0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views40 pages01 Introduction
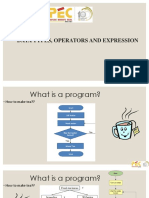
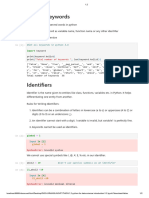
This document serves as an introduction to Python programming, covering essential topics such as syntax, data types, and programming concepts. It outlines learning outcomes, key terms, and the importance of understanding programming languages and their elements. Additionally, it provides guidance on writing, saving, and running Python scripts, as well as handling errors in programs.
Uploaded by
timothythamboonkeatCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views40 pages01 Introduction
This document serves as an introduction to Python programming, covering essential topics such as syntax, data types, and programming concepts. It outlines learning outcomes, key terms, and the importance of understanding programming languages and their elements. Additionally, it provides guidance on writing, saving, and running Python scripts, as well as handling errors in programs.
Uploaded by
timothythamboonkeatCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 40