Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Growth and Dev - T
Uploaded by
Omar EusebioOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Growth and Dev - T
Uploaded by
Omar EusebioCopyright:
Available Formats
THEORY
ERICK ERICKSONS PSYCHOSOCIAL DEVELOPMENT Generativity vs. Stagnation Middle Adulthood (40 to 65 years) In this stage generativity refers to the adult's ability to care for another person. The most important event in this stage is parenting. Does the adult have the ability to care and guide the next generation? Generativity has a broader meaning then just having children. Each adult must have some way to satisfy and support the next generation. According to Erikson, "A person does best at this time to put aside thoughts of death and balance its certainty with the only happiness that is lasting: to increase, by whatever is yours to give, the goodwill and higher order in your sector of the world" The client was able to satisfy this stage because he lives with his own family. He possessed good traits a husband and a father should have and leads his family to the ideal kind of relationship.
SIGMUND FREUDS KOHLBERGS STAGES OF MORAL PSYCHOSEXUAL DEVELOPMENT DEVELOPMENT
JEAN PIAGETS STAGES OF COGNITIVE DEVELOPMENT
STAGES DEFINITION
Genital Stage (Puberty to Adult Life ) This stage begins at the start of puberty when sexual urges are once again awakened. Through the lessons learned during the previous stages, adolescents direct their sexual urges onto opposite sex peers, with the primary focus of pleasure of the genitals.[1] The less energy the child has left invested in unresolved psychosexual developments, the greater his capacity will be to develop normal relationships with the opposite sex.
Post-conventional Social Contract Orientation (Middle Age or Older Adult) In this stage, marked by a growing realization that individuals are separate entities from society, and that the individuals own perspective may take precedence over societys view; individuals may disobey rules inconsistent with their own principles. Post-conventional moralists live by their own ethical principlesprinciples that typically include such basic human rights as life, liberty, and justice.
Formal operational (11 years and up) The formal operational stage is the fourth and final stage of cognitive development in Piaget's theory. This stage, which follows the Concrete Operational stage, commences at around 11 or 12 years of age (puberty) and continues into adulthood. In this stage, individuals move beyond concrete experiences and begin to think abstractly, reason logically, and draw conclusions from the information available as well as apply all these processes to hypothetical situations. This meant using symbols and imagined realities, as well as reasoning systematically. . The client thinks abstractly and solves his problems. He is realistic in a way. There is also consistency of his thoughts and thinking of their future.
REMARKS
The client was able to satisfy this stage for the moment he got married, he decided to live in a separate household from his parents. Taking the responsibility of a husband, and as the bread winner. As a husband he serves as a loving companion to his wife. This factors indicate that our client establish a balance between various areas.
The client was able to satisfy the post conventional stage because client has his own principles in life and also he respects the rules and regulations of the society.
ANALYSIS
This is the longest period of Genital stage is the stage where young humans life. It is the stage in adults have a deepest pleasure that came which people are usually working from the opposite sex. and contributing to society in some way and perhaps raising their children. If one does not find proper way to be productive during this
Individuals are capable of principled reasoning. Their choice of action is based on their principles. Men use an ethic of justice and define moral problems in terms of rules and right. Women define moral problems in terms of obligation to care and to avoid hurt.
Young adulthood is the time where people think about social matter and what they can be in their future. They are capable in responding and solving their problems.
You might also like
- Engaging Youth of Today: Mind Clear, Body Fit, Spirit Well: Designed for Parents and ProfessionalsFrom EverandEngaging Youth of Today: Mind Clear, Body Fit, Spirit Well: Designed for Parents and ProfessionalsNo ratings yet
- Developmental Stages in Middle and Late AdolescenceDocument33 pagesDevelopmental Stages in Middle and Late AdolescenceAldine RaytanNo ratings yet
- Mini CP Skin Avulsion Chap5Document3 pagesMini CP Skin Avulsion Chap5Katherine 'Chingboo' Leonico LaudNo ratings yet
- King Saud University College of Nursing Gorwth & DevelopmentDocument16 pagesKing Saud University College of Nursing Gorwth & Developmenthatem alsrour100% (6)
- YouthologyDocument6 pagesYouthologyDisha ShahNo ratings yet
- Theories of Moral Dev'Document6 pagesTheories of Moral Dev'Yeab TubeNo ratings yet
- Activity 4-EDUC 1Document4 pagesActivity 4-EDUC 1Sheena NavascaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Description:: Module 3: Developmental Skills and Tasks Among AdolescentsDocument8 pagesLesson Description:: Module 3: Developmental Skills and Tasks Among AdolescentsCharles PabalateNo ratings yet
- Erik Erikson 8 Stages TFN PresentationDocument4 pagesErik Erikson 8 Stages TFN PresentationMcnurseNo ratings yet
- Erickson's Theory PDFDocument19 pagesErickson's Theory PDFNatasha ShangeNo ratings yet
- Dev Psy For ClassDocument14 pagesDev Psy For ClassDante MillerNo ratings yet
- Geriatric - Developmental TheoryDocument10 pagesGeriatric - Developmental TheoryCharlene del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Heaven ReportDocument30 pagesHeaven ReportTrisha TamsiNo ratings yet
- AKA Erik Homburger EriksonDocument34 pagesAKA Erik Homburger EriksonvinwaleedNo ratings yet
- Unit-6 Moral DevelopmentDocument24 pagesUnit-6 Moral DevelopmentAsad muhammad azamNo ratings yet
- Erikson's Theory of Psychosocial DevelopmentDocument5 pagesErikson's Theory of Psychosocial DevelopmentPrateek67% (6)
- Infancy: Trust vs. Mistrust (0 To 1 Year)Document5 pagesInfancy: Trust vs. Mistrust (0 To 1 Year)karyl lynNo ratings yet
- Early Adulthood: Stages in The Life SpanDocument6 pagesEarly Adulthood: Stages in The Life SpanAngelica Mae DanaoNo ratings yet
- PERDEVDocument5 pagesPERDEVShimarie lhei CiubalNo ratings yet
- AHS 1053/AHBS 1316 Developmental Psychology For Health Science AHSC Developmental Psychology in Health SciencesDocument45 pagesAHS 1053/AHBS 1316 Developmental Psychology For Health Science AHSC Developmental Psychology in Health SciencesAmin IrfanNo ratings yet
- Written ReportDocument6 pagesWritten ReportIRA MONIQUE CABADENNo ratings yet
- Erickson's Theory of Psychosocial DevelopmentDocument16 pagesErickson's Theory of Psychosocial Developmentjuljuliemer100% (3)
- Reviewer For Understanding CultureDocument4 pagesReviewer For Understanding CultureShen EugenioNo ratings yet
- Adi Bhavya Jha - LSD AssignmentDocument6 pagesAdi Bhavya Jha - LSD Assignmentbhavya jhaNo ratings yet
- D Kohlberg On Moral DevelopmentDocument7 pagesD Kohlberg On Moral DevelopmentRandyNo ratings yet
- Prof Ed 1 Final QuizDocument4 pagesProf Ed 1 Final QuizJohn Paul GalillagaNo ratings yet
- Transactional Analysis: Group Presentation)Document36 pagesTransactional Analysis: Group Presentation)Saachi MahajanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document25 pagesChapter 2janmieNo ratings yet
- Identity Vs Role Confusion - Theory 3Document19 pagesIdentity Vs Role Confusion - Theory 3Marc Anthony SeatonNo ratings yet
- Chap 4-5Document7 pagesChap 4-5Winter Pandora100% (1)
- Your Name Professor Name Institute NameDocument9 pagesYour Name Professor Name Institute NameAbdullah AkmalNo ratings yet
- Adolescents & Sexual DevelopmentDocument15 pagesAdolescents & Sexual DevelopmentBiju SebastianNo ratings yet
- Drug Therapeutic RecordDocument4 pagesDrug Therapeutic RecordAlex SilvanoNo ratings yet
- Module 3Document6 pagesModule 3aeiaeiuaoNo ratings yet
- Developmental Theorty Notes Lesson 3Document12 pagesDevelopmental Theorty Notes Lesson 3NEMSU Guidance CenterNo ratings yet
- Adolescence: Changes in Primary Sex Characterstics. Primary Sex Characteristics Refer To Changes ToDocument5 pagesAdolescence: Changes in Primary Sex Characterstics. Primary Sex Characteristics Refer To Changes ToAntonio Delgado100% (1)
- Developmental TheoriesDocument6 pagesDevelopmental TheoriesSaadia TalibNo ratings yet
- Chapter I-The Problem and Its BackgroundDocument22 pagesChapter I-The Problem and Its Backgroundkerrin galvezNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument5 pagesCase StudysatyamNo ratings yet
- 07: Cognitive Development and The Teenage Years: Student ObjectivesDocument10 pages07: Cognitive Development and The Teenage Years: Student ObjectivesŞterbeţ RuxandraNo ratings yet
- Developmental PsychologyDocument11 pagesDevelopmental Psychologyadiba KhanNo ratings yet
- ADULTHOODDocument2 pagesADULTHOODKinnari AbhyankarNo ratings yet
- MPC-002 - 2020Document14 pagesMPC-002 - 2020Rajni KumariNo ratings yet
- Erikson'S Stages of Psychosocial Development Childhood (Birth To Six Years)Document3 pagesErikson'S Stages of Psychosocial Development Childhood (Birth To Six Years)angel_mtzNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Evaluation of Four Moral Development TheoriesDocument2 pagesAnalysis and Evaluation of Four Moral Development TheoriesEnforcement SectionNo ratings yet
- Interview of An Older AdultDocument5 pagesInterview of An Older AdultankushNo ratings yet
- Matrix On The Theories On Human Development 2 PDFDocument12 pagesMatrix On The Theories On Human Development 2 PDFCarlo AngcanaNo ratings yet
- Unit IIDocument9 pagesUnit IIShoba GuhanNo ratings yet
- Erikson's 8 Stages of Psychosocial DevelopmentDocument6 pagesErikson's 8 Stages of Psychosocial DevelopmentJamesBuensalidoDellavaNo ratings yet
- "Pediatrics 103" Assignment No. 2: What Are Stages of Cognitive Development by Jean Fiaget?Document4 pages"Pediatrics 103" Assignment No. 2: What Are Stages of Cognitive Development by Jean Fiaget?Hannah Leigh CastilloNo ratings yet
- Lawrence Kohlberg's TheoryDocument16 pagesLawrence Kohlberg's TheoryBhelsea100% (1)
- Objectives:: Abm/Gas 11 - Personal DevelopmentDocument7 pagesObjectives:: Abm/Gas 11 - Personal DevelopmentKristine ArbolenteNo ratings yet
- PerdevDocument5 pagesPerdevStephanie Caniban100% (1)
- SDSSC 101 AssignmentDocument7 pagesSDSSC 101 Assignmentshiloh chipendoNo ratings yet
- Psychosocial TheoryDocument30 pagesPsychosocial TheoryChing MaravillaNo ratings yet
- Human Development TheoriesDocument40 pagesHuman Development TheoriesMichelle Villareal CuevasNo ratings yet
- Developing The Whole PersonDocument20 pagesDeveloping The Whole PersonNOREEN PAYOPAYNo ratings yet
- Adolescent PDFDocument46 pagesAdolescent PDFmaryrose100% (1)
- .....Document46 pages.....sanjibk100% (1)
- Human Growth and Development Research Paper TopicsDocument5 pagesHuman Growth and Development Research Paper TopicsjssoulzndNo ratings yet
- ScoreDocument4 pagesScoreOmar EusebioNo ratings yet
- Certification of Statistical Treatment: StatisticianDocument1 pageCertification of Statistical Treatment: StatisticianOmar EusebioNo ratings yet
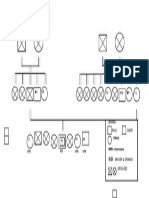
- Family Health Illness Pattern (Genogram) : AC JS TC AP PTP FGDocument1 pageFamily Health Illness Pattern (Genogram) : AC JS TC AP PTP FGOmar EusebioNo ratings yet
- (Patho) PTB COPDDocument1 page(Patho) PTB COPDKyle HannahNo ratings yet
- Myocardial Infarction Pa Tho Physiology - Schematic DiagramDocument3 pagesMyocardial Infarction Pa Tho Physiology - Schematic DiagramChristine AllonarNo ratings yet