Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Summative 3
Summative 3
Uploaded by
Daiseree Salvador0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views21 pagesSummative science
Original Title
summative3
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentSummative science
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views21 pagesSummative 3
Summative 3
Uploaded by
Daiseree SalvadorSummative science
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 21
ENUMERATION
1-3 - Glands that provide
liquid in which sperm
can swim
ENUMERATION
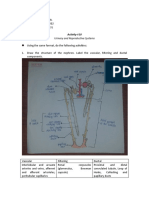
4-8 Parts of the male
reproductive system
ENUMERATION
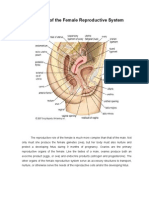
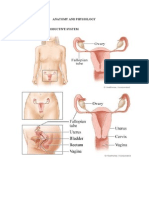
9-12 Parts of the Female
reproductive system
ENUMERATION
13-16 Hormones involved
in the Menstrual Cycle
ENUMERATION
17-20 Phases of
Menstrual Cycle
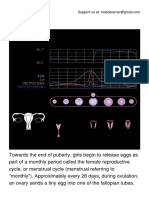
21.If Raziah had her menstruation on
the 3rd day of May, when will be her
next menstruation if she had a 28-
day cycle?
22. When does her ovulation fall?
23. Our human body is a
complex design. Our
ability to reproduce begins
at (adolescence,
adulthood).
24. The periodic or regular
shedding of tissues and blood
from the inner lining of the
uterus is called the
(menopausal, menstruation)
or period.
25. The (follicular, luteal) phase
happens when the uterine
lining/walls starts to thicken with
new layer of tissue. An egg is
developing in the ovary, too.
26. (Menstruation,
Ovulation) is a sign that a
girl is capable of
producing offspring.
27. The length of the
menstrual cycle varies from
woman to woman but the
average cycle is (28, 30)
days
28. The menstrual cycle can
continue in a woman for 40
years, but it temporarily stops
during (ovulation, pregnancy).
29. Our body’s chemical
messengers are the (hormones,
neurotransmitters) produced by
the glands of the endocrine system.
30. Endocrine glands pass
chemical messages straight into
the (bloodstream, organs).
31. Hormones affect various
processes in the body as they
(change, regulate) the activity
of organs, tissues, and cells.
32. Despite the fact that hormones act
in very (large, small) amounts, they
can control many of the changes in the
reproductive system including the
menstrual cycle.
33. (Activity, Feedback) loops
are biological processes that
maintain homeostasis or body
balance.
34. (Negative, Positive) feedback
amplifies the initiating stimulus.
35.. (Negative, Positive) feedback
reduces the stimulus.
You might also like
- Menstrual Cycle Activity Day 2Document2 pagesMenstrual Cycle Activity Day 2Aaliyah CarlobosNo ratings yet
- Menstrual CycleDocument8 pagesMenstrual CycleJULIANNE ANACTANo ratings yet
- Dekey Biology ProjectDocument12 pagesDekey Biology ProjecttseringchondenmakhamNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Female Reproductive SystemDocument9 pagesAnatomy of The Female Reproductive SystemPinkeyinthecityNo ratings yet
- Growing FetusDocument24 pagesGrowing Fetusnc101No ratings yet
- Human Reproductive SystemDocument23 pagesHuman Reproductive SystemQuennie AceronNo ratings yet
- CP Ovarian Cyst Chap5Document11 pagesCP Ovarian Cyst Chap5Katherine 'Chingboo' Leonico LaudNo ratings yet
- Embryology of The Female Reproductive SystemDocument5 pagesEmbryology of The Female Reproductive SystemAndrew LukmanNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System: Synopsis Menstrual Cycle Spermatogenesis Oogenesis Process of Reproduction Pregnancy ParturitionDocument57 pagesReproductive System: Synopsis Menstrual Cycle Spermatogenesis Oogenesis Process of Reproduction Pregnancy ParturitionBlack RoseNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive SystemDocument28 pagesFemale Reproductive System1-LUMALANG Ashley Anne A.No ratings yet
- Femlae Monthly CycleDocument3 pagesFemlae Monthly CycleTHANGES THANGUNo ratings yet
- EmbryologyDocument9 pagesEmbryologyRuhul Qudus NaimNo ratings yet
- 2 Anatomy and Physiology (Female)Document44 pages2 Anatomy and Physiology (Female)AYO NELSONNo ratings yet
- Menstrual CycleDocument2 pagesMenstrual CycleShekinah MaeNo ratings yet
- The Human Reproductive SystemDocument1 pageThe Human Reproductive SystemVATSALA A/P S. VIJIENDRAM KPM-GuruNo ratings yet
- The Reproductive SystemDocument7 pagesThe Reproductive SystemAndri SusantoNo ratings yet
- Good Afternoon: Prepared byDocument102 pagesGood Afternoon: Prepared byKrishna PatelNo ratings yet
- FemrepnotesDocument38 pagesFemrepnotesLibi FarrellNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System: Renthel R. Cueto Bsabe - 1ADocument5 pagesReproductive System: Renthel R. Cueto Bsabe - 1ARenthel CuetoNo ratings yet
- Male - Female ReproDocument11 pagesMale - Female ReproShardin Labawan-Juen,RNNo ratings yet
- What Is Reproduction?: Male Reproductive System GenesDocument4 pagesWhat Is Reproduction?: Male Reproductive System GenesPrada Maya AnggariNo ratings yet
- The Reproductive SystemDocument11 pagesThe Reproductive Systemdevgod729No ratings yet
- Female Reproductive Cycle PDFDocument3 pagesFemale Reproductive Cycle PDFPerry Sin100% (2)
- Reproductive SystemDocument33 pagesReproductive Systemjheannegabriellea.ylaganNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive SystemDocument34 pagesFemale Reproductive SystemMikaela Rose SolivenNo ratings yet
- UNIT 3. ReproductionDocument3 pagesUNIT 3. ReproductionParsel BlehNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Fetal DevelopmentDocument7 pagesModule 3 Fetal DevelopmentRichel TalattagNo ratings yet
- Human ReproductionDocument58 pagesHuman ReproductionFelix HorseradaNo ratings yet
- Female Reproduction Female Reproductive Parts and Functions II. Oogenesis and OvulationDocument4 pagesFemale Reproduction Female Reproductive Parts and Functions II. Oogenesis and OvulationLana GalloNo ratings yet
- Fun With Reproduction: The Big Picture: ReproductionDocument14 pagesFun With Reproduction: The Big Picture: ReproductionAljon AniesNo ratings yet
- DR Mohtaseb Slide 4 EmbryologyDocument40 pagesDR Mohtaseb Slide 4 Embryologyapi-249972919No ratings yet
- Ge 11 Prefinals Human Reproduction Another HandoutDocument9 pagesGe 11 Prefinals Human Reproduction Another HandoutotakukairoNo ratings yet
- The Menstrual Cycle - WorksheetDocument2 pagesThe Menstrual Cycle - WorksheetJustine Kylle Aberin100% (1)
- Intro To Pregnancy LVL 1Document34 pagesIntro To Pregnancy LVL 1Helene NketchouaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 25 Vocab Leo ArrabiDocument2 pagesChapter 25 Vocab Leo ArrabiLeo ArrabiNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in HumansDocument4 pagesReproduction in HumansIsra OmerNo ratings yet
- Charles Z. Ariola JR., MSN., LPT, Rn. Instructor IDocument22 pagesCharles Z. Ariola JR., MSN., LPT, Rn. Instructor ICharlz ZipaganNo ratings yet
- Science 5 Q2 W2Document2 pagesScience 5 Q2 W2GOODWIN GALVANNo ratings yet
- Reproductive Processes: Chapter-34-Lesson-2 Page-961-966Document26 pagesReproductive Processes: Chapter-34-Lesson-2 Page-961-966JanaNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive SystemDocument11 pagesFemale Reproductive SystemLiijohn FlojNo ratings yet
- 3.human ReproductionDocument49 pages3.human ReproductionSubhashakti BeheraNo ratings yet
- 2nd Term j1 Basic ScienceDocument28 pages2nd Term j1 Basic SciencejonahorjiNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy and Human Development: Part ADocument5 pagesPregnancy and Human Development: Part Askatay6189No ratings yet
- Menstrual CycleDocument18 pagesMenstrual CycleKim RamosNo ratings yet
- DelaCruz AlbertBryan Activity#10 MED3Document5 pagesDelaCruz AlbertBryan Activity#10 MED3AlbertNo ratings yet
- Lesson Assignment Lesson 2 Text Assignment Lesson ObjectivesDocument22 pagesLesson Assignment Lesson 2 Text Assignment Lesson ObjectivesSudipta GhoshNo ratings yet
- Grade 6 Human Reproduction New Vocabulary: English WordDocument9 pagesGrade 6 Human Reproduction New Vocabulary: English WordSalome TamaraNo ratings yet
- Grade 6 Human Reproduction New Vocabulary: English WordDocument9 pagesGrade 6 Human Reproduction New Vocabulary: English WordCRISTIAN RAFAEL MENDOZA MALDONADONo ratings yet
- 3 Parts of Sperm CellsDocument3 pages3 Parts of Sperm CellsGlyjade DumadagNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document16 pagesLecture 3Smasher AustineNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument10 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyBurni GuevaraNo ratings yet
- MenstruationDocument4 pagesMenstruationMelgeri Aubrey E. UngosNo ratings yet
- Dr. Dwi Rita Anggraini, M.Kes Dr. Sufitni, M.Kes Anatomy Department Medicine Faculty of North SumatraDocument19 pagesDr. Dwi Rita Anggraini, M.Kes Dr. Sufitni, M.Kes Anatomy Department Medicine Faculty of North SumatraAnnDianaJaiminNo ratings yet
- Human Reproduction 2 Notes (Class 12)Document6 pagesHuman Reproduction 2 Notes (Class 12)Ashok KumarNo ratings yet
- Reproduction System: By: Maharini, S.PD Anik Rahmawati, S.PD SMP Negeri 1 PonorogoDocument31 pagesReproduction System: By: Maharini, S.PD Anik Rahmawati, S.PD SMP Negeri 1 PonorogoYu HasNo ratings yet
- Ection I. The Female Reproductive System 1-1. GENERALDocument9 pagesEction I. The Female Reproductive System 1-1. GENERALNheil_Christop_4211No ratings yet
- Lecture 3. FertilizationDocument52 pagesLecture 3. FertilizationBabbu YadavNo ratings yet
- Menstrual CycleDocument4 pagesMenstrual CycleAyo AyingNo ratings yet
- 2 Nursing Role in Reproductive and Sexual HealthDocument4 pages2 Nursing Role in Reproductive and Sexual HealthHarry Venzon JaboliNo ratings yet
- DRRRDocument9 pagesDRRRDaiseree SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Offcolor After Lap 2Document6 pagesOffcolor After Lap 2Daiseree SalvadorNo ratings yet
- School Card EditedDocument1 pageSchool Card EditedDaiseree SalvadorNo ratings yet
- 3rd Long TestDocument6 pages3rd Long TestDaiseree SalvadorNo ratings yet