Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lesson 6 ENTREP
Uploaded by
Hendre Bacolod0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views19 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views19 pagesLesson 6 ENTREP
Uploaded by
Hendre BacolodCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 19
4 M's of Operations in Relation to the
Business Opportunity and Developing
Business Opportunity
The most serious issues in the whole production system are the inputs
and the transformation process. Their quality determines the quality of
the output.
The factors involved in the input and the production process are usually
referred to as the Four M’s of production, namely Manpower, Method,
Machine, and Materials.
MANPOWER
Talks about the human labor force involved in the
manufacture of products.
It is measured as the most serious and main factor of
production. The entrepreneur must determine, attain, and
match the most competent and skilled employees with
the jobs at the most appropriate time period.
Educational qualifications and experience, status of
employment, number of workers required, and skills and
expertise required for the job are some of the manpower
criteria that must be highly considered by the
entrepreneur.
Talks about raw materials
necessary in the production of a
product. Materials mainly form
part of the finished product. Just in
case the resources are below
standard, the finished product will
be unsatisfactory as well.
MATERIAL
The entrepreneur may consider
cost, quality, availability,
credibility of suppliers, and waste
that the raw material may produce.
Discusses manufacturing equipment used
in the production of goods or delivery of
services.
In the process of selecting the type of
equipment to purchase, the entrepreneur
may consider the types of products to be
produced, production system to be
adopted, cost of the equipment, capacity
MACHINE of the equipment, availability of spare
parts in the local market, the efficiency of
the equipment and the skills required in
running the equipment.
The production method discusses the process or
way of transforming raw materials into finished
products. The resources undergo some stages
before it is finalized and become set for delivery
to the target buyers.
The selection of the method of production is
dependent on the product to produce, mode of
production, manufacturing equipment to use,
and required skills to do the work.
METHOD
Product Description
Is the promotion that explains what a product is and why it’s worth
buying? The purpose of a product description is to provide customers
with details about the features and benefits of the product so they’re
obliged to buy. Know who your target market is, focus on the product
benefits, tell the full story, use natural language and tone, use powerful
words that sell, and use good images. These are guidelines for you to
have a good product description; since some customers are very
particular with it since they consider the welfare of their family if it is safe
to use.
Prototyping
A duplication of a product as it will be produced, which may contain such
details as color, graphics, packaging, and directions. One of the important early
steps in the inventing process is making a prototype. Benefits are the reasons
why customers will decide to buy the products such as affordability, efficiency, or
ease of use. The features of the product or service merely provide a descriptive
fact about the product or service.
It is better to test your product prototype to meet customers’ needs and
expectations; and for your product to be known and saleable. Pretesting of the
product or service is similar to a sample of the product or service given to the
consumer free of cost in order that he/she may try the product before
committing to a purchase.
An entity that offers goods and services to
another business. This entity is among of supply
Supplier chain of a business, which may offer the main
part of the value contained within its products.
Certain suppliers may even be involved in drop
shipping, where they ship goods directly to the
customers of the buyer.
Suppliers
Suppliers are your business partners, without them your business will
not live. You need them as much as you need your customers to be
satisfied. But as an entrepreneur, you have to choose a potential
supplier that has loyalty and values your partnership; a supplier that
would lead you to the fulfillment of your business objectives, mission,
and vision.
is a method or activity by which a company adds
value to an item, with production, marketing,
and the provision of after-sales service. The main
Value chain goal and benefit of the value chain, and
therefore value chain analysis, is to make or
support a competitive benefit.
Supply Chain
A supply chain is a structure of organizations, people, activities,
data, and resources involved in moving a product or service from
supplier to customer.
The main objective of supply chain management includes
management of a varied range of components and procedures, for
instance, storing raw materials, handling the inventory,
warehousing, and movement of finished products from the point of
processing to the point of consumption.
Business Model
The business model describes the reasons how an organization
creates, delivers, and captures value in economic, social, cultural, or
other contexts. The development of business model construction and
variation is also called business model innovation and forms a part of the
business plan.
It is a company's plan for how it will make revenues and make a
profit. It describes what products or services the business plans to
manufacture and market, and how it plans to do so, as well as what
expenses it will incur.
There are important phases in developing your business model,
namely;
identifying the specific audience;
establishing business processes;
recording business resources;
developing a strong value proposition
determining key business partners;
and creating a demand for today’s generation’s strategy and
being open to innovations
Business plan is an important tool for you to have an
idea about the future of your business. Your business
plan will be your guide at the moment you will be
implementing and operating your business proposal.
You can also make use of the business plan to
secure investment capital from financial institutions or
lenders. It can also be used to influence people to work
for your enterprise, to secure credit from suppliers, and
to fascinate potential customers.
COMPONENTS FOUND IN A BUSINESS
PLAN
Introduction - this part discusses what is the business plan all about.
Executive Summary - is part of the business plan which is the first to be
presented but the last to be made.
Management Section - shows how you will manage your business and the
people you need to help you in your operations.
Marketing Section - shows the design of your product/service; pricing,
where you will sell, and how you will introduce your product/service to your
market.
Financial Section - shows the money needed for the business, how much you
will take in, and how much you will pay out.
Production Section - shows the area, equipment, and materials needed for the
business.
Competitive Analysis - is the strategy where you identify major competitors
and research their products, sales, and marketing strategies.
Market - The persons who will buy the product or services.
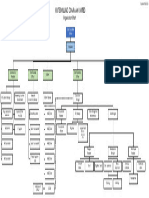
Organizational Chart - is the diagram showing graphically the relation of
one official to another, or others of a company.
THANK YOU
By : Jian Carlo Argoncilo & Ivy M. Dela Cruz
You might also like
- 4 MsDocument54 pages4 MsFelix BermudezNo ratings yet
- Module 6 4Ms of Production and Business ModelDocument40 pagesModule 6 4Ms of Production and Business ModelHoney Grace Dela CernaNo ratings yet
- ENTREPRENEURSHIP 12 Q2 M6 4Ms of Production and Business ModelDocument19 pagesENTREPRENEURSHIP 12 Q2 M6 4Ms of Production and Business ModelMyleen CastillejoNo ratings yet
- Four M's Manpower Method Machine MaterialsDocument3 pagesFour M's Manpower Method Machine MaterialsYancie Siaboc100% (6)
- 4 Ms of OperationsDocument18 pages4 Ms of OperationsJihyun KimNo ratings yet
- Q4 Week 1 2 ENTREP - 4Ms of Production and Business Model James Francis Magdalino G 12 COOKERYDocument23 pagesQ4 Week 1 2 ENTREP - 4Ms of Production and Business Model James Francis Magdalino G 12 COOKERYJames Francis Magdalino89% (9)
- 2 4ms of ProductionDocument31 pages2 4ms of ProductionYancey LucasNo ratings yet
- Mod6 - 4Ms of Production and Business Model - v2Document18 pagesMod6 - 4Ms of Production and Business Model - v2MARY JOY RUSTIANo ratings yet
- 4 Ms of Production and Business ModelDocument21 pages4 Ms of Production and Business ModelEmyren Apuya50% (2)
- Q4-Las-1 - Week 1 - 2 - EntrepreneurshipDocument12 pagesQ4-Las-1 - Week 1 - 2 - EntrepreneurshipCheryl MountainclearNo ratings yet
- Module 6: 4M'S of Production and Business ModelDocument43 pagesModule 6: 4M'S of Production and Business ModelSou MeiNo ratings yet
- Entrep12 Q2 Mod6 4Ms of Production and Business Model v2Document18 pagesEntrep12 Q2 Mod6 4Ms of Production and Business Model v2MrBigbozz21100% (1)
- Q4 Week 1 2 ENTREP - 4Ms of Production and Business Model - StudentsDocument21 pagesQ4 Week 1 2 ENTREP - 4Ms of Production and Business Model - StudentsKyle Tagacay86% (14)
- Entrepreneurship Module 6 10Document97 pagesEntrepreneurship Module 6 10Jocet GeneralaoNo ratings yet
- Entrep Module 5 4Ms of Operation and Business ModelDocument19 pagesEntrep Module 5 4Ms of Operation and Business Modelelaine tizon50% (2)
- Entrep Q2 Module 6 PDFDocument10 pagesEntrep Q2 Module 6 PDFJan BrettNo ratings yet
- 4 M'S of Production and Business Model: Quarter 3-Week 1-2Document6 pages4 M'S of Production and Business Model: Quarter 3-Week 1-2Kimberly Rose GironNo ratings yet
- In Person Week 9 10 Entrep Day 1 2Document14 pagesIn Person Week 9 10 Entrep Day 1 2arrowtachieNo ratings yet
- Entrep LAS 02 Q2 WEEK 1 4Document16 pagesEntrep LAS 02 Q2 WEEK 1 4Rachelle Deinla BenitezNo ratings yet
- Entrep Week 1.Document8 pagesEntrep Week 1.Jumadel FalgueraNo ratings yet
- Northern Mindanao Colleges, Inc.: Directions For The UserDocument12 pagesNorthern Mindanao Colleges, Inc.: Directions For The UserYara King-PhrNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship: Senior High SchoolDocument13 pagesEntrepreneurship: Senior High SchoolEugine Bryan Son CadizNo ratings yet
- Entrep Module Week 6Document6 pagesEntrep Module Week 6LouisseNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship Quarter2 Week1 4editDocument32 pagesEntrepreneurship Quarter2 Week1 4editMarcht PatarayNo ratings yet
- 4 MsDocument11 pages4 Msdanielmangubat36No ratings yet
- ENTREPRENEURSHIP QUARTER 2 MODULE 8 4M's OF PRODUCTION ND BUSINESS MODELDocument12 pagesENTREPRENEURSHIP QUARTER 2 MODULE 8 4M's OF PRODUCTION ND BUSINESS MODELrichard reyesNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship Q4 Module6Document18 pagesEntrepreneurship Q4 Module6Herby OcomenNo ratings yet
- 4Ms of Production and Business ModelDocument14 pages4Ms of Production and Business ModelYsabel Muan100% (1)
- Week 1 2Document28 pagesWeek 1 2Jezrell Cllede B. DizonNo ratings yet
- Presentation 5Document31 pagesPresentation 5Ram BarceloNo ratings yet
- Entrep - Report 074604Document38 pagesEntrep - Report 074604JONESSA GAMBITO100% (1)
- 4Ms of Production - Q2Module1Document10 pages4Ms of Production - Q2Module1NÄ DÏÄNo ratings yet
- Handout 1Document13 pagesHandout 1Krisha ErikaNo ratings yet
- Entrep Q4 4MsDocument7 pagesEntrep Q4 4MsAnecita OrocioNo ratings yet
- Q2 M6 4M'S of Production and Business ModelDocument58 pagesQ2 M6 4M'S of Production and Business ModelIsabel GonzagaNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship 4m'sDocument5 pagesEntrepreneurship 4m'sddearcakailfadeNo ratings yet
- Module 6 - 4M's OF PRODUCTION AND BUSINESS MODELDocument8 pagesModule 6 - 4M's OF PRODUCTION AND BUSINESS MODELRealyn MatandacNo ratings yet
- Q2 M6 4M'S of Production and Business Model.1Document44 pagesQ2 M6 4M'S of Production and Business Model.1Isabel GonzagaNo ratings yet
- 4Ms ENTREPRENEURSHIPDocument8 pages4Ms ENTREPRENEURSHIPIuna CaidoyNo ratings yet
- ENTREPDocument5 pagesENTREPYancey LucasNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship ReviewerDocument3 pagesEntrepreneurship ReviewerApril VargasNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship Module 6Document8 pagesEntrepreneurship Module 6Cync KlayNo ratings yet
- Entrep Q2 SLM Lesson-1Document12 pagesEntrep Q2 SLM Lesson-1akiqt68No ratings yet
- 4 M's of Production and Business ModelDocument23 pages4 M's of Production and Business ModelCecileNo ratings yet
- Entrep Q2 W1Document8 pagesEntrep Q2 W1Jaw Use EmpuestoNo ratings yet
- 4 - EntrepDocument3 pages4 - Entrepzam partyNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship Business ModelDocument14 pagesEntrepreneurship Business ModelMaynard CaspilloNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Discussions AboutDocument30 pagesComprehensive Discussions AboutDimple MontemayorNo ratings yet
- Entrep 6Document38 pagesEntrep 6Monemar VelezNo ratings yet
- 4 Ms of Production and Business Model Entrep 6Document22 pages4 Ms of Production and Business Model Entrep 6Sittie Hana Diamla SaripNo ratings yet
- 4 M's of Operations in Relation To TheDocument39 pages4 M's of Operations in Relation To TheMoshu 4vodaduNo ratings yet
- Q4 Week1 2Document8 pagesQ4 Week1 2Shane HernandezNo ratings yet
- What Is A Product or Service Description?Document3 pagesWhat Is A Product or Service Description?Dimple MontemayorNo ratings yet
- Group 2: Jackline Cletus Mcharo Halima Yusuff Hussein Michonjo James Evelyn Shaibu Makenjura Mosses Ben Device MshoboziDocument32 pagesGroup 2: Jackline Cletus Mcharo Halima Yusuff Hussein Michonjo James Evelyn Shaibu Makenjura Mosses Ben Device MshoboziralphNo ratings yet
- 4Ms Prototype Valuesupply ChainDocument29 pages4Ms Prototype Valuesupply ChainJeftonNo ratings yet
- Q2 Week 3 - ADM ModuleDocument4 pagesQ2 Week 3 - ADM ModuleCathleenbeth MorialNo ratings yet
- Operations MDocument35 pagesOperations MPriyanshu RajNo ratings yet
- Value Chain of BusinessDocument7 pagesValue Chain of BusinessThaiseer MohammedNo ratings yet
- Comprencion de LecturaDocument9 pagesComprencion de LecturaXavier ReyNo ratings yet
- CPAR midtermDocument5 pagesCPAR midtermHendre BacolodNo ratings yet
- CPAR FINALSDocument5 pagesCPAR FINALSHendre BacolodNo ratings yet
- GEN MATH FINALSDocument3 pagesGEN MATH FINALSHendre BacolodNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5a EntrepDocument10 pagesLesson 5a EntrepHendre BacolodNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5B ENTREPDocument15 pagesLesson 5B ENTREPHendre BacolodNo ratings yet
- SG7001 Assignment Guide SlideDocument16 pagesSG7001 Assignment Guide Slidecheckpoint.purpleNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship PPT PositioningDocument12 pagesEntrepreneurship PPT PositioningJewelNo ratings yet
- Aace Evm 82R 13Document22 pagesAace Evm 82R 13eduardomenac2000No ratings yet
- AT08-04 Planning An Audit of Financial StatementsDocument4 pagesAT08-04 Planning An Audit of Financial StatementsEarl EzekielNo ratings yet
- Solution 2223PrdMgmt - HW4Document16 pagesSolution 2223PrdMgmt - HW4Hoang Thao NhiNo ratings yet
- Bijmolt Et Al (2021)Document11 pagesBijmolt Et Al (2021)hafidzah fauziaNo ratings yet
- Free PMF Booklet Customer Problem Fit Idea ValidationDocument17 pagesFree PMF Booklet Customer Problem Fit Idea ValidationDzung NguyenNo ratings yet
- Gay7e Irm Ch14Document39 pagesGay7e Irm Ch14Sophie Tuyen TranNo ratings yet
- Implementing World Class manufacturingDocument69 pagesImplementing World Class manufacturingdspinelliNo ratings yet
- DROPSHIPPING SHOPIFY ECOMMERCE 2021 Beginners Guide To Making Money Working From Home. Profit With Your Online Business... (Jack Mathew (Mathew, Jack) ) (Z-Library)Document125 pagesDROPSHIPPING SHOPIFY ECOMMERCE 2021 Beginners Guide To Making Money Working From Home. Profit With Your Online Business... (Jack Mathew (Mathew, Jack) ) (Z-Library)sebastiantrianam23No ratings yet
- Supply Chain Managment - Chap 2,4,5Document150 pagesSupply Chain Managment - Chap 2,4,5Bùi Nam KhánhNo ratings yet
- Advanced-Strategic-Management Solved MCQs (Set-7)Document8 pagesAdvanced-Strategic-Management Solved MCQs (Set-7)arthurquamenaNo ratings yet
- StratMngt 08 ActivityDocument3 pagesStratMngt 08 ActivitygallaresjeynNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document19 pagesChapter 6yordanosgetahun887No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Quiz EnglishDocument2 pagesChapter 4 - Quiz EnglishFitri-ssiNo ratings yet
- Download textbook Customer Relationship Management V Kumar ebook all chapter pdfDocument53 pagesDownload textbook Customer Relationship Management V Kumar ebook all chapter pdfthora.dalton130100% (9)
- Logistics Execution Integration in SAP SDDocument2 pagesLogistics Execution Integration in SAP SDtosik33721No ratings yet
- ShapeThings LTDDocument15 pagesShapeThings LTDdennisNo ratings yet
- Coso Erm 2017 - Appendices (Vol 2)Document40 pagesCoso Erm 2017 - Appendices (Vol 2)hesam.ezatjahNo ratings yet
- How To Find Suppliers in The Philippines (Complete Guide)Document1 pageHow To Find Suppliers in The Philippines (Complete Guide)jerickinthesky34No ratings yet
- Elite Drilling - Local OrganizationDocument1 pageElite Drilling - Local OrganizationYassineNo ratings yet
- Orange and White Modern Creative Marketing Plan PresentationDocument12 pagesOrange and White Modern Creative Marketing Plan Presentationfakisik582No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Fundamentals of Logistics and Supply Chain ManagementDocument29 pagesChapter 1 - Fundamentals of Logistics and Supply Chain ManagementTrần Thanh TrúcNo ratings yet
- Inventory Management in Supply Chain 2Document208 pagesInventory Management in Supply Chain 2cfakhryNo ratings yet
- Delivery Completion Indicator (DCI) Test Case in SAP MMDocument18 pagesDelivery Completion Indicator (DCI) Test Case in SAP MMuditNo ratings yet
- Module 5Document5 pagesModule 5minshairene9No ratings yet
- 100 Business FrameworksDocument218 pages100 Business FrameworksFarmsleytiNo ratings yet
- MBA Certificate PDFDocument2 pagesMBA Certificate PDFsafety infraNo ratings yet
- The Nature of Sales PromotionDocument3 pagesThe Nature of Sales PromotionMansi VermaNo ratings yet
- Operations Management Processes and Supply Chains, 12e, Chapter9Document62 pagesOperations Management Processes and Supply Chains, 12e, Chapter9hellojeenNo ratings yet