Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Peka SC Year 6
Uploaded by
aqmar77Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Peka SC Year 6
Uploaded by
aqmar77Copyright:
Available Formats
NAME CLASS
: : .
SCHOOL : .
Activity Code Learning Area Learning Objective Learning Outcomes Method Apparatus
: : : : : :
6/1/1/1.1 1.Interaction among living thing 1.1 Understanding that some animals live in group and others live in solitary. 1.1.1-1.1.7 Discussion Chart
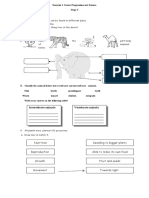
Steps 1.Study the picture of animals shown below. 2.Classify the animals below according to the way they live.
eagle
lion
horse
goat
pangolin
chameleon
giraffe 3.Record your findings Live in group
butterfly SPS 4 C1/C2/C4
Live in solitarily
Questions 1. State two ways of behaving which are characteristics of animals that a) Live in a solitarily i.. SPS 1 C1 SPS 2 C1/C2
SPS 4 ii. C2/C3 b) Live in a groups i.. ii. 2. Give two forms of interaction among animals. i.. ii. 3. Conclusion Some animals live in and some animals live .
Activity Code Learning Area Learning Objective Learning Outcomes Method Apparatus
: 6/1/1/1.2 : 1 Interaction among living things : 1.2 Understanding that competition is a form of interaction among living things : 1.2.5-1.2.6 : Discussion : Picture
Steps 1. The picture showing the interaction among plants in the forest have different height. 2. Record the observation.
Questions 1. List three factors that plants compete to survive ? i... ii..... iii.... 2. How do plants avoid competition among their own species ? .. 3. What will happen to the weaker plant ? .
SPS 2 C2/C3 SPS 4 C1/C3
Activity Code Learning Area Learning Objective Learning Outcomes Method Apparatus
: 6/1/1/1.2 : 1 Interaction among living things : 1.2 Understanding that competition is a form of interaction among living things : 1.2.5-1.2.6 : Experiment : Green bean, two pots, wet cotton wool.
Steps 1. Place some cotton wool into two pots label X and Y of the same size. 2. Put two green bean seeds in pot X and thirty green bean seeds in pot Y 3. Left both pots for a week. 4. Measure the height of the green been seedling. 5. Record your observation.
Pots X Y Questions 1. 2.
Number of green beans 2 30
Height of the seedling (cm)
SPS 1 C1/C3 SPS 7 C6 SPS 5 C3
What do plant compete for ? SMS 2 C1/C2 State . i) What is to change : .. SPS 7 ii) What to measure : C2/C iii) What is keep the same : ..
5
3.
State the relationship between the number of green bean seeds and SPS 7 C1 the height of the seedlings. ... ...
4.
Give a reason for your observation investigation? The seedlings of pot X grow healthy because they get enough : i ii.. iii.
SPS 4 C1
Activity Code Learning Area Learning Objective Learning Outcomes Method Apparatus
: 6/1/1/1.3 : 1 Interaction among living things. : 1.3 Understanding the responsibility of Human being in protecting endangered species. : 1.3.2,1.3.4,1.3.5 : Discussion : Picture of animals.
Steps 1. The picture show the animals facing the threat of extinction. 2. The factors that causing the extinction of animals are identified. 3. The ways to prevent the animals from becoming extinct are defined. Name the animals and state the factors of extinction : 1 i) Name : .. ii) Hunted for ... 2 i) Name : .. ii) Hunted for 3 i) Name : .. ii) Hunted for 4. Why the animals become extinct ? i)... ii). 5. Suggest two ways of preventing animals from becoming extinct? i)... ii).
7
SPS 4 C1/C2/C4
SPS 7 C6
Activity Code Learning Area Learning Objective Learning Outcomes Method Apparatus
: 6/2/1/1.1 : Force : 1.1 Understanding that push and pull are force. : 1.1.1-1.1.2 : Simulation : Pupils
Steps 1. Carry out all the activities given below 2. Find out what happens to the object or what you feel. 3. Record your finding in the table given below 1.Tick (/) in the correct activities : Activities a. Pulling each others hands. b. Pushing each others hands. c. Kicking a ball. d. Pulling a flag. Push Pull SPS 1 C1/C3 SMS 2 C2/C3
2. What is force ? Force is a .. 3. Give two another examples of pushing activities? i. ii 4. Give two another examples of pulling activities? i. ii
8
SPS 7 C6
Activity Code Learning Area Learning Objective Learning Outcomes Method Apparatus
: 6/2/1/1.2 : 1 Force : 1.2 Understanding the effects of a force. : 1.1.3 : Experiment : Plasticine, sponge, spring
Steps 1. Carry out all the activities given below. 2. Draw the observation in the table below to the object after force is applied. Effect of the activities Activities Observation The object becomes ... SPS 1 C1/C3 SPS 7 C6
a. Press the plasticine.
b. Pulling the spring.
c. Squeezing the sponge.
Conclusion Force can .. the shape of an object.
Activity Code Learning Area Learning Objective Learning Outcomes Method Apparatus
: 6/2/1/1.2 : 1.Force : 1.2 Understanding the effects of the force. : 1.2.1-1.2.2 : An experiment : Rubber ball/ ping pong ball
Steps 1. The activities carried out based in table below. 2. Record your findings. Activity (a) Push a stationary ball (b) Pushing the moving ball harder (c) Stop the moving ball Result SPS 1 C1
Questions : 1. A force can .. (i) ...a stationary object. (ii).the speed of an object. (iii) make an object to move ...or . 2. Predict what will happen if a moving object is pushed from directions ? ..
SPS 7 C2/C6
10
Activity Code Learning Area Learning Objective Learning Outcomes Method Apparatus
: 6/2/2.1/1 : Movement : 2.1 Understanding speed : 1. State that an object which moves faster travels a longer distance in a given time : Experiment : Stop watch, measuring tape.
Steps : 1. Mark the starting point before continues the activities. 2. 3. 4. Ask your friend to get ready at the starting point for start their running. Use the stop watch, to record the time taken in 10 second. Record the distance travel by the student into the table given and calculate the speed for each student. Name of student Time taken (s)
10 10 10 10
Distance (m)
Speed (m/s)
SPS3 C1/C2/C3/C4
Answer the questions 1. 2. 3. Who are the fastest? ____________________________________________________ Give your inference based on your observations in the table above. _____________________________________________________ State the trend of speeding by a student from the table above. _____________________________________________________
11
Activity Code Learning Area Learning Objective Learning Outcomes Method Apparatus
: 6/2/2.1/ 2 : Movement : 2.1 Understanding speed : 2. State that an object which moves faster takes a shorter time to travel a given distance : Experiment : Stop watch
Steps : 1. Mark the distance for 50 metres. 2. 3. 4. Ask your friend to get ready at the starting point for start their running. Use the stop watch, to record the time taken for each student Record the time taken by the student into the table given and calculate the speed for each student. Name of student Distance (m)
50 50 50 50
Time taken (s)
Speed (m/s)
SPS3 C1/C2/C3/C4
Answer the questions 1. 2. 3. Who are the fastest? ____________________________________________________ Give your inference based on your observations in the table above. _____________________________________________________ State the trend of speeding by a student from the table above. _____________________________________________________
12
Activity Code
: 6/3/1.2/2
Learning Area : 1. Food preservation Learning object : 1.2 Synthesising the concept of food preservation Learning outcome : 2. Give examples of food for each type of food Method : Discussion Materials : The picture of foods, fruits, Vegetables. Steps: 1. Observe the picture carefully, 2. Classify the picture of food according the correct way of food preservation SPS 1 C1,C2
SPS 2 C1,C2,C3,C4
13
1.
Which food can preserve more than one way? ______________________________________________________
2.
Why the food need to preserve ? ______________________________________________________
3.
What are the similarities between the canning and bottling in the preserving food. ______________________________________________________
4.
Which food can preserve with the freezing, drying and salting process? ______________________________________________________
14
Activity Code Learning Area Learning Objective Learning Outcomes Method Apparatus
: 6/4/2.1/2 : 2. Waste management : 2.1 Understanding the effects of improper disposal of waste on the environment : 1. Identify types of waste in the environment : Discussion : The picture of the waste disposal
Steps : 1. Observe the picture given and classify the type of the waste.
SPS 1 C1,C3 SPS 2 C1,C2
1. ____________________________________________ 2. ____________________________________________
15
SPS 2 C1,C2
1. ____________________________________________ 2. ____________________________________________
2. Based on the place given, state and classify the type of waste produce for each place
SPS 2 C1,C2,C3
Housing
Factories 3. State the similarities the type of waste produce by two places.
________________________________________________________
16
Activity Code Learning Area Learning Objective Learning Outcomes Method Apparatus
: 6/4/1.2/2 :1 : 1.2 Understanding the eclipse of the sun : 2. Explain why an eclipse of the sun occurs. : Simulations : Globe, torch light, ping pong ball, thread and cellophane tape
Steps : 1. Hang up two ends of the thread at the ping pong ball with cellophane tape 2. Place the globe on the table. 3. Place the torch light at the end of the table, and then switch it on. 4. Hang up the ping pong ball parallel with the globe and torch. 5. Move the ping pong ball around the globe and stop between the torch and globe. 6. Observe the surface of the globe .
Thread Globe
Ping pong ball Torch light
17
1.
What can be observed when the ping pong ball was placed between the torch and the globe ___________________________________________________________
SPS 1 C1,C3 SPS 4 C1
2.
State the phenomenon that occurs from the activity. ___________________________________________________________
3.
Draw and label the diagram of the phenomenon occurred.
SPS 4 C2,C3
4.
State how the phenomenon occurs. ______________________________________________________
5.
Why the time taken for this phenomenon shorter than moon eclipse? ______________________________________________________
SPS 5 C1,C4
6.
What will happen if the moon was not placed parallel between the sun and the earth? ______________________________________________________
18
Activity Code Learning Area Learning Objective Learning Outcomes Method Apparatus
: 6/4/1.1/3 :1 : 1.2 Understanding the eclipse of the moon : 2. Explain why an eclipse of the moon occurs. : Simulations : Globe, torch light, ping pong ball, thread and cellophane tape
Steps : 1. Hang up two ends of the thread to the ping pong ball with cellophane tape 2. Place the globe on the table 3. Place the torch light at the end side of the table, and then switch it on 4. Hang up the ping pong ball parallel with the globe and torch light 5. Move the ping pong ball around the globe and stop behind the globe 6. Observe what will happen at the surface of the globe.
Globe Tread
Torch light
Ping pong ball
19
1.
What can be observed when the ping pong ball was placed parallel SPS 1 behind the globe? C1,C3 ______________________________________________________ SPS 4 C1
2.
State the phenomenon that occurs from the activity ______________________________________________________
3.
Draw and label the diagram of the phenomenon occurred
SPS 4 C2,C3
4.
State how the phenomenon occurs. ______________________________________________________
5.
What will happen if the moon was not placed parallel between the sun and the moon? _____________________________________________________ SPS 5 C1,C4
6.
Give a conclusion for the phenomenon above. _____________________________________________________
20
Activity Code Learning Area Learning Objective Learning Outcomes Method Apparatus
: 6/5/1.2/2 : Machine : Analysing a complex machine : Conclude that a complex machine is made up of more than one simple machines : Experimenting : Bicycle, stopwatch.
Steps 1. Work in group . 2. The Investigation must be carried out in a big area 3. Mark a distance of 50m. 3. One pupil walking and one pupil cycling to reach the distance. 4. Record the time taken using the stopwatch in the table below. 5. Record your findings. Type of movement Walking Cycling 1) 2) 3) Which type of movement the pupil take a less time to reach? ...... Give the reasons for your answer in (1). ... List the type of simple machines at the bicycle. i...... ii..... iii.... What is the complex machine? .. State i) What is changed:... ii) What is observed :. iii) What is kept the same :..... Give the conclusion from this experiment. .....
21
Time taken (s)
SPS3 C2
SPS6 C1
SPS1 C3 SPS6 C2
4) 5)
SPS6 C3/C4
. 6)
You might also like
- KSSR Science Year 4 DLPDocument40 pagesKSSR Science Year 4 DLPDaniel44% (9)
- Science Year 4 Notes On HEAT ENERGYDocument1 pageScience Year 4 Notes On HEAT ENERGYNrhfzhjrzfzNo ratings yet
- RPT 2020 DLP Science Year 6 KSSRDocument12 pagesRPT 2020 DLP Science Year 6 KSSRMari GovinNo ratings yet
- Soalan Trial English BI UPSR Paper 1 JohorDocument12 pagesSoalan Trial English BI UPSR Paper 1 Johorsasauball100% (2)
- Science Year 5unit 3 Food Chain and Food WebDocument2 pagesScience Year 5unit 3 Food Chain and Food Webkheshin80No ratings yet
- Case of The Missing Maths TeacherDocument37 pagesCase of The Missing Maths TeacherMurely PonnusamyNo ratings yet
- English SPM Module 1Document18 pagesEnglish SPM Module 1Mohd Yusoff TahirNo ratings yet
- Mid Year Exam Form1 2018 NewDocument10 pagesMid Year Exam Form1 2018 NewMiera MijiNo ratings yet
- Modul Bahasa Inggeris Tahun 6 2020 SK Taman SamudraDocument18 pagesModul Bahasa Inggeris Tahun 6 2020 SK Taman SamudraNur Syaheela Binti ZamriNo ratings yet
- Rekod Perkembangan Murid Science DLP Year 4Document23 pagesRekod Perkembangan Murid Science DLP Year 4Nur HidayahNo ratings yet
- Writing Module For GalusDocument188 pagesWriting Module For GalusLOWNo ratings yet
- Year 3 English Paper 1 AnswersDocument10 pagesYear 3 English Paper 1 AnswersHakmarizan Agil100% (1)
- Science Year 3 Daily Lesson PlanDocument1 pageScience Year 3 Daily Lesson PlanConan X-File100% (1)
- English Remedial ModuleDocument27 pagesEnglish Remedial ModuleRenuga SangaranNo ratings yet
- Institut Pendidikan Guru Jurnal Reflektif Mingguan: (Simpan Dalam Portfolio)Document2 pagesInstitut Pendidikan Guru Jurnal Reflektif Mingguan: (Simpan Dalam Portfolio)Muhammad SyahmiNo ratings yet
- Form 1 Exam PT3 FormattedDocument8 pagesForm 1 Exam PT3 FormattedMohd Hazrin Bin HarunNo ratings yet
- Year 4 English 3Document12 pagesYear 4 English 3NG WEE LUN MoeNo ratings yet
- Form 2 Lesson 70 Enrichment ActivityDocument2 pagesForm 2 Lesson 70 Enrichment ActivityMummy HartiniNo ratings yet
- Teaching and Learning Module KSSR (Semakan 2017) Science Year 5Document180 pagesTeaching and Learning Module KSSR (Semakan 2017) Science Year 5mijnqNo ratings yet
- Sains - Tahun 6 (English)Document46 pagesSains - Tahun 6 (English)Sekolah Portal96% (24)
- Daily Lesson Plan for English ClassDocument11 pagesDaily Lesson Plan for English ClassMuhammad Aliff Abdul Rahman100% (1)
- F1-C1 Intro To ScienceDocument190 pagesF1-C1 Intro To SciencejayaletchumiNo ratings yet
- Reflection Attendance: - / - / - Pupils Were Able To Achieve The ObjectivesDocument6 pagesReflection Attendance: - / - / - Pupils Were Able To Achieve The ObjectivesfarahNo ratings yet
- Soalan Bahasa Inggeris Tahun 6 Ujian 1 Bulan Mac 2018 PEMAHAMANDocument13 pagesSoalan Bahasa Inggeris Tahun 6 Ujian 1 Bulan Mac 2018 PEMAHAMANohmypradaNo ratings yet
- Soalan Matematik Tahun 3 Penilaian 1Document5 pagesSoalan Matematik Tahun 3 Penilaian 1norizan bt awang100% (2)
- Mathematics: Year 3 - Mix Paper (1 & 2) Monthly Test AUGUST 2010Document8 pagesMathematics: Year 3 - Mix Paper (1 & 2) Monthly Test AUGUST 2010Ismail Bin SuhaiNo ratings yet
- Uasa Year 1Document11 pagesUasa Year 1Adilla M. MokhtaruddinNo ratings yet
- DSKP Science Year 6 KSSRDocument86 pagesDSKP Science Year 6 KSSRSofiah Mohd Amir0% (1)
- Docslide - Us Upsr Paper 2 Section A ExerciseDocument1 pageDocslide - Us Upsr Paper 2 Section A ExerciseNor Nadia Hanim ThyeNo ratings yet
- Science Year 4 Paper 1Document15 pagesScience Year 4 Paper 1NormaNo ratings yet
- UJIAN AKHIR SESI AKADEMIK YEAR 3 ENGLISHDocument11 pagesUJIAN AKHIR SESI AKADEMIK YEAR 3 ENGLISHDEVI ALIP KPM-GuruNo ratings yet
- Learn Animal Facts FastDocument14 pagesLearn Animal Facts FastWan Rahanah KhalidNo ratings yet
- Listening to Ghost StoriesDocument12 pagesListening to Ghost Storieswan fazrinNo ratings yet
- Graphic Novel AnalysisDocument33 pagesGraphic Novel AnalysisYeohASeeNo ratings yet
- UPSR English Paper TipsDocument15 pagesUPSR English Paper TipsAl ShamyNo ratings yet
- Paper 2 Science UPSR PMR Answering TechniqueDocument4 pagesPaper 2 Science UPSR PMR Answering Techniquekalaivani_kvNo ratings yet
- 7 Julai RPH Tahun 5-HeatDocument5 pages7 Julai RPH Tahun 5-Heatonesnia88No ratings yet
- Food Tests to Identify Starch, Glucose, Protein and FatDocument3 pagesFood Tests to Identify Starch, Glucose, Protein and FatNursabiha Che MazlanNo ratings yet
- 4p Note Expansion - Sample EssayDocument27 pages4p Note Expansion - Sample EssayAkil NohNo ratings yet
- Rancangan Pengajaran Tahunan Form 1 Science DLP 2021Document19 pagesRancangan Pengajaran Tahunan Form 1 Science DLP 2021SITI SHAHARZAD BINTI WAHAB MoeNo ratings yet
- Latihan PKP Tolak Tahun 1 DLPDocument8 pagesLatihan PKP Tolak Tahun 1 DLPNoraini Abu SepianNo ratings yet
- Year 4 UASA ENGLISH MODEL 5 SETS + ANSWERSDocument45 pagesYear 4 UASA ENGLISH MODEL 5 SETS + ANSWERSPHANG YEEN CHENG Moe100% (2)
- Modul Peka Science Year 6 1 5 JawapanDocument11 pagesModul Peka Science Year 6 1 5 JawapanGeez MaruwanNo ratings yet
- Name: Class: . SCHOOLDocument3 pagesName: Class: . SCHOOLfakhrulfathiNo ratings yet
- 8 de 6 2021Document1 page8 de 6 2021yomika pathiranageNo ratings yet
- WORKSHEET - Feb 22-26Document7 pagesWORKSHEET - Feb 22-26Ngô Kim ChungNo ratings yet
- First Term Exam Science g3Document4 pagesFirst Term Exam Science g3a7med3beed888No ratings yet
- 8 Inter Second Assessment Second Sem 2013Document7 pages8 Inter Second Assessment Second Sem 2013deemahNo ratings yet
- Upsa New Sains - Tahun6Document16 pagesUpsa New Sains - Tahun6puvanesweranNo ratings yet
- 8 de 2 2022Document1 page8 de 2 2022yomika pathiranageNo ratings yet
- Ar2 Science Year 4 Paper 2Document10 pagesAr2 Science Year 4 Paper 2Thevi Sinaya100% (1)
- Devoir de Contrôle N°2: Niveau: 9Document4 pagesDevoir de Contrôle N°2: Niveau: 9Elizabeth CerqueiraNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument6 pagesScienceNimesh BaboolallNo ratings yet
- Happy Science EMDocument88 pagesHappy Science EMOhasa PereraNo ratings yet
- Test DiversityDocument6 pagesTest DiversityKirstie KJSNo ratings yet
- Peka SC Year 5Document14 pagesPeka SC Year 5Ruzz Man100% (1)
- Biodiversity and sustainable agriculture questionsDocument8 pagesBiodiversity and sustainable agriculture questionsLiyana RahimNo ratings yet
- Practise Science Key Stage 2 TestDocument15 pagesPractise Science Key Stage 2 TestYee MeiNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1 Center Progression Test Science Stage 2: Invertebrate Animals: Vertebrate AnimalsDocument5 pagesExercise 1 Center Progression Test Science Stage 2: Invertebrate Animals: Vertebrate AnimalsonniNo ratings yet
- III M Bio p6 16Document8 pagesIII M Bio p6 16gnanabalanNo ratings yet
- Hots SainsDocument51 pagesHots SainsRiduan SeliminNo ratings yet
- Sains Upsr 2008Document35 pagesSains Upsr 2008Helyza HayesNo ratings yet
- Skema Jawapan PKBS2 - 2011Document3 pagesSkema Jawapan PKBS2 - 2011Helyza HayesNo ratings yet
- Sewing Two Pieces TogetherDocument13 pagesSewing Two Pieces TogetherHelyza HayesNo ratings yet
- Interview ReportDocument28 pagesInterview ReportHelyza HayesNo ratings yet
- Yearly Plan For Year 5 ScienceDocument14 pagesYearly Plan For Year 5 ScienceHelyza HayesNo ratings yet
- Assgmt 2 EnglishDocument13 pagesAssgmt 2 EnglishHelyza HayesNo ratings yet
- Percubaan UPSR 2011 Kelantan (BHG A & B) - NewDocument23 pagesPercubaan UPSR 2011 Kelantan (BHG A & B) - NewAini DanNo ratings yet
- Trial Upsr 2011 SC Answer KLDocument2 pagesTrial Upsr 2011 SC Answer KLSamsul IrwanNo ratings yet
- JSU PKBS 2 Tahun 5 - 2011Document2 pagesJSU PKBS 2 Tahun 5 - 2011Helyza HayesNo ratings yet
- English 1 Year 1 (Pkbs 2) 2011Document9 pagesEnglish 1 Year 1 (Pkbs 2) 2011Helyza HayesNo ratings yet
- English 2 Year 1 (Pkbs 2) 2011Document9 pagesEnglish 2 Year 1 (Pkbs 2) 2011Helyza HayesNo ratings yet
- Science Yearly Plan Year Two 2010 Theme: Learning AboutDocument11 pagesScience Yearly Plan Year Two 2010 Theme: Learning AboutHelyza HayesNo ratings yet
- Ujian Pengesanan 1 (Year 6)Document2 pagesUjian Pengesanan 1 (Year 6)Helyza HayesNo ratings yet
- Mind Mapping Year 5 Modul CemerlangDocument45 pagesMind Mapping Year 5 Modul CemerlangHelyza Hayes100% (2)
- Mind Mapping Yaer 6 Modul CemerlangDocument21 pagesMind Mapping Yaer 6 Modul CemerlangHelyza Hayes100% (3)
- Mind Mapping Year 4 Modul CemerlangDocument26 pagesMind Mapping Year 4 Modul CemerlangHelyza Hayes100% (1)
- Science Yearly Plan Year One 2010 Theme: Learning AboutDocument11 pagesScience Yearly Plan Year One 2010 Theme: Learning AboutHelyza HayesNo ratings yet
- Modul Cemerlang Set 5 (B)Document5 pagesModul Cemerlang Set 5 (B)Helyza HayesNo ratings yet
- Modul Cemerlang Set 4 (B)Document5 pagesModul Cemerlang Set 4 (B)Helyza HayesNo ratings yet
- Technology Year 6Document7 pagesTechnology Year 6Helyza HayesNo ratings yet
- Modul Cemerlang Set 3 (B)Document4 pagesModul Cemerlang Set 3 (B)Helyza HayesNo ratings yet
- Earth & Universe Year 6Document4 pagesEarth & Universe Year 6Helyza HayesNo ratings yet
- Modul Cemerlang Set 2 (B)Document7 pagesModul Cemerlang Set 2 (B)Helyza HayesNo ratings yet
- Technology Year 5Document9 pagesTechnology Year 5Helyza HayesNo ratings yet
- Materials Year 6Document6 pagesMaterials Year 6Helyza HayesNo ratings yet
- Modul Cemerlang Set 1 (B)Document7 pagesModul Cemerlang Set 1 (B)Helyza HayesNo ratings yet
- Technology Year 4Document7 pagesTechnology Year 4Helyza HayesNo ratings yet
- Earth & Universe Year 5Document6 pagesEarth & Universe Year 5Helyza HayesNo ratings yet
- Earth & Universe Year 4Document7 pagesEarth & Universe Year 4Helyza HayesNo ratings yet
- GRADE 8 English Lesson on Indian LiteratureDocument3 pagesGRADE 8 English Lesson on Indian LiteratureErold TarvinaNo ratings yet
- 20 Reasons Composers Fail 2019 Reprint PDFDocument30 pages20 Reasons Composers Fail 2019 Reprint PDFAlejandroNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Mass Communication Solved MCQs (Set-3)Document5 pagesIntroduction To Mass Communication Solved MCQs (Set-3)Abdul karim MagsiNo ratings yet
- APSEC Summary of Items Discussed in 4/2020 APSEC ForumDocument15 pagesAPSEC Summary of Items Discussed in 4/2020 APSEC Forumyuki michaelNo ratings yet
- Homeroom Guidance - Activity For Module 1Document3 pagesHomeroom Guidance - Activity For Module 1Iceberg Lettuce0% (1)
- Lecture1 SEODocument24 pagesLecture1 SEOUsman AnwarNo ratings yet
- 1 PPT - Pavement of Bricks and TilesDocument11 pages1 PPT - Pavement of Bricks and TilesBHANUSAIJAYASRINo ratings yet
- Evoe Spring Spa Targeting Climbers with Affordable WellnessDocument7 pagesEvoe Spring Spa Targeting Climbers with Affordable WellnessKenny AlphaNo ratings yet
- Creating Early Learning Environments PDFDocument25 pagesCreating Early Learning Environments PDFkrisnahNo ratings yet
- People V Gona Phil 54 Phil 605Document1 pagePeople V Gona Phil 54 Phil 605Carly GraceNo ratings yet
- Ramesh Dargond Shine Commerce Classes NotesDocument11 pagesRamesh Dargond Shine Commerce Classes NotesRajath KumarNo ratings yet
- CFA三级百题 答案Document163 pagesCFA三级百题 答案vxm9pctmrrNo ratings yet
- BRT vs Light Rail Costs: Which is Cheaper to OperateDocument11 pagesBRT vs Light Rail Costs: Which is Cheaper to Operatejas rovelo50% (2)
- PDF To Sas DatasetsDocument6 pagesPDF To Sas DatasetsSiri KothaNo ratings yet
- W220 Engine Block, Oil Sump and Cylinder Liner DetailsDocument21 pagesW220 Engine Block, Oil Sump and Cylinder Liner DetailssezarNo ratings yet
- Apexocardiograma Precizari PracticeDocument12 pagesApexocardiograma Precizari PracticeDaniel VelciuNo ratings yet
- Life Stories and Travel UnitDocument3 pagesLife Stories and Travel UnitSamuel MatsinheNo ratings yet
- Bravo Jr. v. BorjaDocument2 pagesBravo Jr. v. BorjaMaria AnalynNo ratings yet
- KG Technologies Inc Metric: K119X-DX024P-1AT-90A-C399Document2 pagesKG Technologies Inc Metric: K119X-DX024P-1AT-90A-C399Bhushan PAwarNo ratings yet
- Global GovernanceDocument20 pagesGlobal GovernanceSed LenNo ratings yet
- Intertrigo and Secondary Skin InfectionsDocument5 pagesIntertrigo and Secondary Skin Infectionskhalizamaulina100% (1)
- BSP Memorandum No. M-2022-035Document1 pageBSP Memorandum No. M-2022-035Gleim Brean EranNo ratings yet
- Modification of Core Beliefs in Cognitive TherapyDocument19 pagesModification of Core Beliefs in Cognitive TherapysalalepeNo ratings yet
- Dislocating The Sign: Toward A Translocal Feminist Politics of TranslationDocument8 pagesDislocating The Sign: Toward A Translocal Feminist Politics of TranslationArlene RicoldiNo ratings yet
- 5.1 Physical Farming Constraints in Southern CaliforniaDocument1 page5.1 Physical Farming Constraints in Southern CaliforniaTom ChiuNo ratings yet
- Short EssayDocument3 pagesShort EssayBlue PuppyNo ratings yet
- A Study On Effectiveness of Ware Housing System in Flyton XpressDocument23 pagesA Study On Effectiveness of Ware Housing System in Flyton XpressmaheshNo ratings yet
- Orbit BioscientificDocument2 pagesOrbit BioscientificSales Nandi PrintsNo ratings yet
- 8086 ProgramsDocument61 pages8086 ProgramsBmanNo ratings yet
- Boeing 7E7 - UV6426-XLS-ENGDocument85 pagesBoeing 7E7 - UV6426-XLS-ENGjk kumarNo ratings yet