Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Gentamicin Drug Summ
Uploaded by
WarrenOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Gentamicin Drug Summ
Uploaded by
WarrenCopyright:
Available Formats
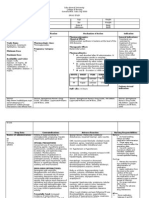
Score: _________ Grade: ___________
DRUG SUMMARY
Name of Drug Date Classification Dose Mechanism Specific Side Effects Nursing Implications
Generic Ordered Frequency of Action Indication
(Brand) Route
BEFORE:
Gentamycin April 29, Anti-infectives 37.5mg Inhibits Treatment of EENT: ototoxicity ~ Assess child for infection (vital
(Garamycin) 07 IVTT od protein serious gram- (vestibular and signs, wound appearance,
sputum, urine, stool, WBC) at
ANST (-) synthesis in negative cochlear). beginning of and throughout
bacteria at bacillary GU: therapy.
level of 30S infections and nephrotoxicity. ~ Obtain specimens for culture
and sensitivity before initiating
ribosome, infections F and E: therapy. First dose may be given
bactericidal caused by hypomagnesemia. before receiving results.
action. staphylococci ~ Monitor intake and output and
daily weight to assess hydration
when MS: muscle status and renal function.
penicillins or paralysis (high ~ Assess child for signs of
other less toxic parenteral doses). superinfection (fever, upper
respiratory infection, vaginal
drugs are Misc: itching or discharge, increasing
contraindicated hypersensitivity malaise, diarrhea).
reactions.
DURING:
~ Advise child of the importance
of drinking plenty of liquids.
~ Missed doses should be taken
as soon as possible if not almost
time for next dose; do not double
doses.
AFTER:
~ Instruct child’s mother to take
as directed for full course of
therapy.
~ Mother should assess skin and
inform health care professional if
skin irritation develops or
infection worsens.
Reference: DAVIS DRUG GUIDE FOR NURSES 8th EDITION___
You might also like
- GENTAMICINDocument3 pagesGENTAMICINjacquejackieNo ratings yet
- GentamicinDocument1 pageGentamicinreinaNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY Amoxicillin PDFDocument2 pagesDRUG STUDY Amoxicillin PDFMc SantosNo ratings yet
- Gentamicin Sulfate Drug StudyDocument7 pagesGentamicin Sulfate Drug StudyGabriel Rosales RM RNNo ratings yet
- Drug Study AmpicillinDocument6 pagesDrug Study AmpicillinDgjj Compuiter100% (1)
- Drugs Study GentamicinDocument3 pagesDrugs Study Gentamicinahmad ryanNo ratings yet
- CephalexinDocument3 pagesCephalexinCiera YoungNo ratings yet
- Drug Study in GentamicinDocument2 pagesDrug Study in Gentamicinanthony_alviar100% (1)
- Drug Study Amphotericin B, Meropenem, Furosemide, Ciprofloxacin, Pentoxifylline, Pip-Tazo, Midazolam, VecuroniumDocument12 pagesDrug Study Amphotericin B, Meropenem, Furosemide, Ciprofloxacin, Pentoxifylline, Pip-Tazo, Midazolam, Vecuroniumpaupaulala100% (4)
- Ibuprofen (Dolan) Drug StudyDocument1 pageIbuprofen (Dolan) Drug Studyanreilegarde33% (3)
- Atracurium BesylateDocument4 pagesAtracurium BesylateStill DollNo ratings yet
- GentamicinDocument2 pagesGentamicinMiguel Sanico0% (2)
- Amoxicillin TrihydrateDocument1 pageAmoxicillin TrihydrateHoney Que BullivantNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: Classification: Indication:: Candida InfectionsDocument1 pageGeneric Name: Classification: Indication:: Candida Infectionscen janber cabrillos0% (1)
- AcetaminophenDocument1 pageAcetaminophenKristine YoungNo ratings yet
- Gentamycin DRUG STUDYDocument2 pagesGentamycin DRUG STUDYMarvie CadenaNo ratings yet
- PiperacillinDocument3 pagesPiperacillinmyer pasandalanNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Cefazolin Module 13Document1 pageDrug Study Cefazolin Module 13Daryl Joy Cortez100% (1)
- CefalexinDocument1 pageCefalexinKenneth InciongNo ratings yet
- Drug Stidy TramadolDocument2 pagesDrug Stidy TramadolRez ApegoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study of AminophyllineDocument6 pagesDrug Study of AminophyllineFrancis CorpuzNo ratings yet
- DRUG ORDER Generic Name: - Ampicillin Brand Name: - AmpicinDocument1 pageDRUG ORDER Generic Name: - Ampicillin Brand Name: - AmpicinRadicalRay100% (3)
- AMINOPHYLLINEDocument2 pagesAMINOPHYLLINEmusiclover017100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyHanna Clarisse PataoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study MetronidazoleDocument2 pagesDrug Study MetronidazoleJha NetNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Nursing DepartmentDocument1 pageDrug Study: Nursing Departmentgiselle chloe100% (1)
- Jose Luis Hernandez BSN Ii - 2Document1 pageJose Luis Hernandez BSN Ii - 2Jose Luis HernandezNo ratings yet
- Drug Study EntecavirDocument4 pagesDrug Study EntecavirClarimae AwingNo ratings yet
- ErythromycinDocument2 pagesErythromycinKathleen PalomariaNo ratings yet
- Nalbuphine (Nubain)Document2 pagesNalbuphine (Nubain)Adrianne Bazo100% (1)
- College of Health Sciences: Urdaneta City UniversityDocument2 pagesCollege of Health Sciences: Urdaneta City UniversityDan Dan Manaois100% (1)
- Dazomet DrugDocument2 pagesDazomet Drugashley11No ratings yet
- Drug Study - AlfuzosinDocument1 pageDrug Study - AlfuzosinKian HerreraNo ratings yet
- XylocaineDocument1 pageXylocaineRozanne BanzaliNo ratings yet
- PhytomenadioneDocument3 pagesPhytomenadioneanareads100% (1)
- AmpicillinDocument2 pagesAmpicillinMar OrdanzaNo ratings yet
- Carbidopa-Levodopa (SINEMET CR)Document1 pageCarbidopa-Levodopa (SINEMET CR)Amanda CoadNo ratings yet
- Povidone Iodine Drug StudyDocument5 pagesPovidone Iodine Drug StudyFaye Andrea Francisco100% (1)
- BetamethasoneDocument3 pagesBetamethasoneMichael KuzbytNo ratings yet
- OfloxacinDocument2 pagesOfloxacinCarla Arciaga100% (1)
- Drug Study - HydrocodoneDocument2 pagesDrug Study - HydrocodoneTarquin Tomada86% (7)
- Casilan, Ynalie Drug Study (Morphine)Document5 pagesCasilan, Ynalie Drug Study (Morphine)Ynalie CasilanNo ratings yet
- Trimethoprim Sulfamethoxazole (TMP SMZ) Co TrimoxazoleDocument1 pageTrimethoprim Sulfamethoxazole (TMP SMZ) Co TrimoxazoleRenmico Aquino0% (1)
- Drugstudy PotassiumchlorideDocument3 pagesDrugstudy Potassiumchloridetrina412No ratings yet
- Generic Name: Amikacin SulfateDocument2 pagesGeneric Name: Amikacin Sulfateichiro017100% (7)
- ONDANSETRONDocument1 pageONDANSETRONJugen Gumba Fuentes Alquizar0% (1)
- Drug Study BISACODYLDocument1 pageDrug Study BISACODYLAnna Sofia ReyesNo ratings yet
- FamotidineDocument1 pageFamotidineMäc LäntinNo ratings yet
- Clarithromycin Drug SummDocument1 pageClarithromycin Drug SummWarrenNo ratings yet
- Drug Mechanis MOF Action Indicatio N and Rationale Contra Indication S Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationDocument1 pageDrug Mechanis MOF Action Indicatio N and Rationale Contra Indication S Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationJordz PlaciNo ratings yet
- University of Northern PhilippinesDocument1 pageUniversity of Northern PhilippinesKrizha Angela NicolasNo ratings yet
- MeropenemDocument3 pagesMeropenemJasmin T LarizaNo ratings yet
- Drug TBDocument1 pageDrug TBjpmNo ratings yet
- FluticasoneDocument4 pagesFluticasonevanNo ratings yet
- Drug Classification Action of Drug Indication and Contraindication Side Effect Nursing ConsiderationDocument2 pagesDrug Classification Action of Drug Indication and Contraindication Side Effect Nursing ConsiderationDanica Kate GalleonNo ratings yet
- Drug Study FormatDocument7 pagesDrug Study FormatShyne HazyNo ratings yet
- Acetaminophen Paracetamol Drug SummDocument1 pageAcetaminophen Paracetamol Drug SummWarren100% (1)
- Drug Study Activity ErythromycinDocument2 pagesDrug Study Activity ErythromycinNELL JOSHUA PANTIGNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - Acetaminophen, ParacetamolDocument1 pageDrug Study - Acetaminophen, ParacetamolmikErlh100% (2)
- TB Drugs RipeDocument4 pagesTB Drugs Riperonletaba100% (1)
- Apr. 8-11 Grp3 Sched For ScribdDocument1 pageApr. 8-11 Grp3 Sched For ScribdWarrenNo ratings yet
- Mar. 19-22 Grp3 Sched For ScribdDocument1 pageMar. 19-22 Grp3 Sched For ScribdWarrenNo ratings yet
- Tentative Sched For Apr 28-30 & May 1Document1 pageTentative Sched For Apr 28-30 & May 1WarrenNo ratings yet
- Group 3 Nurse Volunteer Schedule Feb 7 - 10 & Feb 27 - Mar 2Document3 pagesGroup 3 Nurse Volunteer Schedule Feb 7 - 10 & Feb 27 - Mar 2WarrenNo ratings yet
- Vit.B Complex Drug SummDocument1 pageVit.B Complex Drug SummWarren100% (5)
- NIcardipine Drug SummDocument1 pageNIcardipine Drug SummWarren50% (2)
- Salbutamol Drug SummDocument1 pageSalbutamol Drug SummWarren100% (2)
- Amniodarone (Norvasc) Drug SummDocument1 pageAmniodarone (Norvasc) Drug SummWarrenNo ratings yet
- Clarithromycin Drug SummDocument1 pageClarithromycin Drug SummWarrenNo ratings yet
- Calcium Gluconate Drug SummDocument1 pageCalcium Gluconate Drug SummWarren100% (2)
- Amniodarone (Norvasc) Drug SummDocument1 pageAmniodarone (Norvasc) Drug SummWarrenNo ratings yet
- Acetaminophen Paracetamol Drug SummDocument1 pageAcetaminophen Paracetamol Drug SummWarren100% (1)
- Aspirin Drug SummDocument2 pagesAspirin Drug SummWarren0% (1)
- Ranitidine Drug SummDocument1 pageRanitidine Drug SummWarren100% (3)
- Alzheimer Disease Case StudyDocument6 pagesAlzheimer Disease Case StudyWarren67% (3)
- Bacterial Culture Media: Types and Applications: Mlt422: Clinical Microbiology IDocument13 pagesBacterial Culture Media: Types and Applications: Mlt422: Clinical Microbiology Inuraini sofeaNo ratings yet
- Human Papillomavirus and Oral Cancer: The International Agency For Research On Cancer Multicenter StudyDocument12 pagesHuman Papillomavirus and Oral Cancer: The International Agency For Research On Cancer Multicenter StudyBaloo If CosminNo ratings yet
- Enterocolitis NecrosanteDocument21 pagesEnterocolitis NecrosantedenisNo ratings yet
- Complete Cell DivisionDocument96 pagesComplete Cell DivisionAbegail Reyes100% (1)
- 2019 Book Genome-WideAssociationStudiesDocument216 pages2019 Book Genome-WideAssociationStudiesastridNo ratings yet
- No.22 Ogbeukwu Road Ndoni Rivers StateDocument26 pagesNo.22 Ogbeukwu Road Ndoni Rivers StateGift NkwochaNo ratings yet
- Aiims BiochemDocument39 pagesAiims Biochemshalialoo22No ratings yet
- Fungal Infections & Lulyeva Itra EvaDocument9 pagesFungal Infections & Lulyeva Itra EvaMonod TNo ratings yet
- The Infectious ProcessDocument4 pagesThe Infectious ProcessAdnan Akram, MD (Latvia)100% (1)
- EVMS Critical Care COVID-19 ProtocolDocument38 pagesEVMS Critical Care COVID-19 ProtocolDrivailaNo ratings yet
- DR Lie Khie Chen - Management of MDR Infection in Sepsis Jade 2016Document33 pagesDR Lie Khie Chen - Management of MDR Infection in Sepsis Jade 2016Astria PermanaNo ratings yet
- Isolation and Characterization of RNADocument3 pagesIsolation and Characterization of RNAEvans DionNo ratings yet
- 862 FullDocument37 pages862 Full01Syafira Khairunissa MNo ratings yet
- Acquired Hemolytic AnemiaDocument48 pagesAcquired Hemolytic AnemiaJeena RajNo ratings yet
- Spectrum and Classification of ATP7B Enfermedad de WilsonDocument12 pagesSpectrum and Classification of ATP7B Enfermedad de WilsonKarly BautistaNo ratings yet
- ACOG Practice Bulletin No 199 Use Of.67Document17 pagesACOG Practice Bulletin No 199 Use Of.67YtyNo ratings yet
- Lactobacillus Acidophilus: Characterization of The Species and Application in Food ProductionDocument48 pagesLactobacillus Acidophilus: Characterization of The Species and Application in Food ProductionGRACIELANo ratings yet
- MUST To KNOW in Immunology and SerologyDocument18 pagesMUST To KNOW in Immunology and SerologyRona Salando50% (2)
- VivaChek Bio Products Catalog (En) 092421Document14 pagesVivaChek Bio Products Catalog (En) 092421Emmanuel BonillaNo ratings yet
- SBI3U Grade 11 Biology Prokaryotes Viruses and Eukaryotes Biodiversity TestDocument8 pagesSBI3U Grade 11 Biology Prokaryotes Viruses and Eukaryotes Biodiversity TestMockinjayNo ratings yet
- Osmosis Neuro Physiology and Anatomy Notes by DR of 2027-28Document91 pagesOsmosis Neuro Physiology and Anatomy Notes by DR of 2027-28tariq ullahNo ratings yet
- Ara Operon Notes - 18Document4 pagesAra Operon Notes - 18Khaleeda Ahmad AnuarNo ratings yet
- Application of BiotechnologyDocument1 pageApplication of BiotechnologyscribsunilNo ratings yet
- Antimalarials DrugsDocument27 pagesAntimalarials DrugsAlishba MushtaqNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Pulse Therapy and Rife HealingDocument9 pagesMagnetic Pulse Therapy and Rife HealingHaSophim88% (8)
- Antibiotics ChartDocument10 pagesAntibiotics ChartTrina Si100% (6)
- White Lesions of The Oral MucosaDocument213 pagesWhite Lesions of The Oral MucosaJunaid Ramzan100% (1)
- Hemolytic Disease of The NewbornDocument1 pageHemolytic Disease of The NewbornMASIINo ratings yet
- Tools of Genetic Engineering 23.4.22Document40 pagesTools of Genetic Engineering 23.4.22ELOM OLINENo ratings yet
- Tosoh Bioscience Tosoh Bioscience: CL Aia-Pack ReagentsDocument2 pagesTosoh Bioscience Tosoh Bioscience: CL Aia-Pack ReagentsAleksandar MisicNo ratings yet