0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views15 pagesSkin Disorders
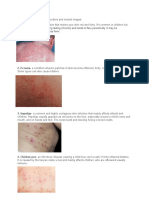
The document provides an overview of various skin disorders, including acne, alopecia areata, and psoriasis, detailing their causes, prevention, and treatment options. It highlights that many conditions are autoimmune or genetic in nature, with no definitive cures available. Preventative measures and treatments vary by condition, often focusing on symptom management and skin care.
Uploaded by
minghuichen4296Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views15 pagesSkin Disorders
The document provides an overview of various skin disorders, including acne, alopecia areata, and psoriasis, detailing their causes, prevention, and treatment options. It highlights that many conditions are autoimmune or genetic in nature, with no definitive cures available. Preventative measures and treatments vary by condition, often focusing on symptom management and skin care.
Uploaded by
minghuichen4296Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd