0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views23 pagesChapter 8-Lecture 2
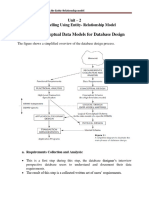
Chapter 8 discusses the essential aspects of database design, including conceptual, logical, and physical design phases. It emphasizes the importance of data modeling, DBMS software selection, security, backup and recovery, and ongoing maintenance. The chapter also highlights the need for performance monitoring and adherence to company standards throughout the database lifecycle.
Uploaded by
timothythamboonkeatCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views23 pagesChapter 8-Lecture 2
Chapter 8 discusses the essential aspects of database design, including conceptual, logical, and physical design phases. It emphasizes the importance of data modeling, DBMS software selection, security, backup and recovery, and ongoing maintenance. The chapter also highlights the need for performance monitoring and adherence to company standards throughout the database lifecycle.
Uploaded by
timothythamboonkeatCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 23