Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Level 1 New Headway Whole Book Review Teacher Notes
Uploaded by
Oum El GhoulCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Level 1 New Headway Whole Book Review Teacher Notes
Uploaded by
Oum El GhoulCopyright:
Available Formats
xA. About ones self Have students briefly write about themselves.
Then ask them questions about their text using the following below:
Subject noun/ pronoun + verb to be Question: Positive Am I? I am/ Im Are you? You are/ Youre Is he? He is/ Hes Is she? She is / Shes Is it? It is / Its Are we? We are/Were Are they? They are/ Theyre Negative I am not/ Im not You are not/ You arent He is not/ He isnt She is not / She isnt It is not / Is isnt We are not/ we arent They are not/ They arent
Then ask students in a telephone conversation to spell their name, email etc.
B. Basic Grammar: Parts of Speech
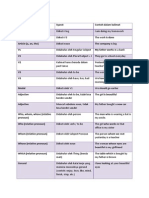
Noun Person, place, object, idea or concept (can be singular or plural) Countable Nouns Nouns are that able to counted simply Uncountable Nouns Nouns that are not able to be counted easily. Usually expressed in groups or type. Possessive Nouns used to show ownership Pronoun replaces the noun in a text Verb describes something about the subject of the text Adverb describes verbs. Makes writing more interesting Adjective modifies a noun or pronoun by describing, identifying, quantifying the noun Preposition shows the space, time, or logical relationship of its object to the rest of the nouns, pronouns and other phrases to other words in the sentence Conjunction links words, phrases or clauses together Articles, Determiners and Quantifiers little words that precede and modify nouns Go over the parts of speech. Each student to give 2 examples for each For the plural form of most nouns, add s. For nouns that end with ch, x, s or s sounds, add es. For nouns, ending in f or fe, change the f to v and add es. Some nouns have different plural forms. Nounds ending in vowels like y or o do not have definite rules. A few nouns have the same singular and plural forms. Noun Examples: bottle bottles cup cups pen pens desk desks girl girls boy boys sheep sheep deer deer baby- babies child- children man men knife- knives wife wives Possessive nouns usually are formed by adding an apostrophes but when a noun is plural just add an Ex: Johns book, Sarahs pen, Karims bike Ex: The students books, My parents house, The girls dolls, David and Sues wedding Pronouns chart
Singular Subject First Second Third Male I you he Singular Object me you him Singular Reflexive myself yourself himself Plural Subject we you they Plural Object us you them Plural Reflexive ourselves yourselves themselves
Third Female she Third Neutral it
her it
herself itself
they they
them them
themselves themselves
Regular and Irregular Verbs: The only real difference between regular and irregular verbs
is that they have different endings for their past tense and past participle forms. For regular verbs, the past tense ending and past participle ending is always the same: -ed. For irregular verbs, the past tense ending and the past participle ending is variable, so it is necessary to learn them by heart. There are approximately 180 irregular verbs. You don't need to learn all of them because some of these are very rare but many others are very useful and you do need to know them. Simple to be verb
Present Positive I am You are He is She is It was We are You are They were Negative I am not You are not (aren't) He is not (isn't) She is not (isn't) It was not (wasn't) We are not (aren't) You are not (aren't) They were not (weren't) Interrogative Am I? Are you? Is he? Is she? Was it? Are we? Are you? Were they?
Action verbs: Most common verb, usually express an action singular or 3rd person text pos or neg form Ex: He eats bread/ He does not bread; She walks to school/ She does not walk to school Adjectives: I like fairy tales. A fairy tale is an imaginary story that has unrealistic characters in a fantastic background. It makes me forget about the realworld and refreshes my tired mind. Conjuctions joins other words, phrases, clauses or sentences. Some conjunctions
are: and, as, because, but, or, neither/nor, for, since, so, until, yet, and while.
Prepositions After flying for many hours, we finally got off the airpla
After flying for many hours, we finally got off the airplane. We walked out the exit and went to the baggage claim area. There were hundreds ofdifferent bags on the conveyer belt. I almost picked up the wrong one because it looked like mine.
Common Contractions: shortened form of text
BE I I'm
WILL I'll
WOULD I'd
HAVE I've
HAD I'd
I am you he she it we they you're you are he's he is she's she is it's (or 'tis) it is we're we are they're they are
I will you'll you will he'll he will she'll she will it'll it will we'll we will they'll they will
I would you'd you would he'd he would she'd she would it'd it would we'd we would they'd they would
I have you've you have he's he has she's she has it's it has we've we have they've they have
I had you'd you had he'd he had she'd she had it'd it had we'd we had
they'd they had
Simple Tense- verb tenses tell you when the action happens. There are 3 main tenses, past, present and future.
Simple Present Past Future finish finished will finish Progressive am/is/are finishing was/were finishing will be finishing Perfect have/has finished had finished will have finished Perfect Progressive have/has been finishing had been finishing will have been finishing
J. Days of the week:
What is the day and time now? What days do you go to English class? Do you eat in restaurants? What do you do on Fridays? e) What are you like to do in your free time/weekend? f) When do you usually wake up in the morning? g) When do you usually eat lunch? Now answer these questions: If you like sunshine, what is the best time of year to visit Vancouver? If you like snow, what is the best time of year to visit Vancouver? What activities can you do outside? What activities can you do inside? Which activities can you do both inside and outside? When would you like to visit Vancouver? What would you do in Vancouver? a) b) c) d)
You might also like
- Daily Points Allowance Checklist: Staying Within LimitsDocument5 pagesDaily Points Allowance Checklist: Staying Within LimitsOum El Ghoul50% (2)
- Smart Foods Guide for Weight Loss & NutritionDocument1 pageSmart Foods Guide for Weight Loss & NutritionOum El Ghoul100% (3)
- Adverbs of Frequency in EnglishDocument1 pageAdverbs of Frequency in EnglishOum El GhoulNo ratings yet
- English exam practice for studentsDocument5 pagesEnglish exam practice for studentsOum El Ghoul100% (1)
- Irregular VerbsDocument6 pagesIrregular VerbsOum El GhoulNo ratings yet
- Prepositional Phrases in EnglishDocument2 pagesPrepositional Phrases in EnglishOum El Ghoul100% (1)
- COLLOCATIONSDocument3 pagesCOLLOCATIONSOum El GhoulNo ratings yet
- Almond Joy Coconut FrostingDocument1 pageAlmond Joy Coconut FrostingOum El GhoulNo ratings yet
- Deeper Look at The Islamic VeilDocument4 pagesDeeper Look at The Islamic VeilOum El GhoulNo ratings yet
- Sahih Muslim English TranslationDocument1,850 pagesSahih Muslim English Translationnounou0018100% (3)
- Business Ethics VocabularyDocument2 pagesBusiness Ethics VocabularyOum El Ghoul80% (59)
- Bookmarks Fact FileDocument1 pageBookmarks Fact FileRita de FigueiredoNo ratings yet
- Action VerbsDocument2 pagesAction VerbsOum El GhoulNo ratings yet
- English Tense SystemDocument25 pagesEnglish Tense SystemMOhammad ZOhaib100% (10)
- Year 4 English Lesson Plan - AlgeriaDocument11 pagesYear 4 English Lesson Plan - AlgeriaOum El GhoulNo ratings yet
- 32 Most Important Email Etiquette TipsDocument2 pages32 Most Important Email Etiquette TipsAdi SuciptaNo ratings yet
- English Tense SystemDocument25 pagesEnglish Tense SystemMOhammad ZOhaib100% (10)
- Verb Patterns List PDFDocument2 pagesVerb Patterns List PDFrudeboy86% (14)
- Comparative and Superlative EnglishDocument2 pagesComparative and Superlative EnglishOum El GhoulNo ratings yet
- Verb PatternsDocument4 pagesVerb PatternsOum El GhoulNo ratings yet
- Practice Nationalities and Verb To BeDocument1 pagePractice Nationalities and Verb To BeOum El GhoulNo ratings yet
- Eid Al Adha Lesson Plan1Document3 pagesEid Al Adha Lesson Plan1Oum El GhoulNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Relative Clauses Def and NonDefDocument3 pagesRelative Clauses Def and NonDefMarta Gil AcacioNo ratings yet
- Making A Banana Split: Chapter SixteenDocument3 pagesMaking A Banana Split: Chapter SixteenIsabele LavadoNo ratings yet
- Group 5Document35 pagesGroup 5Marta AtaNo ratings yet
- 2 SPEAKING 2 Talk Talking About Hometown RevisiDocument9 pages2 SPEAKING 2 Talk Talking About Hometown RevisiPicani ArdiantiNo ratings yet
- Supplementary Material: The Genitive CaseDocument3 pagesSupplementary Material: The Genitive CaseValentina Keilla Perez CidNo ratings yet
- Cycle of Erosion in Arid LandsDocument4 pagesCycle of Erosion in Arid LandsAbhijeet Naik100% (2)
- Suffixes WorksheetDocument6 pagesSuffixes Worksheeti6apparNo ratings yet
- Tabel Error RecognitionDocument4 pagesTabel Error RecognitionNurPiter ThiodorisNo ratings yet
- Legal English Report (Dash and Hyphen)Document2 pagesLegal English Report (Dash and Hyphen)Nadine Malaya NadiasanNo ratings yet
- Frequency of Modal Verbs in English Language CorporaDocument6 pagesFrequency of Modal Verbs in English Language Corporaapi-515559766No ratings yet
- Countable vs Uncountable NounsDocument12 pagesCountable vs Uncountable NounsMiguel Angel ReyesNo ratings yet
- Sperethiel DictionaryDocument16 pagesSperethiel DictionaryDiego VarelaNo ratings yet
- Since For Yet Already Just Ever Never Still Recent Grammar Guides - 13244Document1 pageSince For Yet Already Just Ever Never Still Recent Grammar Guides - 13244Tran Anh TuanNo ratings yet
- Spectrum TRD1 GV U2 1Document1 pageSpectrum TRD1 GV U2 1MARIA TERESA LOPEZ CINTASNo ratings yet
- DERIVED ADJECTIVES: PREFIXES AND SUFFIXESDocument2 pagesDERIVED ADJECTIVES: PREFIXES AND SUFFIXESDarius ProtacioNo ratings yet
- Landslide Risks in Leon BarangaysDocument151 pagesLandslide Risks in Leon BarangaysMark Kelly BalgosNo ratings yet
- Gadec - Present Simple Tense LessonDocument5 pagesGadec - Present Simple Tense LessonRui AbílioNo ratings yet
- ILP German Handout 10may05 V3.0Document48 pagesILP German Handout 10may05 V3.0Venkatraman ChandrasekarNo ratings yet
- Using Prepositions IN, ON, AT (General)Document26 pagesUsing Prepositions IN, ON, AT (General)Jen QuitorioNo ratings yet
- 7 - The Media - Reported SpeechDocument2 pages7 - The Media - Reported SpeechMaria Da Guia Fonseca50% (2)
- UNIT 2. What's ThisDocument20 pagesUNIT 2. What's ThisAndreaNo ratings yet
- Adjective Clause (Penggunaan Who, Whom, Whose, Which, DLL)Document24 pagesAdjective Clause (Penggunaan Who, Whom, Whose, Which, DLL)Wahyu Wiji PamungkasNo ratings yet
- Sushila Academic Plan Eng VDocument6 pagesSushila Academic Plan Eng VsushilbhagasaraNo ratings yet
- Cooly TamilDocument194 pagesCooly TamilVeeramani Mani100% (2)
- Add - Ness To Form Nouns From AdjectivesDocument6 pagesAdd - Ness To Form Nouns From Adjectiveszahra saoudiNo ratings yet
- Definition of Noun:: Any Member of A Class of Words That Typically Can Be Combined With Determiners (SeeDocument2 pagesDefinition of Noun:: Any Member of A Class of Words That Typically Can Be Combined With Determiners (SeeAnonymous emiGm42DtKNo ratings yet
- 6 Thgrade 4 Thgrade EQTSTUDYGUIDEDocument21 pages6 Thgrade 4 Thgrade EQTSTUDYGUIDElilwavy kingNo ratings yet
- 5 Nov 2020 Regular and Irregular Verbs: There Are Mainly Three Types of Irregular VerbsDocument20 pages5 Nov 2020 Regular and Irregular Verbs: There Are Mainly Three Types of Irregular Verbskaziba stephenNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 NounsDocument24 pagesLecture 1 NounsMarija MenchevaNo ratings yet
- Act. 3, Excercises From The TOEFL BookDocument3 pagesAct. 3, Excercises From The TOEFL Bookblack shadowNo ratings yet