Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Presentation 15
Uploaded by
apoorvalokesh12160 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views4 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views4 pagesPresentation 15
Uploaded by
apoorvalokesh1216Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
DIGITAL PAYMENTS
AND THEIR IMPACT
ON THE INDIAN
ECONOMY
This Photo by Unknown author is licensed under CC BY-NC-ND.
India, with a 1.38 billion populaon, has a
huge potenal for digital payments. As of
October 2021, the country had around
1.18 billion mobile connecons, 700
million Internet users, and about 600
million smartphones. These numbers are
growing rapidly each quarter. With about
25.5 billion real-me payment transacons,
India ranked first in the world in terms of
the number of transacons in 2020.
This Photo by Unknown author is licensed under CC BY-NC-ND.
In 2008, the Naonal Payments Corporaon of India (NPCI) started
its journey. It was formed by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) and
Indian Banks’ Associaon (IBA) in order to create a robust payment
and selement infrastructure in India. Since then, it has launched
several products such as Aadhaar Enabled Payments System,
Bharat Bill Payments System (BBPS), BHIM, and Cheque
Transacon System. Newer models are emerging rapidly; currently,
there are around 10 different types of digital payment methods in
India. These include: • Banking Card – This was launched by the
Central Bank of India in India in 1980, in the form of the first
credit card. MasterCard was introduced in 1988, and unl 1993,
several PSU banks started issuing credit cards. • Unstructured
Supplementary Service Data (USSD) – The USSD funconality was
launched in 2016. This is a mobile banking facility enabling users
to use mobile banking without smartphones or an Internet
connecon. • Aadhaar Enabled Payment Systems (AEPS) – This is a
bank-led model which allows online interoperable financial
inclusion transacons at point-of-sale (PoS) through the business
correspondent of any bank using the Aadhaar authencaon.
This Photo by Unknown author is licensed under CC BY-NC-ND.
• Unified Payments Interface (UPI) – UPI was developed
byNPCI in 2016; it facilitates peer-to-peer, person-to-
merchant transacons. • Mobile Wallet – This is a virtual
wallet that stores payment card informaon on a mobile
device. • Bank Pre-Paid Card – Under the moo “Pay Now,
Use Later,” the pre-paid cards allow users to buy things
with funds available in their cards. • Point of Sale – Point
of Sale (PoS) is a technological instrument provided by a
Merchant Establishment (ME) to carry out the sale
of goods or services to customers in a cashless
environment. • Internet Banking – This is an online
banking method that enables customers of a bank or
financial instuon to carry out transacons through a portal. •
Mobile Banking – This is a service provided by banks and
financial instuons to carry out financial transacons through
a mobile device. • Micro ATM – These are portable
devices allowing banking transacons through card
This Photo by Unknown author is licensed under CC BY-NC-ND.
You might also like
- #BWNLLSV #000000Q4T6WXX2A6#000AMP90F Champeil D Lewis 18026 Valley BLVD Apt 96 BLOOMINGTON CA 92316-2083Document4 pages#BWNLLSV #000000Q4T6WXX2A6#000AMP90F Champeil D Lewis 18026 Valley BLVD Apt 96 BLOOMINGTON CA 92316-2083Popo Lewis67% (3)
- Digital Payment (PAYTM)Document35 pagesDigital Payment (PAYTM)Ankit PashteNo ratings yet
- 2011dec07 2012jan06Document2 pages2011dec07 2012jan06Cowdrey Ilan100% (1)
- Business Capability Model: Quick GuideDocument6 pagesBusiness Capability Model: Quick Guidekadeoye75% (4)
- Banking Products and ServicesDocument5 pagesBanking Products and ServicesAikya GandhiNo ratings yet
- Instruction Circular No. 151/2012Document10 pagesInstruction Circular No. 151/2012Samra QasimNo ratings yet
- Digital Payments in IndiaDocument10 pagesDigital Payments in IndiaPrajwal KottawarNo ratings yet
- MR - Bhagyaraja Nagaraju Koppisetty: Page 1 of 2 M-87654321-1Document2 pagesMR - Bhagyaraja Nagaraju Koppisetty: Page 1 of 2 M-87654321-1Bhagyaraj KoppishettyNo ratings yet
- Npa Cbs ProjectDocument56 pagesNpa Cbs ProjectChirag GugnaniNo ratings yet
- Digital Payment & TransactionsDocument91 pagesDigital Payment & Transactionschaliya00767% (3)
- Digital Payments and Their Impact On The IndianDocument20 pagesDigital Payments and Their Impact On The Indiannivethitha aNo ratings yet
- Review of Some Online Banks and Visa/Master Cards IssuersFrom EverandReview of Some Online Banks and Visa/Master Cards IssuersNo ratings yet
- Instruction: Telegraphic TransferDocument4 pagesInstruction: Telegraphic TransferBokulNo ratings yet
- E Banking 1Document12 pagesE Banking 1Zach BellNo ratings yet
- Digital Banking in India: Recent Trends, Advantages and DisadvantagesDocument4 pagesDigital Banking in India: Recent Trends, Advantages and DisadvantagesAmazing VideosNo ratings yet
- Digital Payments (Simran Ruchi) ViewDocument9 pagesDigital Payments (Simran Ruchi) ViewRuchi SawantNo ratings yet
- Increase-The Government's Encouragement To Use Electronic Wallets Has Contributed Much ToDocument3 pagesIncrease-The Government's Encouragement To Use Electronic Wallets Has Contributed Much ToMahima SharmaNo ratings yet
- Innovations in Indian Banking Sector: Piyush GinotraDocument11 pagesInnovations in Indian Banking Sector: Piyush GinotraDeepak AroraNo ratings yet
- TH ST STDocument8 pagesTH ST STSaloni Jain 1820343No ratings yet
- Real-Time Payment System IMPS - Future & ChallengesDocument27 pagesReal-Time Payment System IMPS - Future & ChallengesRahul AminNo ratings yet
- Shubham Kumar Chachan CIA - 1Document12 pagesShubham Kumar Chachan CIA - 1AYUSH TREHAN 20215023No ratings yet
- Recent Trends in BankingDocument2 pagesRecent Trends in BankingFire BoltNo ratings yet
- Banking in 21st CenturyDocument4 pagesBanking in 21st CenturyDr. Ashish Kumar ChaurasiaNo ratings yet
- Class Vii Fin - Lit.pa IVDocument10 pagesClass Vii Fin - Lit.pa IVSaraswati DhanjaniNo ratings yet
- Current Digital Payments Method in India: Submitted By: - Vidit Mittal (317/2020)Document4 pagesCurrent Digital Payments Method in India: Submitted By: - Vidit Mittal (317/2020)Pro BroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document33 pagesChapter 1Crazykiddo 307No ratings yet
- Banking Law FinalDocument17 pagesBanking Law FinalShareen AnwarNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument6 pagesUntitledAparna MohandasNo ratings yet
- Digital Payments: Challenges and Solutions: Srihari Kulkarni, Abdul Shahanaz TajDocument6 pagesDigital Payments: Challenges and Solutions: Srihari Kulkarni, Abdul Shahanaz Tajnilofer shallyNo ratings yet
- A Study On Digital Payment SystemDocument57 pagesA Study On Digital Payment Systemtrishna BillavaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Introduction To Digital BankingDocument9 pagesChapter 1: Introduction To Digital BankingPriyanka JNo ratings yet
- Brijesh Project All Set To PrintDocument59 pagesBrijesh Project All Set To Printv raviNo ratings yet
- BAAANKDocument6 pagesBAAANKHassenNo ratings yet
- New Generation Banks: Presentation By, Mahesh M S3 Mba NO: 32Document16 pagesNew Generation Banks: Presentation By, Mahesh M S3 Mba NO: 32sameerNo ratings yet
- Internet Banking in India:) Information Only SystemDocument3 pagesInternet Banking in India:) Information Only SystemnithyabinodNo ratings yet
- Xavier Institute of Management, Bhubaneswar: M-Banking: Does It Have Potential?Document27 pagesXavier Institute of Management, Bhubaneswar: M-Banking: Does It Have Potential?Neetesh SinghNo ratings yet
- Innovation in Banking SectorDocument21 pagesInnovation in Banking Sectoruma2k10No ratings yet
- Wattal Committee ReportDocument2 pagesWattal Committee ReportKunwarbir Singh lohatNo ratings yet
- INTERNET BANKING SawarnimDocument12 pagesINTERNET BANKING SawarnimSwarnim RamolaNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Customers' Adoption of Electronic Payment: An Empirical AnalysisDocument15 pagesFactors Affecting Customers' Adoption of Electronic Payment: An Empirical Analysisprabin ghimireNo ratings yet
- E-Banking: Impact of Information Technology in India by Vijay KumbharDocument4 pagesE-Banking: Impact of Information Technology in India by Vijay KumbharmulchahiNo ratings yet
- Finance Ipr 2Document42 pagesFinance Ipr 2Navaneeth GsNo ratings yet
- A Study On Digital Payments System & Consumer Perception: An Empirical SurveyDocument11 pagesA Study On Digital Payments System & Consumer Perception: An Empirical SurveyDeepa VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Full Fledge CP Project Work-In-Progress-1Document50 pagesFull Fledge CP Project Work-In-Progress-1Eldorado OSNo ratings yet
- Digital Payments Methods in India A Study of Problems and ProspectsDocument8 pagesDigital Payments Methods in India A Study of Problems and ProspectsNandanNo ratings yet
- Types of Digital Payment Methods in India: Banking Cards: Cards Are Among The Most Widely UsedDocument4 pagesTypes of Digital Payment Methods in India: Banking Cards: Cards Are Among The Most Widely UsedMahimalluru Charan KumarNo ratings yet
- Information Technology in Banking Services - Trends, Issues and ChallengesDocument9 pagesInformation Technology in Banking Services - Trends, Issues and ChallengesSneha ChavanNo ratings yet
- Internet Banking in India:) Information Only SystemDocument3 pagesInternet Banking in India:) Information Only SystemSrishti BansalNo ratings yet
- Recent in BankingDocument25 pagesRecent in BankingSrividya SNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction PartDocument4 pagesChapter 1 Introduction Parttravon8877No ratings yet
- UntitledDocument84 pagesUntitledCrazykiddo 307No ratings yet
- E-Banking: Internet Banking in IndiaDocument4 pagesE-Banking: Internet Banking in IndiaPrasanjeet BhattacharjeeNo ratings yet
- Banking Technology 1Document9 pagesBanking Technology 1Pragathi PriyaNo ratings yet
- HomeDocument3 pagesHomeAishwarya Sharma DawarNo ratings yet
- Electronic and Mobile BankingDocument19 pagesElectronic and Mobile BankingBilal Malick100% (1)
- Net Banking With Refrance To HDFCDocument99 pagesNet Banking With Refrance To HDFCPrakshi PunmiyaNo ratings yet
- The Role of Internet Banking and Society: C.A.Mahesh Kumar, Y.Lokesh Kumar Reddy, B.SreenivasuluDocument9 pagesThe Role of Internet Banking and Society: C.A.Mahesh Kumar, Y.Lokesh Kumar Reddy, B.SreenivasuluPavan PaviNo ratings yet
- Digital IndiaDocument28 pagesDigital IndiahumairaNo ratings yet
- Delivery Channels in Retail BankingDocument5 pagesDelivery Channels in Retail BankingSahibaNo ratings yet
- AWAIS Operation ManagementDocument9 pagesAWAIS Operation Managementawais tariqNo ratings yet
- Final Report - RamyaDocument38 pagesFinal Report - RamyaMahammad AliNo ratings yet
- Adrit Main FileDocument65 pagesAdrit Main Filevishwas mishraNo ratings yet
- Banking Sector - Survival of The FittestDocument9 pagesBanking Sector - Survival of The FittestSwati SinghNo ratings yet
- Our Heritage: Mobile Banking: A Tool For Digital IndiaDocument7 pagesOur Heritage: Mobile Banking: A Tool For Digital IndiaSamil MusthafaNo ratings yet
- Digital Journey IndiaDocument2 pagesDigital Journey IndiaAlaukik VarmaNo ratings yet
- Alternative Banking An Modern Practice in India: Mr. Vijay M. KumbharDocument7 pagesAlternative Banking An Modern Practice in India: Mr. Vijay M. KumbharSubhendu MishraNo ratings yet
- Notes For MBA 3Document213 pagesNotes For MBA 3Pramod VasudevNo ratings yet
- Consolidated Invoice - Nexa Equity - Project ScubaDocument3 pagesConsolidated Invoice - Nexa Equity - Project ScubarhenkeNo ratings yet
- Ifc Digital Scoping: Country Report: PalestineDocument31 pagesIfc Digital Scoping: Country Report: PalestineManvi PareekNo ratings yet
- MbfiDocument29 pagesMbfiSujith DeepakNo ratings yet
- Terms and Conditions For Usage of SI On CC-Bill Pay ServicesDocument4 pagesTerms and Conditions For Usage of SI On CC-Bill Pay Services201CI051 Sethu Ramachandra.RNo ratings yet
- Threat of New Entry in The Philippine Banking IndustryDocument2 pagesThreat of New Entry in The Philippine Banking IndustryGerardNo ratings yet
- 1Document7 pages1Krishna guptaNo ratings yet
- CH 08Document4 pagesCH 08flrnciairnNo ratings yet
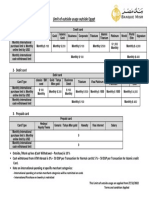
- Limit of Outside Usage Outside Egypt ENDocument1 pageLimit of Outside Usage Outside Egypt ENIbrahem EmamNo ratings yet
- Short Term InvestmentDocument16 pagesShort Term Investmentluckey racerNo ratings yet
- This Content Downloaded From 157.42.109.45 On Wed, 02 Jun 2021 20:36:05 UTCDocument9 pagesThis Content Downloaded From 157.42.109.45 On Wed, 02 Jun 2021 20:36:05 UTCuttam krNo ratings yet
- Annual Report 2020 - 06-04-2021Document342 pagesAnnual Report 2020 - 06-04-2021PrincessNo ratings yet
- CHAP - 03 - Managing and Pricing Deposit Services and Non-Deposit LiabilitiesDocument60 pagesCHAP - 03 - Managing and Pricing Deposit Services and Non-Deposit LiabilitiesPhuc Hoang DuongNo ratings yet
- Business Finance-Module 1Document15 pagesBusiness Finance-Module 1Alex PrioloNo ratings yet
- Financial Wellbeing Capability UK Adults Poverty Debt Saving Numeracy InfographicDocument1 pageFinancial Wellbeing Capability UK Adults Poverty Debt Saving Numeracy InfographicerioNo ratings yet
- Accounting VoucherDocument6 pagesAccounting VoucherHappy Surjya DaimaryNo ratings yet
- Books of Original Entry (An Introduction)Document5 pagesBooks of Original Entry (An Introduction)Joshua BrownNo ratings yet
- Corporate Financial Management 6Th New Edition Edition Glen Arnold Deborah Lewis Full ChapterDocument51 pagesCorporate Financial Management 6Th New Edition Edition Glen Arnold Deborah Lewis Full Chapterwm.baker518100% (9)
- DR Mohammed Obaidullah: Recent Publications (Books and Monographs)Document4 pagesDR Mohammed Obaidullah: Recent Publications (Books and Monographs)pkt_prabhuNo ratings yet
- MCQs Chapter 3 - What Is MoneyDocument17 pagesMCQs Chapter 3 - What Is MoneyPhạm Trương Uyên ThyNo ratings yet
- 07 Chapter 1Document72 pages07 Chapter 1Motiram paudelNo ratings yet
- Contemporary Issues in Development FinanceDocument461 pagesContemporary Issues in Development FinanceBrenda AwuorNo ratings yet
- AR Vietcombank2019 EnglishDocument111 pagesAR Vietcombank2019 EnglishHuong Mai VuNo ratings yet