Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Trends, Network-WPS Office
Trends, Network-WPS Office
Uploaded by
nifrashyline0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views10 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views10 pagesTrends, Network-WPS Office
Trends, Network-WPS Office
Uploaded by
nifrashylineCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 10
Trends, Networks and Critical
Thinking in the 21st Century
Quarter 4 – Module 6:
Parallelism between Neural
and Social Networks
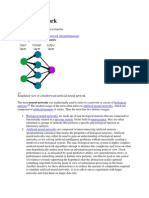
NEURAL NETWORK
Neural networks referred to as connectionist
systems (Garson, 2018) are a computational
approach, which is based on a large collection
of neural units (AKA artificial neurons), loosely
modeling how the brain of a human solves
problems with a large cluster of biological
neurons connected by axons (Garson, 2018).
Dynamic neural networks are the
most advanced in that they
dynamically can, based on rules,
form new connections and even new
neural units while disabling others.
Each neural unit is linked with many
others, and links can be enforcing or
Inhibitory in their effect on the
activation state of connected neural
units. Each Individual neural unit
may have a summation function
which combines the values of all its
inputs together
The goal of the neural network is to solve
problems in the same way that the human
brain would, although several neural
networks are more abstract. Modern neural
network projects typically work with a few
thousand to a few million neural units and
millions of connections, which is still several
orders magnitudeless complex than the
human brain and closer to the computing
power of a worm
SOCIAL NETWORK
A social network is a social structure
made up of a set of social actors (such as
individuals or organizations),sets of
dyadic ties, and other social interactions
between actors. The social network
perspective provides a set of methods for
analyzing the structure of whole social
entities as well as a variety of theories
explaining the patterns observed in these
structures.
Social networks and the analysis of
them is an inherently
interdisciplinary academic field
which emerged from social
psychology, sociology, statistics, and
graph theory. Georg Simmel
authored early structural theories in
sociology emphasizing the dynamics
of triads and "web of group
affiliations".
Social network analysis is now one
of the major paradigms in
contemporary sociology, and is also
employed in a number of other
social and formal sciences. Together
with other complex networks, it
forms part of the nascent field of
network science.
Thank you for listening !!
You might also like
- WK 6 Neural and Social NetworksDocument12 pagesWK 6 Neural and Social NetworksMARY LORD GERALDINE VELASCO100% (1)
- Trends, Network and Critical Thinking in The 21st CenturyDocument6 pagesTrends, Network and Critical Thinking in The 21st CenturyGyle Contawe Garcia83% (12)
- Neural NetworkDocument16 pagesNeural NetworkOlayiwola OpoosunNo ratings yet
- PLANT, S. - The Virtual Complexity of CultureDocument14 pagesPLANT, S. - The Virtual Complexity of CultureIsabel ÁvilaNo ratings yet
- The evolution of Soft Computing - From neural networks to cellular automataFrom EverandThe evolution of Soft Computing - From neural networks to cellular automataRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Article On Neural NetworksDocument5 pagesArticle On Neural NetworksSaad ZahidNo ratings yet
- Putational Neuroscience - HandbookDocument26 pagesPutational Neuroscience - Handbookdetki007No ratings yet
- Neuroscience-Inspired Artificial IntelligenceDocument15 pagesNeuroscience-Inspired Artificial IntelligenceGOGUNo ratings yet
- Neural Network: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument9 pagesNeural Network: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaLeonardo Kusuma PNo ratings yet
- Q3 Module 6Document3 pagesQ3 Module 6Alex Abonales DumandanNo ratings yet
- TechnologyDocument2 pagesTechnologyGwyneth GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Neural: Social NetworksDocument2 pagesNeural: Social NetworksEhna VillarealNo ratings yet
- The Human Connectome A Complex NetworkDocument17 pagesThe Human Connectome A Complex NetworkAnirban NathNo ratings yet
- On Neural Networks and Application: Submitted By: Makrand Ballal Reg No. 1025929 Mca 3 SemDocument14 pagesOn Neural Networks and Application: Submitted By: Makrand Ballal Reg No. 1025929 Mca 3 Semmakku_ballalNo ratings yet
- Q4 W5 6 TrendsDocument5 pagesQ4 W5 6 Trendsann kathrina mariz velascoNo ratings yet
- 1.2a From Cognitivism To ConnectionismDocument14 pages1.2a From Cognitivism To ConnectionismnumeletrandafiruluiNo ratings yet
- Soft Computing: IntroductionDocument24 pagesSoft Computing: IntroductionPriyank ..No ratings yet
- Connectionism theory-WPS OfficeDocument2 pagesConnectionism theory-WPS Officeblessy blessyNo ratings yet
- Trends Neural NetworksDocument3 pagesTrends Neural Networksfrancine100% (3)
- Neural and Social NetworksDocument6 pagesNeural and Social NetworksVincent Miles SustiguerNo ratings yet
- Neural and SocjfjdkgharfkgysiDocument12 pagesNeural and SocjfjdkgharfkgysiNiel Beronia VargasNo ratings yet
- Neural Systems and Artificial Life Group, Institute of Psychology, National Research Council, RomeDocument34 pagesNeural Systems and Artificial Life Group, Institute of Psychology, National Research Council, RomeKunwar Mahipal Singh KheecheeNo ratings yet
- Neural NetworkDocument20 pagesNeural NetworkNuhamin AsratNo ratings yet
- The Official Journal of The International Neural Network Society, European Neural Network Society and Japanese Neural Network SocietyDocument10 pagesThe Official Journal of The International Neural Network Society, European Neural Network Society and Japanese Neural Network SocietyQoernhea BachtiarNo ratings yet
- 1.2b From Cognitivism To Connectionism - TextDocument5 pages1.2b From Cognitivism To Connectionism - TextnumeletrandafiruluiNo ratings yet
- Artificial Neural Network: 1 BackgroundDocument13 pagesArtificial Neural Network: 1 Backgroundyua_ntNo ratings yet
- Neuroscience of Psychoanalytic Object Relations Theory MineDocument59 pagesNeuroscience of Psychoanalytic Object Relations Theory MineTatjana Jočić VelimirovićNo ratings yet
- Understanding Complexity in The Human Brain: Danielle S. Bassett and Michael S. GazzanigaDocument10 pagesUnderstanding Complexity in The Human Brain: Danielle S. Bassett and Michael S. Gazzanigaquico21No ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Conventional Network Theory: Nodes. in This Chapter, I Shall Discuss The Origins and Development of ThisDocument16 pagesChapter 5 - Conventional Network Theory: Nodes. in This Chapter, I Shall Discuss The Origins and Development of ThisSasi KumarNo ratings yet
- A Brief History of ConnectionismDocument42 pagesA Brief History of Connectionismpaula d´alessandroNo ratings yet
- Hybrid Neural Networks: Fundamentals and Applications for Interacting Biological Neural Networks with Artificial Neuronal ModelsFrom EverandHybrid Neural Networks: Fundamentals and Applications for Interacting Biological Neural Networks with Artificial Neuronal ModelsNo ratings yet
- 2018 OPMBM Swarm NetworkDocument11 pages2018 OPMBM Swarm NetworkCarlos AdrianoNo ratings yet
- Neural Networks: An Overview of Early Research, Current Frameworks and New ChallengesDocument27 pagesNeural Networks: An Overview of Early Research, Current Frameworks and New ChallengesArmin AminiNo ratings yet
- Polyakov - Arpsychology and Structured Design of Artificial Intelligent SystemsDocument369 pagesPolyakov - Arpsychology and Structured Design of Artificial Intelligent SystemsViktoria LukàcsNo ratings yet
- 2Document7 pages2Rt GyNo ratings yet
- CMC Group-3 3104 Network-TheoryDocument27 pagesCMC Group-3 3104 Network-TheoryAbigael D. RiveraNo ratings yet
- An Artificial Neural Networ1Document1 pageAn Artificial Neural Networ1Manoj SreeramNo ratings yet
- Final Trends Module 5Document4 pagesFinal Trends Module 5Jan russel PenafielNo ratings yet
- Network Neuroscience and PersonalityDocument14 pagesNetwork Neuroscience and PersonalityPaula Manalo-SuliguinNo ratings yet
- The Brain of Prof. Le CunDocument16 pagesThe Brain of Prof. Le CunjmchauvetNo ratings yet
- TKilic A Brain Inspired View of LifeDocument6 pagesTKilic A Brain Inspired View of LifedrqubitNo ratings yet
- Artificial Neural NetworksDocument3 pagesArtificial Neural NetworksSpockDataNo ratings yet
- A Critical Appraisal On Deep Neural NetworkDocument23 pagesA Critical Appraisal On Deep Neural NetworkGabriel DAnnunzioNo ratings yet
- Reviews: Richard R. SHIVELY, Book Reviews EditorDocument2 pagesReviews: Richard R. SHIVELY, Book Reviews EditorSaad FaruquiNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence in The Context of Noosphere StudiesDocument7 pagesArtificial Intelligence in The Context of Noosphere StudiesΜακης ΣακεταςNo ratings yet
- 2017 - Network NeuroscienceDocument12 pages2017 - Network NeuroscienceMaria Eugenia Amaya ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Critical EmergentDocument10 pagesCritical EmergentIgor FernandesNo ratings yet
- Defining Artificial Neural NetworksDocument3 pagesDefining Artificial Neural NetworksAkash PayunNo ratings yet
- Defining Artificial Neural NetworksDocument3 pagesDefining Artificial Neural NetworksAkash PayunNo ratings yet
- Defining Artificial Neural NetworksDocument3 pagesDefining Artificial Neural NetworksAkash PayunNo ratings yet
- Defining Artificial Neural NetworksDocument3 pagesDefining Artificial Neural NetworksAkash PayunNo ratings yet
- Handouts TNCTDocument1 pageHandouts TNCTJohn CedrickNo ratings yet
- Neural Network Research PaperDocument8 pagesNeural Network Research PaperKen CookNo ratings yet
- Consciousness - What Is Consciousness - (2005)Document6 pagesConsciousness - What Is Consciousness - (2005)P. R. SREENIVASANNo ratings yet
- Plos One 2012 DumasDocument11 pagesPlos One 2012 DumasGuillaume DumasNo ratings yet
- Human Connectome 2013Document9 pagesHuman Connectome 2013GsNo ratings yet
- Elephants Dont Play ChessDocument12 pagesElephants Dont Play ChessAmit ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Elephants Don't Play ChessDocument12 pagesElephants Don't Play ChessringpieceNo ratings yet
- 2019 - The Cortical Conductor Theory Towards Addressing Consciousness in Ai ModelsDocument11 pages2019 - The Cortical Conductor Theory Towards Addressing Consciousness in Ai Modelsvincent.wienerroither1287No ratings yet