees K Ac Circuit-Electronics 2020-2021Document15 pagesPure Inductive Circuit AND L R Circuit: Nimisha Lonees K Ac Circuit-Electronics 2020-2021mahmoud yarahmadiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 28-Direct Current CircuitsDocument47 pagesChapter 28-Direct Current CircuitsGled HysiNo ratings yet
- Ac CircuitsDocument6 pagesAc CircuitsMurugeswariNo ratings yet
- AC Circuit: Technical College of Electrical and Electronic EngineeringDocument7 pagesAC Circuit: Technical College of Electrical and Electronic Engineeringاياد النعيميNo ratings yet
- ALTERNATING CURRENT 2020 Together With Physics 21012020Document3 pagesALTERNATING CURRENT 2020 Together With Physics 21012020UTSAV JAINNo ratings yet