0% found this document useful (0 votes)
189 views10 pagesFuzzy Data Analysis
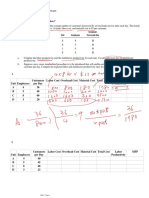
Fuzzy data analysis utilizes fuzzy set theory to interpret imprecise and uncertain data, allowing for partial membership rather than strict binary classifications. The process involves data collection, defining fuzzy sets, fuzzification, and aggregation to derive insights, making it applicable in decision-making, pattern recognition, control systems, and forecasting. This approach effectively handles uncertainty and mimics human reasoning in decision-making processes.
Uploaded by
issa sawagedCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
189 views10 pagesFuzzy Data Analysis
Fuzzy data analysis utilizes fuzzy set theory to interpret imprecise and uncertain data, allowing for partial membership rather than strict binary classifications. The process involves data collection, defining fuzzy sets, fuzzification, and aggregation to derive insights, making it applicable in decision-making, pattern recognition, control systems, and forecasting. This approach effectively handles uncertainty and mimics human reasoning in decision-making processes.
Uploaded by
issa sawagedCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd