0% found this document useful (0 votes)
37 views11 pagesPopulation Balance Model.
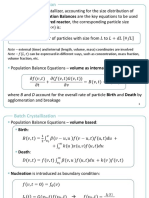
Population Balance Modelling (PB Modelling) is crucial for understanding how particles interact with their environment in various fields, including chemical engineering and biophysics. It involves analyzing the behavior of particle populations based on their internal and external coordinates, as well as processes such as birth and death of particles. Applications in chemical engineering include modeling crystallizers, gas-solid dispersions, and bioreactors, among others.
Uploaded by
godricgryffindorseekerCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
37 views11 pagesPopulation Balance Model.
Population Balance Modelling (PB Modelling) is crucial for understanding how particles interact with their environment in various fields, including chemical engineering and biophysics. It involves analyzing the behavior of particle populations based on their internal and external coordinates, as well as processes such as birth and death of particles. Applications in chemical engineering include modeling crystallizers, gas-solid dispersions, and bioreactors, among others.
Uploaded by
godricgryffindorseekerCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd