Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1.1 Principle of Combustion For Marine Boiler
Uploaded by
Aiman Firdaus0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views11 pagesOriginal Title
1.1 Principle of Combustion for Marine Boiler
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views11 pages1.1 Principle of Combustion For Marine Boiler
Uploaded by
Aiman FirdausCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 11
PRINCIPLES OF COMBUSTION
FOR MARINE BOILER
1.1
COMBUSTIO
N
FUNDAMENT
ALS
What are the components for
combustion to take place?
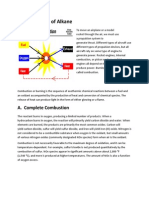
FIRE TRIANGLE
1. Heat
• A source of heat is required in order for ignition to occur,
and different materials have different ‘flash points’ e.g. the
lowest temperature at which they ignite.
• Unfortunately, combustion reactions also produce heat as
they burn, further increasing the temperature of the fuel.
2. Fuel
• A fire cannot begin if there is no material to burn. Homes
and businesses are full of flammable materials, such as
paper, oil, wood and fabrics. Any of these can serve as a
fuel for a fire.
• Some materials burn more easily than others. Fuels are
probably the most difficult ‘side’ of the fire triangle to
remove, so it’s wise to store them appropriately to prevent
them becoming a fire hazard.
FIRE TRIANGLE
3. Oxygen
• To sustain the combustion reaction, oxygen (or an
oxidising agent) is needed, as it reacts with the
burning fuel to release heat and CO2. Earth’s
atmosphere consists of 21% oxygen, so there is
plenty available to trigger a fire if the other two
components are present.
COMBUSTIO
N PROCESS
• Combustion is a chemical process. It
is a reaction between the fossil fuels
such as coal or natural gas and
oxygen. The main products of the
combustion process are carbon
dioxide and water. The combustion
process is always exothermic and it
liberates heat. The actual reaction
taking place due to combustion can
be written down as-
• Fuel + O2 -> Product + Heat
COMBUSTION PROCESS
• The process of combustion can be completely carried out only in
the presence of adequate amount of oxygen. Rapid fuel
oxidation results in large amount of heat. Almost 79% of air
which is not oxygen is nitrogen. Nitrogen is considered as
temperature reducing diluter.
• Nitrogen absorbs heat and reduces the combustion efficiency of
the fuel. The amount of heat which is available for use is also
reduced. At high temperatures, nitrogen combines with oxygen
to produce oxides of nitrogen, which are toxic pollutants.
• Under certain conditions, carbon combines with oxygen to form
carbon monoxide. This incomplete combustion releases small
amount of energy as compared when carbon combines with
carbon dioxide.
COMBUSTION PROCESS
• It's important to remember that combustion reactions are easy to
recognize because the products always contain carbon dioxide and
water. Here are several examples of balanced equations for
combustion reactions. Note that while oxygen gas is always
present as a reactant, in the trickier examples, the oxygen comes
from another reactant.
• Combustion of methane
CH4(g) + 2 O2(g) → CO2(g) + 2 H2O(g)
• Burning of naphthalene
C10H8 + 12 O2 → 10 CO2 + 4 H2O
• Combustion of ethane
2 C2H6 + 7 O2 → 4 CO2 + 6 H2O
• Combustion of butane (commonly found in lighters)
2C4H10(g) +13O2(g) → 8CO2(g) +10H2O(g)
COMBUSTION
PROCESS
• Complete Combustion: Also called "clean combustion," complete
combustion is the oxidation of a hydrocarbon that produces only carbon
dioxide and water. An example of clean combustion would be burning a
wax candle: The heat from the flaming wick vaporizes the wax (a
hydrocarbon), which in turn, reacts with oxygen in the air to release carbon
dioxide and water. Ideally, all the wax burns so nothing remains once the
candle is consumed, while the water vapor and carbon dioxide dissipate
into the air.
• Incomplete Combustion: Also called "dirty combustion," incomplete
combustion is hydrocarbon oxidation that produces carbon monoxide
and/or carbon (soot) in addition to carbon dioxide. An example of
incomplete combustion would be burning coal (a fossil fuel), during which
quantities of soot and carbon monoxide are released. In fact, many fossil
fuels—including coal—burn incompletely, releasing waste products into the
environment.
COMBUSTION PRODUCT
COMBUSTION
PRODUCT
• Poor combustion creates smoke, which
pollutes the atmosphere and wastes fuel
and reduces the efficiency of the engine or
boiler.
• production of smoke may lead to
prosecution.
• MARPOL Annex VI - prevention of air
pollution from ships
What means available at marine boiler
to monitor perfect combustion?
• Physically
• Instrumentation
You might also like
- Welding SymbolsDocument5 pagesWelding Symbolsjojo_323100% (3)
- Farm and Workshop Welding: Everything You Need to Know to Weld, Cut, and Shape Metal (Fox Chapel Publishing) Over 400 Step-by-Step Photos to Help You Learn Hands-On Welding and Avoid Common Mistakes - Andrew PearceDocument6 pagesFarm and Workshop Welding: Everything You Need to Know to Weld, Cut, and Shape Metal (Fox Chapel Publishing) Over 400 Step-by-Step Photos to Help You Learn Hands-On Welding and Avoid Common Mistakes - Andrew Pearcecazikoce0% (1)
- Gasifiers Wood Gasification & Off Grid PowerFrom EverandGasifiers Wood Gasification & Off Grid PowerRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- LPT ReportDocument2 pagesLPT ReportAnonymous OEUUoKHYR100% (1)
- CombustionDocument8 pagesCombustionbekkuNo ratings yet
- Day 1 AnswersDocument31 pagesDay 1 Answershaoues23100% (2)
- Rotary Drilling Products Raise Bore PDFDocument3 pagesRotary Drilling Products Raise Bore PDFmanuel_plfNo ratings yet
- Course On Masonry HeatersDocument16 pagesCourse On Masonry Heaterscountless100% (3)
- Astm A47 - A47m 99 PDFDocument5 pagesAstm A47 - A47m 99 PDFJavier Ricardo Romero BohorquezNo ratings yet
- Combustion and Oxidation: Summary SheetsDocument2 pagesCombustion and Oxidation: Summary Sheetsanna russuNo ratings yet
- Fuel AnalysisDocument34 pagesFuel AnalysisYedla Santosh kumar100% (2)
- MODEL ANSWER - Combustion - Flame - Class - VIIIDocument12 pagesMODEL ANSWER - Combustion - Flame - Class - VIIIRajarshi100% (1)
- Chapter 2 Fuel and Combustion Lecture NoteDocument40 pagesChapter 2 Fuel and Combustion Lecture NoteHabtamu Tkubet Ebuy100% (1)
- Incineration of Solid WastesDocument12 pagesIncineration of Solid WastesSyazwina AziziNo ratings yet
- Combustion ReactionsDocument6 pagesCombustion ReactionsGess LabradorNo ratings yet
- Notes Chemviiich Combustion and Flame S.kaushikDocument12 pagesNotes Chemviiich Combustion and Flame S.kaushikjeetjyoti787No ratings yet
- Combustion and Flame Note 2Document32 pagesCombustion and Flame Note 2anupNo ratings yet
- Com But IonDocument8 pagesCom But IonhetalhetviNo ratings yet
- Combustion and FlameDocument9 pagesCombustion and Flamebhumi tiwariNo ratings yet
- Lecture CH II - MCE 419 - CombustionDocument21 pagesLecture CH II - MCE 419 - CombustionRaji RidwanNo ratings yet
- Combustion AND Flames: by Vasu Manchanda Viii-ADocument9 pagesCombustion AND Flames: by Vasu Manchanda Viii-Abhumi tiwariNo ratings yet
- Combustion Basic InformationDocument11 pagesCombustion Basic InformationbekkuNo ratings yet
- Untitled 5Document1 pageUntitled 5Baraa Al SayedNo ratings yet
- Lecture6 .Thermal Properties of Biomass-Complete Combustion of Biomass and Energy ReleaseDocument20 pagesLecture6 .Thermal Properties of Biomass-Complete Combustion of Biomass and Energy ReleaseWaridho IskandarNo ratings yet
- Cumbustion and FlameDocument20 pagesCumbustion and FlameSanjaya SahooNo ratings yet
- Combustion and FlameDocument24 pagesCombustion and FlameVikranth PonnalaNo ratings yet
- Combustion ENG.Document27 pagesCombustion ENG.Fahad SaoudNo ratings yet
- Combustion and FlameDocument9 pagesCombustion and Flamesirswal kingNo ratings yet
- Principle of CombustionDocument9 pagesPrinciple of CombustionTin Aung KyiNo ratings yet
- Power Plant Chapter ThreeDocument74 pagesPower Plant Chapter ThreeGETACHEWNo ratings yet
- Combustion: 4 2 2 2 2 2 4 6 (Discuss)Document5 pagesCombustion: 4 2 2 2 2 2 4 6 (Discuss)Ren H. RoxasNo ratings yet
- Combustion and Flame 2022Document11 pagesCombustion and Flame 2022Debomoy PatraNo ratings yet
- NOTESDocument16 pagesNOTESAadi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Combustion & Flue Gas Analysis 1Document37 pagesCombustion & Flue Gas Analysis 1Daphne Cosi LealNo ratings yet
- CBSE 8 Science CBSE - Combustion and Flame, Free Test Papers, Sample Questions, HOTS Questions and Notes, CBSE - Combustion and FlameDocument9 pagesCBSE 8 Science CBSE - Combustion and Flame, Free Test Papers, Sample Questions, HOTS Questions and Notes, CBSE - Combustion and FlameR.Shruti 1040-12No ratings yet
- Fuel L2 (1) ,,ATDocument30 pagesFuel L2 (1) ,,ATVishvas SinghhNo ratings yet
- Combustion Note 1Document2 pagesCombustion Note 1Haradip MahilaryNo ratings yet
- 3 Combustion FlameDocument11 pages3 Combustion FlamethinkiitNo ratings yet
- 4.1.4,5,6 Properties of Gaseous FuelsDocument5 pages4.1.4,5,6 Properties of Gaseous FuelsOkky Kusumo Indradi100% (1)
- Combustion: Flames Fuel Exothermic Fuel Oxidant Heat Light Flames Radical Thermal RunawayDocument7 pagesCombustion: Flames Fuel Exothermic Fuel Oxidant Heat Light Flames Radical Thermal RunawayVel MuruganNo ratings yet
- Incineration - Gasification - PyrolysisDocument65 pagesIncineration - Gasification - Pyrolysistatchanok1525No ratings yet
- 6 - Combustion & Fossil FuelsDocument12 pages6 - Combustion & Fossil FuelsFadillah RyanNo ratings yet
- Combustion Booklet 2006Document22 pagesCombustion Booklet 2006Largat El HassenNo ratings yet
- Post Lab Discussion: - Experiment No.2Document48 pagesPost Lab Discussion: - Experiment No.2Lovelyn Cantollas EugenioNo ratings yet
- Intro Boiler CombustionDocument30 pagesIntro Boiler Combustiondhanush.exeNo ratings yet
- On FuelDocument42 pagesOn Fuelapi-280572108100% (1)
- Unit V Fuels and Combustion 9Document19 pagesUnit V Fuels and Combustion 9Er S Karthick AnnamalaiNo ratings yet
- CombustionDocument3 pagesCombustionJeancy SenosinNo ratings yet
- ARSONDocument16 pagesARSONStephanie De La CruzNo ratings yet
- Combustion of AlkanesDocument7 pagesCombustion of AlkanesA-ar FebreNo ratings yet
- 8E ChemistryDocument56 pages8E ChemistryNazNo ratings yet
- Motors in Chemical Eng.Document6 pagesMotors in Chemical Eng.Guillermo CúmezNo ratings yet
- Organic ChemistryDocument9 pagesOrganic ChemistryShammah MakowaniNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Project (1) (Mohamed Part)Document6 pagesChemistry Project (1) (Mohamed Part)mohamed amirNo ratings yet
- 875542-QA-Combustion and FlameDocument7 pages875542-QA-Combustion and FlameNikita RajNo ratings yet
- Group 5 Combustion EngineeringDocument21 pagesGroup 5 Combustion Engineeringirewen de laraNo ratings yet
- Note 1475054739Document10 pagesNote 1475054739Thiyaga RajanNo ratings yet
- 4 - Oxygen Is Needed For CombustionDocument14 pages4 - Oxygen Is Needed For CombustionmizwhiteNo ratings yet
- Combustion and Flame 8thDocument13 pagesCombustion and Flame 8thPratibha GuptaNo ratings yet
- Fuels and CombustionDocument24 pagesFuels and Combustionmukirir47No ratings yet
- Combustion: Combustion and Flames Class 8 Notes - Chapter 6Document14 pagesCombustion: Combustion and Flames Class 8 Notes - Chapter 6Prabal SinghNo ratings yet
- In - Situ CombustionDocument21 pagesIn - Situ Combustionحسين رامي كريم A 12No ratings yet
- Combustion and FlameDocument15 pagesCombustion and FlameArjunNo ratings yet
- ENGL 202c - CombustionDocument5 pagesENGL 202c - Combustionluckybuck7No ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY - COMBUSTION AND FLAME NOTES - Indumathi VenugopalDocument13 pagesCHEMISTRY - COMBUSTION AND FLAME NOTES - Indumathi VenugopalSanthosh 456No ratings yet
- Marvels of Scientific Invention An Interesting Account in Non-technical Language of the Invention of Guns, Torpedoes, Submarine Mines, Up-to-date Smelting, Freezing, Colour Photography, and many other recent Discoveries of ScienceFrom EverandMarvels of Scientific Invention An Interesting Account in Non-technical Language of the Invention of Guns, Torpedoes, Submarine Mines, Up-to-date Smelting, Freezing, Colour Photography, and many other recent Discoveries of ScienceNo ratings yet
- CNC Canned CyclesDocument1 pageCNC Canned CyclesAllan HarrisNo ratings yet
- BST 22741 Topic 10 Rendering - Plastering - Tiling - Paint 8.20 Doc TsDocument14 pagesBST 22741 Topic 10 Rendering - Plastering - Tiling - Paint 8.20 Doc TsaaaNo ratings yet
- Open End Wrench: Product Features ProfilesDocument3 pagesOpen End Wrench: Product Features ProfileskasanaNo ratings yet
- ConsumablesDocument28 pagesConsumablesadeoye_okunoyeNo ratings yet
- Annexure-I Specifications For Austenitic Stainless Steel 316L PlatesDocument1 pageAnnexure-I Specifications For Austenitic Stainless Steel 316L PlatesSharat ChandraNo ratings yet
- 51 Tectyl 846 K 19 (200612)Document2 pages51 Tectyl 846 K 19 (200612)windsurferke007No ratings yet
- MS and GI Pipes-Types, Features & ApplicationsDocument4 pagesMS and GI Pipes-Types, Features & ApplicationssureshkanuboyinaNo ratings yet
- Alloy 276 Spec SheetDocument3 pagesAlloy 276 Spec SheetermusatNo ratings yet
- Jiangsu Senolo Medical Technology Co., LTD.: NO.88 4 Road, Private Venture Park, Jianhu Contry JiangsuDocument2 pagesJiangsu Senolo Medical Technology Co., LTD.: NO.88 4 Road, Private Venture Park, Jianhu Contry JiangsuPedro Ant. Núñez UlloaNo ratings yet
- List Katalog Fire Hydrant (Box)Document3 pagesList Katalog Fire Hydrant (Box)Sales1 mpicaNo ratings yet
- SEC-I - Physics Workshop Skill Sample Questions With AnswersDocument20 pagesSEC-I - Physics Workshop Skill Sample Questions With AnswersMousam ChakraborttyNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Summer 2019Document4 pagesQuestion Paper Summer 2019pranav langdeNo ratings yet
- ABC Tile AdhesiveDocument1 pageABC Tile AdhesiveTeomnerCabreraNo ratings yet
- Astm A335 11Document10 pagesAstm A335 11Mily MundacaNo ratings yet
- List Kekurangan Isometric DrawingDocument8 pagesList Kekurangan Isometric DrawingIksan Adityo MulyoNo ratings yet
- Surfas HardeningDocument14 pagesSurfas HardeningBodo AmatNo ratings yet
- Ciranova Catalogus EDocument20 pagesCiranova Catalogus EJerzyNo ratings yet
- Amtech: LF-4300 Lead-Free Water Washable No-Clean Solder PasteDocument2 pagesAmtech: LF-4300 Lead-Free Water Washable No-Clean Solder PastebehzadNo ratings yet
- Project Department Kuwait National Petroleum Company: Daily Welding Inspection ReportDocument1 pageProject Department Kuwait National Petroleum Company: Daily Welding Inspection ReportMuthazhagan SaravananNo ratings yet
- X-Span & Setting ToolsDocument18 pagesX-Span & Setting ToolsDenier RubianoNo ratings yet
- Elements of Mechanical EngineeringDocument3 pagesElements of Mechanical EngineeringHarish Murthy60% (5)
- Influence of Friction Stir Welding Pin Probe Taper Angle On Tensile Properties in Aluminum Alloys 2024Document17 pagesInfluence of Friction Stir Welding Pin Probe Taper Angle On Tensile Properties in Aluminum Alloys 2024istyawan priyahapsaraNo ratings yet
- Engine PC LS160 LS170 1 EUDocument82 pagesEngine PC LS160 LS170 1 EUsassine khouryNo ratings yet
- DOICT - Technical SpecificationsDocument6 pagesDOICT - Technical Specificationsahmadmukit0No ratings yet