0% found this document useful (0 votes)
54 views79 pagesModule 3
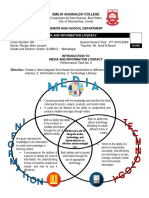
Module 3 focuses on integrating non-digital and digital skills in technology-enhanced lessons, emphasizing the development and use of instructional materials and ICT tools for teaching. It covers various instructional materials, the use of digital tools like QR codes and infographics, and the creation of ePortfolios to document learning. Additionally, it highlights the importance of collaborative tools in education and the evolving definition of digital literacy in the 21st century.
Uploaded by
glaydieescudero.knpCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
54 views79 pagesModule 3
Module 3 focuses on integrating non-digital and digital skills in technology-enhanced lessons, emphasizing the development and use of instructional materials and ICT tools for teaching. It covers various instructional materials, the use of digital tools like QR codes and infographics, and the creation of ePortfolios to document learning. Additionally, it highlights the importance of collaborative tools in education and the evolving definition of digital literacy in the 21st century.
Uploaded by
glaydieescudero.knpCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd