Professional Documents
Culture Documents
This Presentation Is Under Guidance Of:-Mr Praveen Kumar Singh Sir Miss Vineeta Gurjar Mam
Uploaded by
Deomani Pandey0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views14 pagesOriginal Title
Bluetooth
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views14 pagesThis Presentation Is Under Guidance Of:-Mr Praveen Kumar Singh Sir Miss Vineeta Gurjar Mam
Uploaded by
Deomani PandeyCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 14
This presentation is under guidance of :-
Mr Praveen Kumar Singh Sir
Miss Vineeta Gurjar Mam
Presented by
CHARU TRIPATHI
5TH SEM,,MECHANICAL BRANCH
Definition of Bluetooth
Bluetooth is a short range (10-100 m)
and low-cost wireless
network system to replace cables and
give RF connection
between consumer devices.
• What is Bluetooth?
o Bluetooth is a short-range wireless communications
technology.
• Why this name?
o It was taken from the 10th century Danish King Harald
Blatand who unified Denmark and Norway.
• When does it appear?
o 1994 – Ericsson study on a wireless technology to link
mobile phones & accessories.
o 5 companies (Ericssn,Nokia,IBM,Toshiba & Intel)joined
to form the Bluetooth Special Interest Group (SIG) in
1998 named.
o First specification released in July 1999.
• Uses the radio range of 2.45 GHz
• Theoretical maximum bandwidth is 1 Mb/s
• Several Bluetooth devices can form an ad
hoc network called a “piconet”
– In a piconet one device acts as a master (sets
frequency hopping behavior) and the others as
slaves
– Example: A conference room with many
laptops wishing to communicate with each
Other
• Laptops
• Cellular phones
• Personal Digital Assistants
• Headsets
• Printers
• Keyboards/mice
• GPS, etc…
• Major use in consumer electronics
• Allows up to 8 devices to communicate in a local
network called a Piconet, also known as a Personal
Area Network or PAN
• Because of its low power consumption, its range is
limited to 10 m.
• However, range can be increased to 100 m by
employing a scatternet topology or a higher powered
antenna
• Three classes of Bluetooth devices
-Class 3 radios – have a range of up to 1 meter or 3
Feet.
-Class 2 radios – most commonly found in mobile
devices – have a range of 10 meters or 30 feet
-Class 1 radios – used primarily in industrial use
cases – have a range of 100 meters or 300 feet
• The Bluetooth standard is maintained and published
by the Bluetooth Special Interest Group (SIG)
• Includes thousands of member companies
• Covers topics such as interoperability, testing and
qualification of bluetooth devices
• Most important, outlines the specifications for:
- Bluetooth Radio
- Baseband
- LMP – Link Manager Protocol
• Responsible for link set-up between devices,
including security functions :
– Authentication
– Encryption
• Infrared IrDA (WPAN) : synchronization, link
between a phone and a laptop…
– Less flexible than Bluetooth, need of a line of site
– Comparable data rate
• Wi-Fi (WLAN) : Wireless LAN access
– Far higher bandwidth and data rate than Bluetooth
– Higher power consumption than Bluetooth
– Requires infrastructure investment
• Success of Bluetooth depends on how well it is
integrated into consumer products
-Consumers are more interested in applications than the
technology
-Bluetooth must be successfully integrated into consumer
-- products
-Must provide benefits for consumer
-Must not destroy current product benefits
• Key Success Factors
-Interoperability
-Mass Production at Low Cost
-Ease of Use
-End User Experience
THANKS FOR YOUR ATTENTION
You might also like
- Respected Ma'am & Dear FriendsDocument14 pagesRespected Ma'am & Dear FriendsKrishnakant Singh BhadoriaNo ratings yet
- Bluetooth: A Short-Range Wireless TechnologyDocument14 pagesBluetooth: A Short-Range Wireless TechnologyVaibhav SinghNo ratings yet
- Respected Ma'am & Dear FriendsDocument13 pagesRespected Ma'am & Dear Friendsagrawal_ruchi8No ratings yet
- Respected Ma'am & Dear FriendsDocument14 pagesRespected Ma'am & Dear Friendsarya2aryaNo ratings yet
- BluetoothDocument13 pagesBluetoothvamsi_battu1No ratings yet
- Presented By: HARMEET, 240 SNEHA, 223Document14 pagesPresented By: HARMEET, 240 SNEHA, 223Sneha MahaverNo ratings yet
- Presented By: Ranjit KoiriDocument9 pagesPresented By: Ranjit KoiriGeetanjali KumariNo ratings yet
- Bluetooth: Wire Less TechnologyDocument13 pagesBluetooth: Wire Less Technologykrishna495No ratings yet
- Bluetooth Technology Prepared By: SunilDocument32 pagesBluetooth Technology Prepared By: SunilSurya6556No ratings yet
- Bluetooth SecurityDocument72 pagesBluetooth SecurityPalash BalaniNo ratings yet
- Bluetooth Voice Communication Interference With Ieee 802.11 ModelingDocument72 pagesBluetooth Voice Communication Interference With Ieee 802.11 ModelingHaruna TofaNo ratings yet
- Bluetooth TechnologyDocument22 pagesBluetooth TechnologyShubhu Lubz NaanuNo ratings yet
- Bluetooth SecurityDocument72 pagesBluetooth Securityabhi_badNo ratings yet
- BT TECHNOLOGY SECURITYDocument34 pagesBT TECHNOLOGY SECURITYGanesh KwaradiNo ratings yet
- Bluetooth Technology: A Wireless RevolutionDocument29 pagesBluetooth Technology: A Wireless RevolutionHonest ManNo ratings yet
- Presentation On BluetoothDocument16 pagesPresentation On BluetoothAshis karmakarNo ratings yet
- An Introduction to Bluetooth TechnologyDocument17 pagesAn Introduction to Bluetooth TechnologyShrijeet PugaliaNo ratings yet
- Seminar Report On BluetoothDocument51 pagesSeminar Report On Bluetoothsunil85% (13)
- Bluetooth Technology DakharaDocument8 pagesBluetooth Technology DakharaDakhara PradipNo ratings yet
- Bluetooth Wireless Tech BriefDocument30 pagesBluetooth Wireless Tech BriefEkta SinghNo ratings yet
- By Naga Santhan Reddy.D: Wireless Networks-Bluetooth TechnologyDocument20 pagesBy Naga Santhan Reddy.D: Wireless Networks-Bluetooth TechnologyRaghava SaiNo ratings yet
- FAJEMILUYI SAMUEL Seminar ReportDocument27 pagesFAJEMILUYI SAMUEL Seminar ReportBobby ZackNo ratings yet
- Bluetooth TechnologiesDocument21 pagesBluetooth TechnologiespoojaqNo ratings yet
- BLUETOOTH SECURITY BY Jim BurleyDocument11 pagesBLUETOOTH SECURITY BY Jim BurleyHanmanthNo ratings yet
- Akanksha Patel: Hod: Dr. Pushpendra Singh Co-Ordinator: MR - Mratyunjay Singh Guided By: Dr. Mohd Tauseef KhanDocument17 pagesAkanksha Patel: Hod: Dr. Pushpendra Singh Co-Ordinator: MR - Mratyunjay Singh Guided By: Dr. Mohd Tauseef Khandeepak mauuNo ratings yet
- Experiment No 3Document5 pagesExperiment No 3Priti RumaoNo ratings yet
- 01 03 01 BluetoothDocument12 pages01 03 01 BluetoothMuhammad HattaNo ratings yet
- A Seminar Presentation On: Bluetooth TechnologyDocument15 pagesA Seminar Presentation On: Bluetooth TechnologyAshish GoelNo ratings yet
- Bluetooth Technology in Wireless Communications: Paper Presentation OnDocument11 pagesBluetooth Technology in Wireless Communications: Paper Presentation Onpraveen_449100% (2)
- Bluetooth: Quote of The DayDocument8 pagesBluetooth: Quote of The DayShahid MehmoodNo ratings yet
- Bluetooth Based Wireless Sensor NetworksDocument50 pagesBluetooth Based Wireless Sensor NetworksDegusa PatelNo ratings yet
- Bluetooth technology - a guide to wireless connectivityDocument4 pagesBluetooth technology - a guide to wireless connectivityIshan ChoubeyNo ratings yet
- BLT LIST OF CONTENTS AND TECHNOLOGY OVERVIEWDocument13 pagesBLT LIST OF CONTENTS AND TECHNOLOGY OVERVIEWBedigi SridharNo ratings yet
- BluetoothDocument17 pagesBluetoothSashank D ChampNo ratings yet
- Bluetooth: Prepared By: Sanjay SinghalDocument14 pagesBluetooth: Prepared By: Sanjay SinghalsanjaysinghalNo ratings yet
- Prajapati Nirav G (Roll No: 1531) : Faculty of Engineering & I.T. Department Gujarat Technological UniversitDocument14 pagesPrajapati Nirav G (Roll No: 1531) : Faculty of Engineering & I.T. Department Gujarat Technological UniversitNirav PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Bluetooth TechnologyDocument48 pagesBluetooth TechnologyAnonymous dClVzfNNo ratings yet
- Bluetooth TechnologyDocument26 pagesBluetooth TechnologyAjay Dagar100% (1)
- History of WirelessDocument7 pagesHistory of WirelessHarshaNo ratings yet
- Overview of Bluetooth TechnologyDocument29 pagesOverview of Bluetooth TechnologyRahul SharmaNo ratings yet
- WC - U4 - S5 - Bluetooth StandardDocument11 pagesWC - U4 - S5 - Bluetooth StandardrkpvvvNo ratings yet
- Prepared By: Sanjay SinghalDocument16 pagesPrepared By: Sanjay SinghalsanjaysinghalNo ratings yet
- Wifi Vs BluetoothDocument17 pagesWifi Vs BluetoothSIVA PRASADNo ratings yet
- Bluetooth Technology ExplainedDocument18 pagesBluetooth Technology ExplainedSaurabh YadavNo ratings yet
- Wireless Communication Bluetooth TechnologyDocument22 pagesWireless Communication Bluetooth Technologyhima_intNo ratings yet
- Wimax PosterDocument9 pagesWimax PosterMukesh SaiNo ratings yet
- Project On Bluetooth Technology: Presented ByDocument9 pagesProject On Bluetooth Technology: Presented BySanjeev Kumar SahuNo ratings yet
- Bluetooth Protocol 1Document10 pagesBluetooth Protocol 1Nida AzizahNo ratings yet
- Bluetooth Seminar Report SummaryDocument16 pagesBluetooth Seminar Report SummarytravelnagaNo ratings yet
- Bluetooth PrakashDocument18 pagesBluetooth PrakashLoverboy6556No ratings yet
- Bluetooth: The Wireless Technology RevolutionDocument8 pagesBluetooth: The Wireless Technology Revolutionmohd shafeeNo ratings yet
- Final Project Data Communication and NetworksDocument19 pagesFinal Project Data Communication and NetworksjanshairkhanNo ratings yet
- Bluetooth Seminar: An Overview of the TechnologyDocument17 pagesBluetooth Seminar: An Overview of the Technologyharivardhanreddy bokkaNo ratings yet
- BluetoothDocument18 pagesBluetoothsiba_sagarNo ratings yet
- WINSEM2022-23 CSE3009 ETH VL2022230503000 2023-02-02 Reference-Material-IDocument54 pagesWINSEM2022-23 CSE3009 ETH VL2022230503000 2023-02-02 Reference-Material-IArvind KumarNo ratings yet
- Bluetooth Seminar: An Overview of the Technology and ApplicationsDocument17 pagesBluetooth Seminar: An Overview of the Technology and ApplicationsmritunjayNo ratings yet
- Bluetooth DelatorreDocument11 pagesBluetooth DelatorreGinu Rodavia Dela TorreNo ratings yet
- Bluetooth (Seminar Report)Document20 pagesBluetooth (Seminar Report)TB88% (8)
- What is Bluetooth? The complete guide to the wireless technology standardDocument4 pagesWhat is Bluetooth? The complete guide to the wireless technology standardArpit SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Errors While Importing Matplotlib:: General FAQ's of Week-3 (PDS)Document5 pagesErrors While Importing Matplotlib:: General FAQ's of Week-3 (PDS)Ragunathan SmgNo ratings yet
- Math 8 Q1 Week 1Document10 pagesMath 8 Q1 Week 1lau dash100% (2)
- PHD Thesis Electrical EngineeringDocument7 pagesPHD Thesis Electrical Engineeringehudyxbaf100% (2)
- An Early Look at The Parler Online Social NetworkDocument8 pagesAn Early Look at The Parler Online Social NetworkGabriel DAnnunzioNo ratings yet
- Introduction To 3d Drawing UpdatedDocument29 pagesIntroduction To 3d Drawing UpdatedSidrak MekuriaNo ratings yet
- Literature Review of Iot Based Plant Watering SystemDocument8 pagesLiterature Review of Iot Based Plant Watering SystemJulie RyneNo ratings yet
- Erp ProposalDocument4 pagesErp ProposalHabibaNo ratings yet
- Liumy LM2001Document36 pagesLiumy LM2001Carles Molins LopezNo ratings yet
- DLL (Intro. To Computer1)Document10 pagesDLL (Intro. To Computer1)mary joyce ariem100% (1)
- Tutorialspoint Examples: How To Use JSON Object in Java?Document2 pagesTutorialspoint Examples: How To Use JSON Object in Java?Khaliq Dawood BuxNo ratings yet
- Assignment1 622Document3 pagesAssignment1 622Vyshnavi ThottempudiNo ratings yet
- IT - Group 3 ProjectDocument90 pagesIT - Group 3 ProjectAmanuel Kassa100% (1)
- Bai Tap Tieng Anh Lop 4 Chuong Trinh Moi Unit 18 What S Your Phone NumberDocument5 pagesBai Tap Tieng Anh Lop 4 Chuong Trinh Moi Unit 18 What S Your Phone NumberDevil -.-No ratings yet
- Digital Electronics FundamentalsDocument109 pagesDigital Electronics FundamentalsBùi Thị HoànNo ratings yet
- Argantix KDC Series 02-2005Document4 pagesArgantix KDC Series 02-2005Hung BushidoNo ratings yet
- Fiducial Markers For Pose EstimationDocument26 pagesFiducial Markers For Pose EstimationÃd ÄmNo ratings yet
- Citra LogDocument9 pagesCitra Logblackszero7No ratings yet
- Respondus Lock Down BrowserDocument2 pagesRespondus Lock Down BrowserDonald MacapazNo ratings yet
- ThesisDocument39 pagesThesisSunidhi MishraNo ratings yet
- Ca Mid1 2017Document9 pagesCa Mid1 2017hruitNo ratings yet
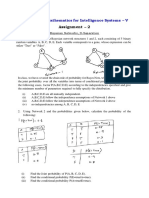
- 19MAT301 - Mathematics For Intelligence Systems - V: Assignment - 2Document4 pages19MAT301 - Mathematics For Intelligence Systems - V: Assignment - 2Blyss BMNo ratings yet
- Mopping Module Design and Experiments of A Multifunction Floor Cleaning RobotDocument6 pagesMopping Module Design and Experiments of A Multifunction Floor Cleaning RobotAntonio MoisesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 03Document41 pagesChapter 03Tuan Anh LeeNo ratings yet
- CNC Turning ExamplesDocument69 pagesCNC Turning ExamplesThenarasumohanvelu100% (2)
- 6sr41 SeriesDocument202 pages6sr41 Seriesfireza husnulNo ratings yet
- 2021-Bateria FE AdolescentesDocument23 pages2021-Bateria FE AdolescentesISABELANo ratings yet
- 3320702Document5 pages3320702glennfreyola0% (1)
- Azure Data and Ai Architect Handbook Adopt A Structured Approach To Designing Data and Ai Solutions at Scale Team Ira 1803234865 9781803234861 CompressDocument284 pagesAzure Data and Ai Architect Handbook Adopt A Structured Approach To Designing Data and Ai Solutions at Scale Team Ira 1803234865 9781803234861 CompresspascalburumeNo ratings yet
- ODiSI 6100 User GuideDocument99 pagesODiSI 6100 User GuideDaniel DarNo ratings yet
- Asynchronous Sequential Circuits: E&CE223 Digital Circuits and SystemsDocument45 pagesAsynchronous Sequential Circuits: E&CE223 Digital Circuits and SystemskirthicaNo ratings yet