Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Financial Analysis Audit and Performance
Uploaded by
mileyhabbel0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views20 pagesOriginal Title
Financial-Analysis-Audit-and-Performance
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views20 pagesFinancial Analysis Audit and Performance
Uploaded by
mileyhabbelCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 20
Financial Analysis, Audit and
Performance
Chapter 6
David Campbell, David Edgar & George Stonehouse
Business Strategy: an introduction
Learning Objectives
• understand what is meant by financial analysis
• identify the sources of funds available to companies
and the relative advantages and disadvantages of
each
• understand the cost and non-cost issues involved in
raising and using various forms of capital
• understand the importance of the cost of capital
• understand the limitations of a company report and
accounts as a source of data for financial analysis
• describe the major tools that can be used to analyse
a company’s financial position
• explain the importance of audit and understand the
concept of social audit
David Campbell, David Edgar & George Stonehouse
Business Strategy: an introduction
Sources of Finance
Share capital has, A rights issue is when a
historically, comprised company issues new shares
the majority of capital to the stock market.
for a limited company’s
start-up and subsequent Retained profit, that
development. element of operating profit
not paid to shareholders
A placing involves the in the form of a dividend,
selling of shares directly to is the most common
a small number of investors, method of funding strategic
usually large financial developments.
institutions.
David Campbell, David Edgar & George Stonehouse
Business Strategy: an introduction
Gearing
Gearing is an indication of how the company has
arranged its capital structure
borrowed capital, that is, debt
total capital employed, that is,
borrowings plus shareholders’ capital
or as:
borrowed capital, that is, debt
shareholders’ capital, that is, equity.
David Campbell, David Edgar & George Stonehouse
Business Strategy: an introduction
Cost of Capital
The cost of capital can be viewed as the annual
amount payable (as a percentage) against the
principal amount of money.
Cost of share capital (equity) as a percentage =
(current net dividend per share divided by current
market price of share) × 100 + average percentage
annual growth rate.
David Campbell, David Edgar & George Stonehouse
Business Strategy: an introduction
Models of capital costing
The CAPM model
The Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM) is a more
complex but widely-used model used for this calculating
the cost of share capital.
Cost of share capital = Ri +(Rm-Ri)
The WACC model
Weighted Average Cost of Capital (WACC) can be
used to determine the overall cost of funding to a
company.
WACC = (proportion of loan finance x cost of loan
finance) + (proportion of shareholders' funds x cost of
shareholders' funds)
David Campbell, David Edgar & George Stonehouse
Business Strategy: an introduction
Financial Analysis and
Performance Evaluation
There are three areas of financial analysis and
these are:
1.longitudinal analysis (sometimes called trend
analysis);
2.cross-sectional analysis (or comparison
analysis);
3.ratio analysis.
David Campbell, David Edgar & George Stonehouse
Business Strategy: an introduction
Longitudinal Analysis
The simplest means of assessing
any aspect of a company's finances
is to compare the data for two or
more years and see what has
increased and what has decreased
over that time period, and by how
much.
David Campbell, David Edgar & George Stonehouse
Business Strategy: an introduction
Cross Sectional Analysis
It is for the purposes of
comparisons of this nature that
cross-sectional analyses are
important. As well as comparing
accounting numbers like
turnover, it is often helpful to
compare two or more
companies’ ratios.
David Campbell, David Edgar & George Stonehouse
Business Strategy: an introduction
Ratio Analysis
For most purposes, we can divide
ratios into five broad categories:
1. Performance ratios
2. Efficiency ratios
3. Liquidity ratios
4. Investors' ratios
5. Financial structure ratios
David Campbell, David Edgar & George Stonehouse
Business Strategy: an introduction
Ratios: Performance
David Campbell, David Edgar & George Stonehouse
Business Strategy: an introduction
Ratios: Efficiency
David Campbell, David Edgar & George Stonehouse
Business Strategy: an introduction
Ratios: Liquidity
• Quick Ratio / Acid Test Ratio
• Cash Ratio
• Current Ratio
David Campbell, David Edgar & George Stonehouse
Business Strategy: an introduction
Ratios: Investment
David Campbell, David Edgar & George Stonehouse
Business Strategy: an introduction
Ratios: Financial Structure
David Campbell, David Edgar & George Stonehouse
Business Strategy: an introduction
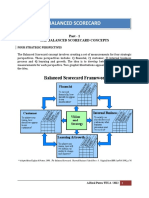
Balanced Scorecard
The balanced scorecard
is a management tool for
managers to ‘balance’ ■ Financial indicators: financial results
the various indicators of ■ Behaviour and loyalty of customers:
success (or ‘perspectives’) customers are an indication of how
for a given business. sustainable, in financial terms, a given
financial performance is
■ Internal business processes: these are
vital because they indicate the ‘health’ of
the business and its long-term viability
■ Learning and growth: the ability of the
business to learn and grow helps to
measure the longer term prospects in
terms of innovation, creativity and
entrepreneurship.
David Campbell, David Edgar & George Stonehouse
Business Strategy: an introduction
Other Tools
• Financial benchmarking
• Common size accounts
David Campbell, David Edgar & George Stonehouse
Business Strategy: an introduction
Audit and Social Audit
David Campbell, David Edgar & George Stonehouse
Business Strategy: an introduction
Reading
Allen, D. (1997) An Introduction to Strategic Financial Management.
London: CIMA/Kogan Page.
Department of Trade & Industry 1992. Best Practice Benchmarking.
London: DTI.
Camp, R.C. (1994). Business Process Benchmarking. ASQC
Quality Press.
Ellis, J. and Williams, D. (1993) Corporate Strategy & Financial
Analysis. London: Pitman Publishing.
Franks, J.R. and Broyles, J.E. (1979). Modern Managerial Finance.
Chichester: John Wiley
Higson, C. (1995) Business Finance. Oxford: Butterworth-
Heinemann
Mott, G. (1991). Management Accounting for Decision Makers.
London: Pitman Publishing.
David Campbell, David Edgar & George Stonehouse
Business Strategy: an introduction
Review Questions
1. Explain what we mean by a financial analysis
2. Explain what the limitations are of a company report when
used for financial analysis.
3. Evaluate the alternative options for funding a company’s
developments based on current position, future prospects
and past performance.
4. Describe the main tools used to analyse a company’s
financial position.
ANSWER THE QUESTIONS ABOVE IN
NOT LESS THAN 200 WORDS EACH QUESTION
David Campbell, David Edgar & George Stonehouse
Business Strategy: an introduction
You might also like
- Equity Research Report - Sun Pharma 2023Document8 pagesEquity Research Report - Sun Pharma 2023Dikshant Dahivaley100% (1)
- Finance Team As Business PartnerDocument78 pagesFinance Team As Business PartnerTubagus Donny SyafardanNo ratings yet
- Sales Compensation: Establishing Design PrinciplesDocument26 pagesSales Compensation: Establishing Design Principlessmoothy_14100% (1)
- MCP FinalDocument26 pagesMCP FinalSushma ChandraShekarNo ratings yet
- Finance Team As Business PartnerDocument78 pagesFinance Team As Business PartnerTubagus Donny SyafardanNo ratings yet
- Prospective Analysis Theory and ConceptDocument32 pagesProspective Analysis Theory and ConceptEster Sabatini100% (1)
- Financial Analysis, Audit and Performance: David Campbell, David Edgar & George StonehouseDocument20 pagesFinancial Analysis, Audit and Performance: David Campbell, David Edgar & George StonehouseRabiya MalikNo ratings yet
- Financial Analysis, Audit and Performance: David Campbell, David Edgar & George StonehouseDocument20 pagesFinancial Analysis, Audit and Performance: David Campbell, David Edgar & George StonehouseRabiya MalikNo ratings yet
- ACF 361 Chapter 1 To 3Document148 pagesACF 361 Chapter 1 To 3edithyemehNo ratings yet
- Buku Bab 1.1Document15 pagesBuku Bab 1.1Theresa EditNo ratings yet
- ICAI Corporate ValuationDocument47 pagesICAI Corporate Valuationqamaraleem1_25038318No ratings yet
- SM CH - 2Document23 pagesSM CH - 2Thë FähãdNo ratings yet
- Name: Olatunde Jackson Adeoye: Student Number:31002792Document8 pagesName: Olatunde Jackson Adeoye: Student Number:31002792Adeoye JacksonNo ratings yet
- New-Venture ValuationDocument7 pagesNew-Venture ValuationBurhan Al MessiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document25 pagesChapter 6HM.No ratings yet
- @@@valuation 5-15-2021Document39 pages@@@valuation 5-15-2021Mark LesterNo ratings yet
- Chp.1 OVERVIEW OF FINANCIAL STATEMENT ANALYSISDocument28 pagesChp.1 OVERVIEW OF FINANCIAL STATEMENT ANALYSIS6042001147No ratings yet
- Final PPT Team 3Document118 pagesFinal PPT Team 3Arushi GuptaNo ratings yet
- Fiche Cours - Strategic Management: Chapter 1 - The Concept of StrategyDocument42 pagesFiche Cours - Strategic Management: Chapter 1 - The Concept of StrategyMaxime MassonNo ratings yet
- Business Plan Intro To OrgDocument33 pagesBusiness Plan Intro To Orgrjcabuyadao97No ratings yet
- FinancialPerformaceTools April 2020Document7 pagesFinancialPerformaceTools April 2020Jason RecanaNo ratings yet
- Invesment Banking Fundamentals.Document275 pagesInvesment Banking Fundamentals.Nitin GuptaNo ratings yet
- Letter To Shareholders Assignment Details: From The Text That Apply To All Areas of This LetterDocument5 pagesLetter To Shareholders Assignment Details: From The Text That Apply To All Areas of This LetterSonali SahooNo ratings yet
- Entrep Business PlanningDocument20 pagesEntrep Business PlanningLetecia SimeonNo ratings yet
- CH 12Document60 pagesCH 12Vansh manojNo ratings yet
- Week 4 Learning Team Reflection PaperDocument5 pagesWeek 4 Learning Team Reflection PaperCisco CarbajalNo ratings yet
- 10 BSC ConceptDocument34 pages10 BSC ConceptindahNo ratings yet
- Financial Analysis GuideDocument6 pagesFinancial Analysis GuideRomelyn Joy JangaoNo ratings yet
- Five Stages of Strategic Management Process.Document3 pagesFive Stages of Strategic Management Process.Nurul HawaNo ratings yet
- Financial Modeling By: CA Tapan Kumar DasDocument16 pagesFinancial Modeling By: CA Tapan Kumar DasLAMOUCHI RIMNo ratings yet
- Writing A Business Plan: How To Win Backing To Start Up or Grow Your Business (Bahasa Indonesia)Document79 pagesWriting A Business Plan: How To Win Backing To Start Up or Grow Your Business (Bahasa Indonesia)MiraNo ratings yet
- Strategic Financial Management-Balanced Score Card: Assignment-2Document19 pagesStrategic Financial Management-Balanced Score Card: Assignment-2jhafjfNo ratings yet
- IGNOU MBA MS04 Solved Assignments Dec 2012Document10 pagesIGNOU MBA MS04 Solved Assignments Dec 2012Amit DungdungNo ratings yet
- Corporatre ValuationDocument46 pagesCorporatre ValuationVipin MehtaNo ratings yet
- Faca ShristiDocument11 pagesFaca Shristishristi BaglaNo ratings yet
- Financial MNGT Chapter IDocument33 pagesFinancial MNGT Chapter ICjhay MarcosNo ratings yet
- 2007 01Document16 pages2007 01GeetanjaliRVijayaNo ratings yet
- BS Report IA2Document23 pagesBS Report IA2Shreyas JoshiNo ratings yet
- Cases in Finance Assignment FinalDocument22 pagesCases in Finance Assignment FinalIbrahimNo ratings yet
- Value Added Metrics: A Group 3 PresentationDocument43 pagesValue Added Metrics: A Group 3 PresentationJeson MalinaoNo ratings yet
- Overview of Financial ManagementDocument26 pagesOverview of Financial ManagementAnthony DyNo ratings yet
- Financial Evaluation Report With SampleDocument12 pagesFinancial Evaluation Report With SamplemaidangphapNo ratings yet
- 2002 MeasuringthemoatDocument52 pages2002 MeasuringthemoatPhilNo ratings yet
- CH02Document19 pagesCH02Min WilsNo ratings yet
- Niven Balanced Scorecard PresentationDocument40 pagesNiven Balanced Scorecard PresentationBranimir Stefanov100% (1)
- IBA101 ActivityDocument12 pagesIBA101 ActivityJAN PAOLO LUMPAZNo ratings yet
- Capital FormationDocument13 pagesCapital FormationqamarulislamNo ratings yet
- InterpretationonFinancialStatementsByMr V AnojanDocument30 pagesInterpretationonFinancialStatementsByMr V AnojankhinthetzunNo ratings yet
- BUS 800 Supplemental Chapter F 2015, W 2016Document16 pagesBUS 800 Supplemental Chapter F 2015, W 2016Charlie XiangNo ratings yet
- Roland Berger TAB The Winners 20140709Document24 pagesRoland Berger TAB The Winners 20140709Anuj PandeyNo ratings yet
- Entrep 2nd QTR Lecture NotesDocument10 pagesEntrep 2nd QTR Lecture NoteskryssmegannnnnNo ratings yet
- BSBMGT617 Task 5Document3 pagesBSBMGT617 Task 5jot jotNo ratings yet
- Financial Measures To Measure Corporate PerformanceDocument21 pagesFinancial Measures To Measure Corporate PerformanceArushi GuptaNo ratings yet
- Financial Statement Analysis, Balance Sheet, Income Statement, Retained Earnings StatementDocument57 pagesFinancial Statement Analysis, Balance Sheet, Income Statement, Retained Earnings StatementMara LacsamanaNo ratings yet
- Finance Compendium PartI DMS IIT DelhiDocument29 pagesFinance Compendium PartI DMS IIT Delhinikhilkp9718No ratings yet
- Lecture 1-2 CF UMT Spring 2020Document32 pagesLecture 1-2 CF UMT Spring 2020ASAD ULLAHNo ratings yet
- Economic Value Added EVADocument7 pagesEconomic Value Added EVAvishal_patel2088No ratings yet
- Keys For An Effective Business Plan: Business Planning Workshop September 27, 2006Document61 pagesKeys For An Effective Business Plan: Business Planning Workshop September 27, 2006Tan Tok HoiNo ratings yet
- 561 (FIN) - CF Kazi MD. Muhaiminul IslamDocument67 pages561 (FIN) - CF Kazi MD. Muhaiminul IslamMuhaiminul IslamNo ratings yet
- What Makes A New Business Start-Up Successful?: ArticleDocument19 pagesWhat Makes A New Business Start-Up Successful?: ArticleGavi NnamdiNo ratings yet
- Business Plan Alchemy: Transforming Ideas Into Successful Business VenturesFrom EverandBusiness Plan Alchemy: Transforming Ideas Into Successful Business VenturesNo ratings yet
- Finance Report 2022Document191 pagesFinance Report 2022Cam TuNo ratings yet
- Carta AccountDocument1 pageCarta Accountzhenxian lohNo ratings yet
- 2017 Al Accounting Marking Scheme Sinhala Medium Alevelapi. Com PDFDocument25 pages2017 Al Accounting Marking Scheme Sinhala Medium Alevelapi. Com PDFIma LiyanageNo ratings yet
- Dig 011179Document8 pagesDig 011179WHRNo ratings yet
- Exercicios Do Capitulo 6 (Finanças Empresariais)Document2 pagesExercicios Do Capitulo 6 (Finanças Empresariais)Gonçalo AlmeidaNo ratings yet
- Capital Structure Theories VivaDocument43 pagesCapital Structure Theories VivaPuttu Guru PrasadNo ratings yet
- YNH Ar2023Document174 pagesYNH Ar2023Hew Jhet NungNo ratings yet
- e-StatementBRImo 365101028091534 Jul2023 20230719 170434-1Document6 pagese-StatementBRImo 365101028091534 Jul2023 20230719 170434-1Nyonya OvieNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document62 pagesLecture 4Liyazhi LiuNo ratings yet
- Tally Practical Examinaion Paper 2018 22 Nov 2018final 4 SetsDocument9 pagesTally Practical Examinaion Paper 2018 22 Nov 2018final 4 SetsAbhyudai Pratap SinghNo ratings yet
- Nach FormatDocument1 pageNach FormatArun MotorsNo ratings yet
- ACC106 P2 Quiz 1 Questions Set A KDocument2 pagesACC106 P2 Quiz 1 Questions Set A KShane QuintoNo ratings yet
- Download pdf Investment Analysis And Portfolio Management 11Th Edition Frank K Reilly ebook full chapterDocument53 pagesDownload pdf Investment Analysis And Portfolio Management 11Th Edition Frank K Reilly ebook full chaptermargaret.redd792100% (1)
- File 11Document1 pageFile 11Anubhav DobhalNo ratings yet
- ABM1compilation NotesDocument9 pagesABM1compilation NotesMa Geneva Metille BroñolaNo ratings yet
- Cost of Acquisition Under Section 49 (2C)Document2 pagesCost of Acquisition Under Section 49 (2C)CA. Rajesh GujarathiNo ratings yet
- Koyas PerfumeryDocument2 pagesKoyas PerfumeryTANUJ CHAKRABORTYNo ratings yet
- Soc Wef 311017Document18 pagesSoc Wef 311017sohel311094No ratings yet
- FM II - Chapter 03, Financial Planning & ForecastingDocument14 pagesFM II - Chapter 03, Financial Planning & ForecastingHace AdisNo ratings yet
- P5 8Document4 pagesP5 8laurentinus fikaNo ratings yet
- Ias 1 SummaryDocument11 pagesIas 1 Summarynur iman qurrataini abdul rahmanNo ratings yet
- Milestone 2 - Prompt 2Document12 pagesMilestone 2 - Prompt 2Peter PapelNo ratings yet
- M Arkan Hafidz - 2602297301 - Assignment Week 2Document6 pagesM Arkan Hafidz - 2602297301 - Assignment Week 2Arkan HafidzNo ratings yet
- BF ADM Module 1 Q1 WK 1 To 5 Introduction To Financial Management AutosavedDocument48 pagesBF ADM Module 1 Q1 WK 1 To 5 Introduction To Financial Management AutosavedCharlan Amansec IIINo ratings yet
- Financial Management PDFDocument7 pagesFinancial Management PDFdishu kumarNo ratings yet
- Lab Assisst InstructionsDocument7 pagesLab Assisst InstructionsOlumideNo ratings yet
- 16 Consolidation Subsequent To The Date of AcquisitionDocument3 pages16 Consolidation Subsequent To The Date of AcquisitionMila Casandra CastañedaNo ratings yet
- Igcse May 2023 1 QPDocument20 pagesIgcse May 2023 1 QPtroyrodrigues36No ratings yet
- Maf253 Q Dec 2019Document12 pagesMaf253 Q Dec 2019alisatasnimNo ratings yet