Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bluetooth Technology: Ankit Vashishtha 200201017 Sunny Gupta 200201073
Uploaded by
ainugiri0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
268 views17 pagesMajor telecom companies formed Bluetooth SIG to develop interoperable, cross platform applications. 2000+ members in SIG Development Center Global headquarters in bellevue, washington, USA. Present applications wireless keyboards, mouse, USB adapter, modems, pc cards. Data transfer. Headsets, music players. GPS receiver. Data sharing. Gaming. Barcode scanner.
Original Description:
Original Title
Bluetooth
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentMajor telecom companies formed Bluetooth SIG to develop interoperable, cross platform applications. 2000+ members in SIG Development Center Global headquarters in bellevue, washington, USA. Present applications wireless keyboards, mouse, USB adapter, modems, pc cards. Data transfer. Headsets, music players. GPS receiver. Data sharing. Gaming. Barcode scanner.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
268 views17 pagesBluetooth Technology: Ankit Vashishtha 200201017 Sunny Gupta 200201073
Uploaded by
ainugiriMajor telecom companies formed Bluetooth SIG to develop interoperable, cross platform applications. 2000+ members in SIG Development Center Global headquarters in bellevue, washington, USA. Present applications wireless keyboards, mouse, USB adapter, modems, pc cards. Data transfer. Headsets, music players. GPS receiver. Data sharing. Gaming. Barcode scanner.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 17
Bluetooth Technology
Ankit Vashishtha 200201017
Sunny Gupta 200201073
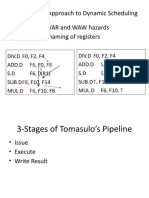
Why Bluetooth ?
• It’s wireless.
• It’s simple.
• It’s inexpensive.
• Open platform.
• Provision for both voice and data.
Development History
• Project started in 1995 by Swedish
telecommunications manufacturer LM
Ericsson.
• In 1998 major telecom companies formed
Bluetooth SIG to develop interoperable,
cross platform applications.
• 2000+ members in SIG
Development Center
• Global headquarters in Bellevue,
Washington, USA.
• Major promoters companies include
Ericsson, IBM, Intel, Microsoft, Motorola,
Nokia and Toshiba.
• SIG has several working groups working on
various projects.
Bluetooth vs. Infrared
• Infrared is line of sight and one-to-one.
• Its advantage
– Low interference, reliable transfer.
Technology Used
• Radio Frequency at 2.45 GHz.
• This is internationally agreed frequency for
Bluetooth.
• Very low signal power ( ~1mw )
• Operation range around 10m.
• Omni directional signals and can pass
through walls and briefcases.
Working of Bluetooth
• Auto conversation between Bluetooth enabled
devices.
• Formation of personal area network (PAN) or
piconet.
• Spread-spectrum frequency hopping.
• Device works on 79 individual, random frequency
within a designated range.
• Transmitter changes 1600 frequencies/sec.
• Data rate upto 1 Mbitsps.
Typical Bluetooth Networks
Working (cont…)
• Inquire
• Page
• Establish a link using Link Manager Protocol
• Discover services using SDP
• Create a channel
• Authenticate
• Send and receive data
Avoiding Interference
• Many applications and devices work
independently in same area without
interference.
• Low Power
• Frequency Hopping
• Software for correcting small errors.
Present applications
• Wireless keyboards, mouse, USB adapter,
modems, pc cards.
• File transfer.
• Headsets, music players.
• GPS receiver.
• Data sharing.
• Gaming.
• Barcode scanner.
Future applications
• Home networking for convenient, safe and
secure house.
• Retail and Mobile e-Commerce.
• Travel
– Ticket less travel, Hotel industry
• Medical
– remote patient monitoring, wireless biometric
data.
Future applications (cont..)
• Automotive Industry
– activating garage doors, and home lighting and
heating systems.
• Bluetooth Messaging.
Bluetooth Security
• 3 modes of communication
– Mode 1 or Insecure mode
– Mode 2 is known as service-level enforced
security
– Mode 3 is known as link-level enforced
security
Bluetooth security (cont..)
• Security is provided in three ways
– pseudo-random frequency hopping
– authentication
– encryption.
Bluetooth Security (cont..)
• Security issues
– Bluejacking
– Bluebugging
– Bluesnarfing
– Cabir Worm
Sensor Network and Bluetooth
• Wide application of Bluetooth technology
in Sensor Area Network (SAN)
• Environment Monitoring, Agriculture,
Security, Infrastructure health
• Research for energy conservation in
Bluetooth senor network
You might also like
- Transmission Lines and Wave Guides Ec 1305Document27 pagesTransmission Lines and Wave Guides Ec 1305ainugiri67% (3)
- LCT APT NPT-1200 ConfigurationDocument23 pagesLCT APT NPT-1200 ConfigurationJaime Garcia De ParedesNo ratings yet
- Network Security Bangla BookDocument69 pagesNetwork Security Bangla BookMd Nurul Islam75% (8)
- Fundamentals of MIMO Wireless CommunicationsDocument371 pagesFundamentals of MIMO Wireless CommunicationsYuvaraj BaskaranNo ratings yet
- Bluetooth: Wire Less TechnologyDocument13 pagesBluetooth: Wire Less Technologykrishna495No ratings yet
- Bluetooth TechnologiesDocument21 pagesBluetooth TechnologiespoojaqNo ratings yet
- A Seminar Presentation On: Bluetooth TechnologyDocument15 pagesA Seminar Presentation On: Bluetooth TechnologyAshish GoelNo ratings yet
- BLUETOOTH SECURITY BY Jim BurleyDocument11 pagesBLUETOOTH SECURITY BY Jim BurleyHanmanthNo ratings yet
- Bluetooth: Presenters: Group 6Document31 pagesBluetooth: Presenters: Group 6Sumit KhilariNo ratings yet
- Bluetooth Based Wireless Sensor NetworksDocument50 pagesBluetooth Based Wireless Sensor NetworksDegusa PatelNo ratings yet
- 5G The NanocoreDocument35 pages5G The NanocoreKhushboo Soni100% (1)
- Bluetooth PresentatioDocument17 pagesBluetooth PresentatioCHNo ratings yet
- WINSEM2022-23 CSE3009 ETH VL2022230503000 2023-02-02 Reference-Material-IDocument54 pagesWINSEM2022-23 CSE3009 ETH VL2022230503000 2023-02-02 Reference-Material-IArvind KumarNo ratings yet
- Bluetooth Technology Prepared By: SunilDocument32 pagesBluetooth Technology Prepared By: SunilSurya6556No ratings yet
- Bluetooth DelatorreDocument11 pagesBluetooth DelatorreGinu Rodavia Dela TorreNo ratings yet
- Bluetooth SecurityDocument72 pagesBluetooth SecurityPalash BalaniNo ratings yet
- Bluetooth Technology: Mohamed Ahmed and MuazDocument29 pagesBluetooth Technology: Mohamed Ahmed and MuazHonest ManNo ratings yet
- Bluetooth SecurityDocument72 pagesBluetooth Securityabhi_badNo ratings yet
- Bluetooh Based Smart Sensor Networks - PresentationDocument27 pagesBluetooh Based Smart Sensor Networks - PresentationTarandeep Singh100% (7)
- BluetoothDocument13 pagesBluetoothvamsi_battu1No ratings yet
- Wireless Communication Bluetooth TechnologyDocument22 pagesWireless Communication Bluetooth Technologyhima_intNo ratings yet
- Bluetooth 121219060937 Phpapp01Document15 pagesBluetooth 121219060937 Phpapp01Rit HoanNo ratings yet
- By Naga Santhan Reddy.D: Wireless Networks-Bluetooth TechnologyDocument20 pagesBy Naga Santhan Reddy.D: Wireless Networks-Bluetooth TechnologyRaghava SaiNo ratings yet
- Abstract:: A Technology For FutureDocument20 pagesAbstract:: A Technology For FuturesahoonirojNo ratings yet
- Bluetooth Technology: Ashutosh Chauhan ROLL NO-090103055Document18 pagesBluetooth Technology: Ashutosh Chauhan ROLL NO-090103055Saurabh YadavNo ratings yet
- Bluetooth TechnologyDocument22 pagesBluetooth TechnologyShubhu Lubz NaanuNo ratings yet
- Bluetooth Voice Communication Interference With Ieee 802.11 ModelingDocument72 pagesBluetooth Voice Communication Interference With Ieee 802.11 ModelingHaruna TofaNo ratings yet
- Infrared and Bluetooth Technology: Prepared By:-Guided ByDocument25 pagesInfrared and Bluetooth Technology: Prepared By:-Guided Byvijay jethavaNo ratings yet
- BluetoothDocument17 pagesBluetoothmritunjayNo ratings yet
- Ch3. ConnectivityDocument70 pagesCh3. ConnectivityMohan RajNo ratings yet
- BluetoothDocument18 pagesBluetoothsiba_sagarNo ratings yet
- Bluetooth SecurityDocument34 pagesBluetooth SecurityGanesh KwaradiNo ratings yet
- Respected Ma'am & Dear FriendsDocument13 pagesRespected Ma'am & Dear Friendsagrawal_ruchi8No ratings yet
- BluejackingDocument28 pagesBluejackingSumaiya KauserNo ratings yet
- Bluetooth Technology: A Gift of TechnologyDocument27 pagesBluetooth Technology: A Gift of TechnologySai Kiran Nomula0% (1)
- Seminar TopicsDocument15 pagesSeminar TopicsUsha MarigoudarNo ratings yet
- Respected Ma'am & Dear FriendsDocument14 pagesRespected Ma'am & Dear FriendsKrishnakant Singh BhadoriaNo ratings yet
- Bluetooth Technology: A Gift of TechnologyDocument24 pagesBluetooth Technology: A Gift of TechnologySumit KumarNo ratings yet
- Respected Ma'am & Dear FriendsDocument14 pagesRespected Ma'am & Dear FriendsVaibhav SinghNo ratings yet
- Principles of Digital Communications: Majd Hallak 170701119Document30 pagesPrinciples of Digital Communications: Majd Hallak 170701119Majd Hallak100% (1)
- This Presentation Is Under Guidance Of:-Mr Praveen Kumar Singh Sir Miss Vineeta Gurjar MamDocument14 pagesThis Presentation Is Under Guidance Of:-Mr Praveen Kumar Singh Sir Miss Vineeta Gurjar MamDeomani PandeyNo ratings yet
- Lecture7 WirelessDocument31 pagesLecture7 WirelessndanghaoNo ratings yet
- Lecture10 WirelessDocument34 pagesLecture10 WirelessDr PNo ratings yet
- BluetoothDocument17 pagesBluetoothSashank D ChampNo ratings yet
- Batch2 - 31-35 - Cloud Storage and Communication Techniques For IoT SystemsDocument28 pagesBatch2 - 31-35 - Cloud Storage and Communication Techniques For IoT SystemsVaibhavNo ratings yet
- Bluetooth Technology PresentationDocument29 pagesBluetooth Technology PresentationMihai BogdanNo ratings yet
- Wireless CommunicationDocument20 pagesWireless CommunicationAradhana MehraNo ratings yet
- BLUETOOTH TECHNOLOGY SeminorDocument17 pagesBLUETOOTH TECHNOLOGY Seminorchanda SindhuraNo ratings yet
- Bluetooth Based Sensor Network: A Technical Seminar Presentation OnDocument17 pagesBluetooth Based Sensor Network: A Technical Seminar Presentation OnDipak AryalNo ratings yet
- Mobile Communications: Summer Term 2008Document31 pagesMobile Communications: Summer Term 2008Vivekanandhan VijayanNo ratings yet
- FAJEMILUYI SAMUEL Seminar ReportDocument27 pagesFAJEMILUYI SAMUEL Seminar ReportBobby ZackNo ratings yet
- Bluetooth PrakashDocument18 pagesBluetooth PrakashLoverboy6556No ratings yet
- Bluetooth Technology DakharaDocument8 pagesBluetooth Technology DakharaDakhara PradipNo ratings yet
- Bluetooth Based Smart Sensor Networks 14 JUy5nIZDocument21 pagesBluetooth Based Smart Sensor Networks 14 JUy5nIZitsmeyourlover01No ratings yet
- Respected Ma'am & Dear FriendsDocument14 pagesRespected Ma'am & Dear Friendsarya2aryaNo ratings yet
- Wifi BT Zigbee NFCDocument37 pagesWifi BT Zigbee NFCJadTahhanNo ratings yet
- WNF Wpan 4Document17 pagesWNF Wpan 4oobaa bbbssaNo ratings yet
- Mobile Computing: PresentationDocument16 pagesMobile Computing: Presentationreach2ghoshNo ratings yet
- CN IntroductionDocument73 pagesCN Introductionpatela1No ratings yet
- Subject Computer Network: Prepared by Prof.A.H.RokadeDocument31 pagesSubject Computer Network: Prepared by Prof.A.H.Rokadesandhya bhujbalNo ratings yet
- Building the Internet of Things with IPv6 and MIPv6: The Evolving World of M2M CommunicationsFrom EverandBuilding the Internet of Things with IPv6 and MIPv6: The Evolving World of M2M CommunicationsNo ratings yet
- GPRS and 3G Wireless Applications: Professional Developer's GuideFrom EverandGPRS and 3G Wireless Applications: Professional Developer's GuideRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- Securing VoIP: Keeping Your VoIP Network SafeFrom EverandSecuring VoIP: Keeping Your VoIP Network SafeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Ge6075 Professional Ethics in EngineeringDocument47 pagesGe6075 Professional Ethics in Engineeringainugiri100% (1)
- CS1601 Computer ArchitectureDocument389 pagesCS1601 Computer Architectureainugiri100% (1)
- Updates Resume Giri PrasadDocument4 pagesUpdates Resume Giri PrasadainugiriNo ratings yet
- Wireless Local Area NetworkDocument331 pagesWireless Local Area Networkainugiri100% (2)
- CS1623 Mobile Communication Dr. Hari's Question Bank Part ADocument6 pagesCS1623 Mobile Communication Dr. Hari's Question Bank Part AainugiriNo ratings yet
- Random Access Memory and ProblemsDocument89 pagesRandom Access Memory and ProblemsainugiriNo ratings yet
- Computer ArchitectureDocument100 pagesComputer ArchitectureainugiriNo ratings yet
- When A New Line Is Loaded Into The Cache, OneDocument2 pagesWhen A New Line Is Loaded Into The Cache, OneainugiriNo ratings yet
- Theoretical Study of Cache Systems: Dmitry DolgikhDocument17 pagesTheoretical Study of Cache Systems: Dmitry DolgikhainugiriNo ratings yet
- 07 11 04Document224 pages07 11 04xenocid3rNo ratings yet
- Memory Hierarchy and Cache ManagementDocument100 pagesMemory Hierarchy and Cache ManagementainugiriNo ratings yet
- SortingDocument24 pagesSortingainugiri0% (1)
- The Anatomy of The GridDocument2 pagesThe Anatomy of The GridainugiriNo ratings yet
- RTP TutorialDocument85 pagesRTP Tutorialainugiri100% (3)
- RTP SlidesDocument42 pagesRTP Slidesainugiri0% (1)
- SdarticleDocument9 pagesSdarticleainugiriNo ratings yet
- Sockets NotesDocument15 pagesSockets Notesom18sahuNo ratings yet
- Cache FundamentalsDocument4 pagesCache FundamentalsainugiriNo ratings yet
- SDocument4 pagesSainugiriNo ratings yet
- Peterson's Algorithm in A Multi Agent Database SystemDocument14 pagesPeterson's Algorithm in A Multi Agent Database SystemainugiriNo ratings yet
- Question Bank CS1601Document19 pagesQuestion Bank CS1601ainugiriNo ratings yet
- Peterson's Algorithm in A Multi Agent Database SystemDocument14 pagesPeterson's Algorithm in A Multi Agent Database SystemainugiriNo ratings yet
- EC1402 Optical CommunicationDocument25 pagesEC1402 Optical CommunicationarunecethebossNo ratings yet
- Microwave Engineering Ec 432Document25 pagesMicrowave Engineering Ec 432ainugiriNo ratings yet
- PHD Thesis Ef Cient Algorithms For Sorting andDocument115 pagesPHD Thesis Ef Cient Algorithms For Sorting andGabryel BogdanNo ratings yet
- Nist SP 800-48Document119 pagesNist SP 800-48Shukur MohammedNo ratings yet
- Notification InstructionsDocument5 pagesNotification InstructionsainugiriNo ratings yet
- MG 1351 - Principles of ManagementDocument15 pagesMG 1351 - Principles of ManagementainugiriNo ratings yet
- Memtech 2005 Am 09Document15 pagesMemtech 2005 Am 09ainugiriNo ratings yet
- Practical Design For Transferring Signals Between Clock DomainsDocument4 pagesPractical Design For Transferring Signals Between Clock DomainsbikirangNo ratings yet
- ABB Servomotors Manual 02 - 0310e 8c SeriesDocument74 pagesABB Servomotors Manual 02 - 0310e 8c SeriesmelanitisNo ratings yet
- Hping3 ExamplesDocument5 pagesHping3 ExamplesfakefaultNo ratings yet
- Module 3Document71 pagesModule 3nandiniNo ratings yet
- Unit Iii Routing Routing (RIP, OSPF, and Metrics)Document17 pagesUnit Iii Routing Routing (RIP, OSPF, and Metrics)akashNo ratings yet
- VPN HackingDocument6 pagesVPN HackingGayan MadushankaNo ratings yet
- Anus Naseem - Jan 2019Document4 pagesAnus Naseem - Jan 2019Anus NaseemNo ratings yet
- HP Scan Setup Wizard v1.1.0.30: User GuideDocument24 pagesHP Scan Setup Wizard v1.1.0.30: User GuidesamantharathnasiriNo ratings yet
- Thinkserver Config Raid 100 ts140 ts440 TR PDFDocument24 pagesThinkserver Config Raid 100 ts140 ts440 TR PDFnizamNo ratings yet
- Platinum 2.5K Fault Recorder - RochesterDocument2 pagesPlatinum 2.5K Fault Recorder - RochesterAyyanar NeyanNo ratings yet
- MicroPoint II Data Sheet enDocument4 pagesMicroPoint II Data Sheet enYohannes ArefayneNo ratings yet
- Autobus 36 - Nedzarici - Naselje AerodromDocument2 pagesAutobus 36 - Nedzarici - Naselje AerodromededovicNo ratings yet
- 02 EtherCAT Introduction PDFDocument95 pages02 EtherCAT Introduction PDFPablo Andrés Sanhueza CarvajalNo ratings yet
- WDM 4.8 Installation Guide JUL2010Document50 pagesWDM 4.8 Installation Guide JUL2010oldgifferNo ratings yet
- ISO27001 Compliance With NetwrixDocument27 pagesISO27001 Compliance With Netwrixnomad6666No ratings yet
- Firewall ProcedureDocument17 pagesFirewall ProcedurejldtecnoNo ratings yet
- Lab - Securing The Router For Administrative Access: Taller 2Document28 pagesLab - Securing The Router For Administrative Access: Taller 2murcielago189No ratings yet
- Zte Umts Ur15 Enhanced DL Cell - Fach Feature GuideDocument40 pagesZte Umts Ur15 Enhanced DL Cell - Fach Feature GuideSherinPmNo ratings yet
- IT6223BDocument14 pagesIT6223BTREMsZ GAMINGNo ratings yet
- CAN Interface For FMS General: Important!Document12 pagesCAN Interface For FMS General: Important!Daniel Henrique PiovesaniNo ratings yet
- Ec8004-Wireless Networks - HandoutsDocument30 pagesEc8004-Wireless Networks - HandoutsGtecEceNo ratings yet
- Fadli (Bahasa Inggris)Document30 pagesFadli (Bahasa Inggris)ChikalNo ratings yet
- TIBCO Adapter For LDAP - User's GuideDocument272 pagesTIBCO Adapter For LDAP - User's GuideNaveenNo ratings yet
- NBD8025R UlDocument1 pageNBD8025R UlНастя паюшинаNo ratings yet
- Hybrid Port KnockingDocument16 pagesHybrid Port KnockingPrasanna Reddy100% (1)
- Guide HP SR DashDocument38 pagesGuide HP SR Dashfranc_estorsNo ratings yet
- ISDP Sample - FinalsDocument25 pagesISDP Sample - FinalsJunskhie Yap0% (1)