Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Kumpulan Berlian
Uploaded by
Jaaizah JaafarCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Kumpulan Berlian
Uploaded by
Jaaizah JaafarCopyright:
Available Formats
(c)
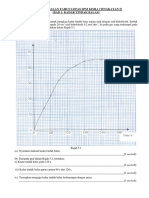
An experiment is carried out to construct an ionic equation for an insoluble salt, lead (II) chromate (VI). A fixed volume of 5.00 cm3 of 1.0 mol dm-3 lead (II) nitrate, Pb(NO3)2 solution is placed into each of the 8 test tubes of the same size. Different volume of 1.0 mol dm-3 potassium chromate (VI), K2CrO4 solution is added to each test tube. The height of the yellow precipitate, lead (II) chromate (VI) formed into each test tube is measured, recorded and plotted in Graph 8. Satu eksperimen dijalankan untuk membina persamaan ion untuk garam tak terlarukan, plumbum (II) kromat(VI). Isipadu tetap 5.00 cm3 1.0 mol dm-3 larutan plumbum(II) nitrat Pb(NO3)2 diisikan ke dalam setiap 8 tabung uji yang sama saiz. Isipadu yang berbeza larutan kalium kromat (VI), K2CrO4 1.0 mol dm-3 ditambahkan ke dalam setiap tabung uji. Tinggi mendakan kuning plumbum (II) kromat (VI) yang terbentuk dalam setiap tabung uji diukur, direkod dan diplot dalam Graf 8.
Height of lead (II) chromate (VI) precipitate / cm Tinggi mendakan plumbum (II) kromat (VI) / cm
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
8
Volume of potassium chromate (VI) solution, K2CrO4 / cm3 Isipadu larutan kalium kromat(VI), K2CrO4 / cm3
Based on Graph 8 Berdasarkan Graf 8 (i) Calculate Hitungkan The number of moles of lead (II) ions used. Bilangan mol ion plumbum (II) yang digunakan. The number of moles of potassium chromate (VI) that has reacted completely with 5.00 cm3 of lead (II) nitrate. Bilangan mol kalium kromat (VI) yang bertindak balas selengkapnya dengan 5.00 cm3 plumbum (II) nitrat. [4 marks] [4 markah] (ii) Based on the answer in (c) (i), construct an ionic equation for the formation of lead (II) chromate (VI). Berdasarkan jawapan anda di (c) (i), bina persamaan ion untuk pembentukan plumbum (II) kromat (VI). [2 marks] [2 markah] (iii) Explain why Terangkan mengapa The height of precipitate formed increases and then remain constant Tinggi mendakan bertambah dan kemudian menjadi malar. The colour change in the solution above the precipitate. Perubahan warna larutan di bahagian atas mendakan. The eight test tubes used are of the same size. Kelapan-lapan tabung uji yang digunakan adalah bersaiz sama. [6 marks] [6 markah]
(i)
Number of moles of lead(II) ions, Pb2+ = number of moles of lead(II) nitrate, Pb(NO3)2 5 = 1.0 x 1000 = 0.005 mol Number of moles of chromate(VI) ions, CrO42= number of moles of potassium chromate(VI), K2CrO4 = 1.0 x 5 1000
= 0.005 mol (ii)1 mol of chromate(VI) ions, CrO42- reacted completely with 1 mol of lead(II) ions, Pb2+. The ionic equation for the reaction is: Pb2+ + CrO42PbCrO4
(iii)- The height of precipitate formed increases for the first 4 test tubes because as the volume of potassium chromate(VI) increases, more PRECIPITATE /lead(II) chromate(VI) is formed - The height of precipitate formed becomes constant when all Pb2+ have reacted completely. - colourless to yellow - Presence of chromate(VI) ions give the yellow colour to the solution // Chromate(VI) ions in the first 5 test tubes are all reacted // In the last 3 test tubes, chromate(VI) ions are in excess -To ensure the height of precipitate represents the amount of precipitate formed - because diameter of the test tubes are the same
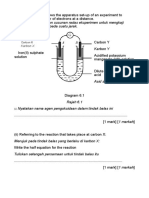
Diagram 4.1 shows the apparatus set-up for the neutralisation reaction between nitric acid and potassium hydroxide solution for preparation of salt X.
Rajah 4.1 menunjukkan susunan radas untuk tindak balas peneutralan antara asid nitrik dan larutan kalium hidroksida untuk penyediaan garam X.
20.0 cm3 of 0.5 mol dm-3 nitric acid
20.0 cm3 asid nitrik 0.5 mol dm-3
20.0 cm3 of 0.5 mol dm 3 potassium hydroxide solution + phenolphthalein indicator
20.0 cm3 larutan kalium hidroksida 0.5 mol dm-3 + penunjuk fenolftalein
Diagram 4.1
Rajah 4.1
(a) State the colour change of the solution in the conical flask at the end point.
Nyatakan perubahan warna larutan dalam kelalang kon pada takat akhir.
. . [1 mark] (b) Calculate the maximum mass of the salt X formed. [Molar mass of salt X = 101 g mol-1]
Hitungkan jisim maksimum garam X yang terbentuk. [Jisim molar garam X = 101 g mol-1]
[3 marks] (c) (i) The experiment is repeated with 0.5 mol dm-3 sulphuric acid to replace nitric acid. Predict the volume of sulphuric acid needed to neutralize completely.
Eksperimen itu diulangi dengan menggunakan 0.5 mol dm-3 asid sulfurik bagi menggantikan asid nitrik. Ramalkan isipadu asid sulfurik yang diperlukan untuk peneutralan lengkap.
(ii)
. [1 mark] Explain your answer in (c) (i).
Terangkan jawapan anda dalam (c) (i).
. . . [2 marks] (iii) Write the ionic equation for the reaction in (c) (i).
Tuliskan persamaan ion bagi tindak balas dalam (c) (i).
. [1 mark]
(d) Explain this statement. (i) In acid-base titration, only 2 or 3 drops of an indicator should be used.
(ii) Burette and pipettes must be rinsed with the solution to be measured .
(i)
This is because most of the indicators are weak acid or base that will affect the pH of the solution if used in excess.
(ii) To make sure the solution used is not diluted by droplets of water on the walls of burette or pipette.
You might also like
- GaramDocument7 pagesGaramMichael WeissNo ratings yet
- K2 KedahDocument29 pagesK2 Kedahryder1man6433No ratings yet
- Asid Dan BesDocument5 pagesAsid Dan BesArbayana AmbranNo ratings yet
- Latihan Kimia Bab 7Document3 pagesLatihan Kimia Bab 7ssproject50% (2)
- Kimia YPM 2Document9 pagesKimia YPM 2nik mohd padlulah mat sallehNo ratings yet
- Ujian 1 Kimia Ting 5 2019Document20 pagesUjian 1 Kimia Ting 5 2019rosminiaisyah100% (1)
- Modul Potensi Kimia Melaka Gemilang SPM 2014 PDFDocument40 pagesModul Potensi Kimia Melaka Gemilang SPM 2014 PDFMJACHRISNo ratings yet
- Pecutan Akhir Kimia BHGN B & C 2018 + Skema PDFDocument53 pagesPecutan Akhir Kimia BHGN B & C 2018 + Skema PDFSyarfa FurzanneNo ratings yet
- Bengkel Pecutan Kimia 2023Document31 pagesBengkel Pecutan Kimia 2023sitizabidahnawayiNo ratings yet
- Modul Kimia Tingkatan 4Document7 pagesModul Kimia Tingkatan 4Ain FarhaniNo ratings yet
- Bab Garam Teknik MenjawabDocument8 pagesBab Garam Teknik MenjawabHannan NashruddinNo ratings yet
- Kimia SPM Kimia k3 Set 2Document5 pagesKimia SPM Kimia k3 Set 2api-3841296No ratings yet
- Lat Formula t3Document10 pagesLat Formula t3Rohana Mat RejabNo ratings yet
- k2 f4 BC KIMIADocument12 pagesk2 f4 BC KIMIAAzalida Md YusofNo ratings yet
- Formula EmpirikDocument1 pageFormula EmpirikshintasamtoNo ratings yet
- Teknik Asas KimiaDocument10 pagesTeknik Asas KimiaMuhd AsrulNo ratings yet
- Trial KIMIA 2 PerlisDocument25 pagesTrial KIMIA 2 Perlisyusa_mdNo ratings yet
- PPC SPM 2023 K2 BHGN A No 1-4Document13 pagesPPC SPM 2023 K2 BHGN A No 1-4NORHEDAYAH BINTI MOHD JANI KPM-GuruNo ratings yet
- Percubaan Kimia k3 2014 (Edit)Document6 pagesPercubaan Kimia k3 2014 (Edit)Norita Mohd SahidanNo ratings yet
- F5 S1 Tuisyen Kimia Muafakat SoalanDocument7 pagesF5 S1 Tuisyen Kimia Muafakat Soalanqlysyen tasyaNo ratings yet
- Pat Kimia f.4, 2015 (II)Document26 pagesPat Kimia f.4, 2015 (II)Nur HafezaNo ratings yet
- p1 Oti 1 TG 5 Chemistry 2011Document34 pagesp1 Oti 1 TG 5 Chemistry 2011Jaaizah JaafarNo ratings yet
- Chem 2Document5 pagesChem 2Lucia SabliNo ratings yet
- Checklist For Scoring Gred A Kimia 2015Document14 pagesChecklist For Scoring Gred A Kimia 2015Daniel TaylorNo ratings yet
- Tajuk 7Document18 pagesTajuk 7Anonymous PPYjNttNo ratings yet
- Set 6 Kertas 1 AdapDocument30 pagesSet 6 Kertas 1 AdapWan Zaharah Wan ZainuddinNo ratings yet
- Menguasai Pengiraan Yang Melibatkan Konsep KemolaranDocument3 pagesMenguasai Pengiraan Yang Melibatkan Konsep Kemolaranzulaiha0% (1)
- Formula EmpirikDocument1 pageFormula EmpirikshintasamtoNo ratings yet
- Kimia Bab 7Document14 pagesKimia Bab 7Izyan Marissa MarissaNo ratings yet
- KUMPULAN 2 (Bengkel Pemantapan Akademik Kimia SPM)Document3 pagesKUMPULAN 2 (Bengkel Pemantapan Akademik Kimia SPM)REDZUAN BIN SULAIMAN -100% (2)
- SPM 4541 2009 Chemistry k2Document28 pagesSPM 4541 2009 Chemistry k2pss smk selandarNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3Document5 pagesTutorial 3CikguKimiNo ratings yet
- Ulangkaji Pra SPM 2013Document175 pagesUlangkaji Pra SPM 2013Jaaizah JaafarNo ratings yet
- Nota Internet Kadar Tindak BalasDocument12 pagesNota Internet Kadar Tindak BalasNise Alis50% (2)
- 2014 Kluster K2Document8 pages2014 Kluster K2Madyha AzmiNo ratings yet
- Soalan 3Document4 pagesSoalan 3ZantusNo ratings yet
- Kimia SPMDocument57 pagesKimia SPMummu AhmadNo ratings yet
- Latihan Kimia Dis 2016Document11 pagesLatihan Kimia Dis 2016Mohd Jamalil Azam MustafaNo ratings yet
- BAB 8 (Naskah Murid Cemerlang)Document12 pagesBAB 8 (Naskah Murid Cemerlang)Nur Anida IsmailNo ratings yet
- SOALAN Amali f4 PPT OgosDocument4 pagesSOALAN Amali f4 PPT OgosAzalida Md YusofNo ratings yet
- Kimia SPM Kimia k2 Set 2Document15 pagesKimia SPM Kimia k2 Set 2api-3841296No ratings yet
- Pandual Makmal Sains SekolahDocument92 pagesPandual Makmal Sains SekolahUmmi Ain60% (10)
- Pecutan Akhir Kimia SPM 2018Document25 pagesPecutan Akhir Kimia SPM 2018Theesha SophieNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3: Chemical Formulae and Equations SPM2006P2S2Document11 pagesCHAPTER 3: Chemical Formulae and Equations SPM2006P2S2mia adrinaNo ratings yet
- SPM Kimia Kimia k2 Set2Document13 pagesSPM Kimia Kimia k2 Set2api-3841296100% (1)
- Laporan Amali 1Document11 pagesLaporan Amali 1Mohd Hakimi MD SetapaNo ratings yet
- Struk TurDocument12 pagesStruk TurSiva GuruNo ratings yet
- Latihan SPM Kimia (Kadar Tindak Balas) 21Document2 pagesLatihan SPM Kimia (Kadar Tindak Balas) 21Meen Leen0% (1)
- Analisis Kualitatif Kimia Tak OrganikDocument4 pagesAnalisis Kualitatif Kimia Tak OrganikSiti Norasikin MuhyaddinNo ratings yet
- Ar2 Kimia Kertas 2 Bahagian BDocument4 pagesAr2 Kimia Kertas 2 Bahagian BNurain Babu OsmanNo ratings yet
- Soalan 1.: Marshals Chemistry SPM 2022 at 0.6Document8 pagesSoalan 1.: Marshals Chemistry SPM 2022 at 0.6mikael gattaNo ratings yet
- PKSM f4Document8 pagesPKSM f4NurImanNo ratings yet
- Kimia F4 US1 2017Document5 pagesKimia F4 US1 2017Reneelda HassanNo ratings yet
- Menguasai Pengiraan Yang MelibatkanDocument2 pagesMenguasai Pengiraan Yang Melibatkanzulaiha100% (1)
- Skema Jawapan UAS KIMIADocument1 pageSkema Jawapan UAS KIMIAwan nor azlina wan abdullahNo ratings yet
- Latihan Pengukuhan 4Document6 pagesLatihan Pengukuhan 4Jaaizah JaafarNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 2015 Paper 1 Aras TinggiDocument70 pagesChemistry 2015 Paper 1 Aras TinggiJaaizah JaafarNo ratings yet
- Modul Teknik Menjawab Soalan SPM SNDocument29 pagesModul Teknik Menjawab Soalan SPM SNJaaizah JaafarNo ratings yet
- RadiasiDocument10 pagesRadiasiJaaizah JaafarNo ratings yet
- Pep Awal Tahun F5 2015Document20 pagesPep Awal Tahun F5 2015Jaaizah JaafarNo ratings yet
- Dokumen Makmal SainsDocument9 pagesDokumen Makmal SainsJaaizah JaafarNo ratings yet
- Kpi JPNDocument2 pagesKpi JPNJaaizah JaafarNo ratings yet
- Latihan Pengukuhan 3Document6 pagesLatihan Pengukuhan 3Jaaizah JaafarNo ratings yet
- p1 Oti 1 TG 5 Chemistry 2011Document34 pagesp1 Oti 1 TG 5 Chemistry 2011Jaaizah JaafarNo ratings yet
- Ulangkaji Pra SPM 2013Document175 pagesUlangkaji Pra SPM 2013Jaaizah JaafarNo ratings yet
- Kertas Cadangan PROSPEKDocument3 pagesKertas Cadangan PROSPEKJaaizah JaafarNo ratings yet
- Latihan Pengukuhan 2Document7 pagesLatihan Pengukuhan 2Jaaizah JaafarNo ratings yet