Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pa Tho Physiology
Uploaded by
davica0413Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pa Tho Physiology
Uploaded by
davica0413Copyright:
Available Formats
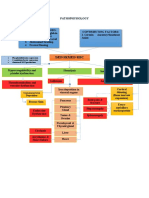
Pathophysiology
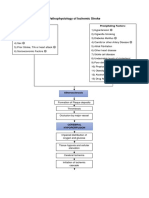
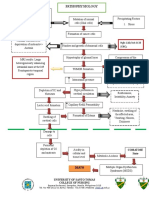
Modifiable Factors Non Modifiable Factors
1) Diabetes Meliitus 1) Age
2) Atrial Fibrillation 2) Heredity
3) Other heart disease 3) Sex
4) Poor diet 4) Prior Stroke, TIA or heart attack
5) Physical inactivity
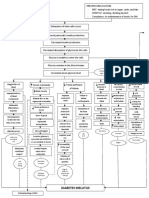
Destruction of alpha
and beta cells of the
pancreas
Failure to produce Production of excess
insulin glucagon
Increase Increase serum glucose
Polyuria osmolarity due level Production of
to glucose glucose from
protein and fat
Glycoprotein stores
cell wall
deposits
Wasting of lean
Impaired immune body mass
function (decrease Small vessel
level of disease
morphonuclear
leukocytes) Diabetic DX: CT Scan
Nephropathy Accelerated Arteriosclerotic cardiovascular
atherosclerosis disease with prominent left
ventricle and signs of bilateral
Infection Delayed Diabetic pulmonary congestion.
wound Retinopathy
healing
Blurred Vision
Pus Cell Renal
Affectation
Urinalysis
Albumin: Trace
Sugar: (+++) Glucosuria Decreased
Pus cells: 5- Production of
Erythropoeitin
10 /hpf Proteinuria
RBC: 0-1 /hpf
WBC: 11.6
(06/12/10)
Decreased RBC
production in the
bone marrow
Lab results:
Hemoglobin: 3.99
(4.0-6.0)
Anemia Hematocrit: .367
(.370-.540)
(06/12/10)
Paleness of the skin,
conjunctiva, lips, buccal
mucosa and gums was
observed
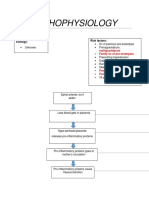
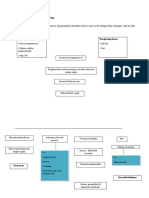
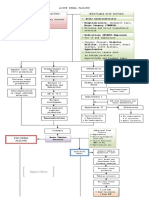
Thrombus CEREBROVASCULAR
ACCIDENT
Emboli
Decreased Tissue
perfusion (brain)
Cerebral Hypoxia
Cerebral ischemia
Short term
Eschemia
(<10-
15mins)
Temporary
Deficit
No
permanent
damage
VERTEBROBASILA
MID CEREBRAL ANTERIOR POSTERIOR R ARTERY
ARTERY CEREBRAL A. CEREBRAL A.
Dysarthia
Apraxia
Ataxia Hemisensory loss Left
upper extremities
Hemiparesis (left upper
extremities) Hemiplegia
(left lower extremities)
You might also like
- Pathophysiology of CVADocument7 pagesPathophysiology of CVAsarzlasco0967% (3)
- Cva PathoDocument2 pagesCva Pathokriska_ortizNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Ischemic Stroke FinalDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Ischemic Stroke FinalAcohCChao75% (4)
- Pathophysiology - Diabetes Mellitus Type 2Document3 pagesPathophysiology - Diabetes Mellitus Type 2Francis Kevin Sagudo100% (10)
- Nstemi PathoDocument2 pagesNstemi PathoSheana TmplNo ratings yet
- Cerebrovascular Accident (CVA) vs. Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA)Document37 pagesCerebrovascular Accident (CVA) vs. Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA)Grace IgnacoNo ratings yet
- Pa Tho Physiology of Sepsis Secondary To Typhoid IleusDocument6 pagesPa Tho Physiology of Sepsis Secondary To Typhoid IleusPhatsee PangilinanNo ratings yet
- Menigitis & EncephalitisDocument38 pagesMenigitis & EncephalitisKim GonzalesNo ratings yet
- O High Fat, High Carbohydrate o Caffeinated and Carbonated o 73 Years Old o MaleDocument4 pagesO High Fat, High Carbohydrate o Caffeinated and Carbonated o 73 Years Old o MaleJoherNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus Is A Condition in Which A Person Has A High Blood SugarDocument4 pagesDiabetes Mellitus Is A Condition in Which A Person Has A High Blood SugarisonkutonNo ratings yet
- Transient Ischemic Attack Precipitating Factors Predisposing FactorsDocument6 pagesTransient Ischemic Attack Precipitating Factors Predisposing FactorsYosef OxinioNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus: Hyperglycemia (304 MG/DL, 13.2 MG/DL)Document3 pagesDiabetes Mellitus: Hyperglycemia (304 MG/DL, 13.2 MG/DL)John Henry ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysio of HCDDocument3 pagesPathophysio of HCDhoney requermeNo ratings yet
- FracturesDocument39 pagesFracturesKim Gonzales100% (5)
- Pathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus Type 2Document7 pagesPathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus Type 2jnrue_aerith96% (28)
- Pathophysiology: Prince Carl P. Magluyan BSN - 2GDocument1 pagePathophysiology: Prince Carl P. Magluyan BSN - 2GPrinceNo ratings yet
- Anemia Table283Document2 pagesAnemia Table283Bridget ParkerNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology For HELLP SyndromeDocument2 pagesPathophysiology For HELLP SyndromeRosemarie CarpioNo ratings yet
- Cerebrospinal Fluid: Physiology Specimen CollectionDocument4 pagesCerebrospinal Fluid: Physiology Specimen Collectionrmt cutieNo ratings yet
- Case 2Document3 pagesCase 2Joselyn M. LachicaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysio - Stemi - FinalDocument4 pagesPathophysio - Stemi - FinalPrincessDianneNo ratings yet
- Physiosynthesis of SCLCDocument4 pagesPhysiosynthesis of SCLCkuro hanabusaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology AML DiagramDocument4 pagesPathophysiology AML DiagramKlerra Hope60% (5)
- Checklist STEP1Document46 pagesChecklist STEP1وائل عبداللطيف عبدالقادرNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology: Predisposing Factors Precipitating FactorsDocument3 pagesPathophysiology: Predisposing Factors Precipitating FactorsFc ßobby HechanovaNo ratings yet
- Cerebral Blood Flow StrokeDocument122 pagesCerebral Blood Flow Strokeapi-3748748No ratings yet
- Stroke PathophysioDocument3 pagesStroke PathophysioKrystele CangaNo ratings yet
- Sindrom Koroner Akut.ADocument55 pagesSindrom Koroner Akut.AwidiyaNo ratings yet
- Acute Kidney Injury (ARF)Document23 pagesAcute Kidney Injury (ARF)Aizaz AhmadNo ratings yet
- Schematic Diag DMDocument1 pageSchematic Diag DMReynaKatNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology - Tia VS CvaDocument6 pagesPathophysiology - Tia VS CvaZeo Zafaralla100% (1)
- Lecture Notes CALCIUM HOMEOSTASISDocument8 pagesLecture Notes CALCIUM HOMEOSTASISREMAN ALINGASANo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of cholangiocarcinomaJAYCERDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of cholangiocarcinomaJAYCERirish_estrellaNo ratings yet
- 6 Med Ward (WK - 1) PathophysiologyDocument3 pages6 Med Ward (WK - 1) PathophysiologyZaijean Kate Dianne LigutomNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology (Cerebrovascular Accident Hemorrhagic Right Lobe)Document4 pagesPathophysiology (Cerebrovascular Accident Hemorrhagic Right Lobe)jhonkivenNo ratings yet
- Hematologic MalignanciesDocument5 pagesHematologic MalignanciesPrisbert W. AlejoNo ratings yet
- Asuhan Keperawatan Pada Pasien Dengan Chronic Kidney DiseasesDocument24 pagesAsuhan Keperawatan Pada Pasien Dengan Chronic Kidney DiseasestidaktahudiriNo ratings yet
- Blood FunctionsDocument3 pagesBlood FunctionshelloaNo ratings yet
- ObobDocument1 pageObobNikkie SalazarNo ratings yet
- Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsDocument3 pagesAcute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsKasandra Dawn Moquia BerisoNo ratings yet
- 3 Inflammation Repair & Blood Disorder - Group 3Document6 pages3 Inflammation Repair & Blood Disorder - Group 3Denvic Nove G. BarberoNo ratings yet
- Pa ThoDocument1 pagePa ThoDoris Glenn FloresNo ratings yet
- PaThoPhysiology of EclampsiaDocument5 pagesPaThoPhysiology of Eclampsiahailleyann100% (2)
- Pathophysiology ThalassemiaDocument1 pagePathophysiology ThalassemiaSTORAGE FILENo ratings yet
- Precipitating Factors:: Myocardial Cell Death (NecrosisDocument2 pagesPrecipitating Factors:: Myocardial Cell Death (NecrosisLean Ashly MacarubboNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of AllDocument1 pagePathophysiology of AllBGHMC PEDIAHONo ratings yet
- Predisposing Factors: Precipitating Factors:: KidneysDocument1 pagePredisposing Factors: Precipitating Factors:: KidneysChe CacatianNo ratings yet
- Pre Eclampsia of Severe FeaturesDocument3 pagesPre Eclampsia of Severe FeaturesPrincess Diane S. VillegasNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology EclampsiaDocument5 pagesPathophysiology EclampsiaYael EzraNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Acute Renal FailureDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Acute Renal Failureminangsung minangnengNo ratings yet
- Path o PhysiologyDocument9 pagesPath o PhysiologyKyle Ü D. CunanersNo ratings yet
- Fluid Therapy in ICU: Dr. Basuki Rahmat SP - AnDocument84 pagesFluid Therapy in ICU: Dr. Basuki Rahmat SP - AndianNo ratings yet
- Cerebral Blood Flow and Ischemic Brain Disease: Bernardo L. Conde, M.DDocument70 pagesCerebral Blood Flow and Ischemic Brain Disease: Bernardo L. Conde, M.DIon UrsuNo ratings yet
- Fast Facts: Deficit di piruvato chinasi per pazienti e sostenitori: Una rara malattia genetica che colpisce I globuli rossi Informazioni + assunzione del controllo = migliore risultatoFrom EverandFast Facts: Deficit di piruvato chinasi per pazienti e sostenitori: Una rara malattia genetica che colpisce I globuli rossi Informazioni + assunzione del controllo = migliore risultatoNo ratings yet
- Fast Facts: Le déficit en pyruvate kinase pour les patients et les accompagnants: Une maladie génétique rare qui affecte les globules rouges Informations + Prise de contrôle = Meilleur résultatFrom EverandFast Facts: Le déficit en pyruvate kinase pour les patients et les accompagnants: Une maladie génétique rare qui affecte les globules rouges Informations + Prise de contrôle = Meilleur résultatNo ratings yet
- Fast Facts: Déficit en pyruvate kinase: Sensibilisation à cette maladie génétique rareFrom EverandFast Facts: Déficit en pyruvate kinase: Sensibilisation à cette maladie génétique rareRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Giant Cell Arteritis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related DiseasesFrom EverandGiant Cell Arteritis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related DiseasesNo ratings yet
- First Term Strand Unit Topic WeekDocument6 pagesFirst Term Strand Unit Topic WeekStella ElytraNo ratings yet
- Jarvis Chapter 21 Study Guide 6th EditionDocument6 pagesJarvis Chapter 21 Study Guide 6th EditionlauramwoodyardNo ratings yet
- Measuring The Difficulty Watching Video With HemianopiaDocument10 pagesMeasuring The Difficulty Watching Video With HemianopiaEvelin HarrizonNo ratings yet
- Cranial NervesDocument65 pagesCranial Nervessarguss14100% (13)
- Brain Anatomy ThesisDocument4 pagesBrain Anatomy Thesisbrittanyjonescolumbia100% (2)
- Ravizza Et Al. 2011Document8 pagesRavizza Et Al. 2011JD SánchezNo ratings yet
- 180 Critical IllnessDocument7 pages180 Critical IllnessAudrey ThenNo ratings yet
- Management of Patient With Neurological Dysfunction: Rowena R, Tosoc RN, Man, PHDDocument97 pagesManagement of Patient With Neurological Dysfunction: Rowena R, Tosoc RN, Man, PHDMARICRIS NEBIARNo ratings yet
- Sample ROS, PE PDFDocument4 pagesSample ROS, PE PDFKASIA SyNo ratings yet
- CXX - Neurosurgery NSDocument5 pagesCXX - Neurosurgery NSFarah FarahNo ratings yet
- Monro-Kellie 2.0: The Dynamic Vascular and Venous Pathophysiological Components of Intracranial PressureDocument13 pagesMonro-Kellie 2.0: The Dynamic Vascular and Venous Pathophysiological Components of Intracranial PressureLeandro NogueiraNo ratings yet
- Overview of Pediatric Physical AssessmentDocument7 pagesOverview of Pediatric Physical AssessmentLloyd Jay LinNo ratings yet
- Presentation1 150221070554 Conversion Gate01Document75 pagesPresentation1 150221070554 Conversion Gate01yellymarlianapatuNo ratings yet
- PCPI HacksDocument49 pagesPCPI HacksReichelle Reine Lising100% (1)
- Cervical Radiculopathy: Cervical Injuries and Treatment (HJ Kim, Section Editor)Document9 pagesCervical Radiculopathy: Cervical Injuries and Treatment (HJ Kim, Section Editor)bandiiitzNo ratings yet
- ApoptosisDocument35 pagesApoptosisEka ErmayaniNo ratings yet
- Module 1: Human Development, Meaning, Concepts and Approaches Content OutlineDocument28 pagesModule 1: Human Development, Meaning, Concepts and Approaches Content OutlineCristine Joy CalingacionNo ratings yet
- Palatal Swellings: 1. Anatomy of The PalateDocument6 pagesPalatal Swellings: 1. Anatomy of The PalateKatelyn_F0% (1)
- Socio 102 Prelim (2) Anatomy & Physiology of Female Reproductive SystemDocument7 pagesSocio 102 Prelim (2) Anatomy & Physiology of Female Reproductive System12B-Bracero Meg R.No ratings yet
- Auditory ReceptorsDocument15 pagesAuditory ReceptorsJeanette RiosNo ratings yet
- Special SensesDocument7 pagesSpecial SensesKryssha NatalieNo ratings yet
- (OPHTHA) 7.1-Pediatric Ophthalmology-Strabismus and Amblyopia - Dr. AtienzaDocument14 pages(OPHTHA) 7.1-Pediatric Ophthalmology-Strabismus and Amblyopia - Dr. AtienzaMaria Gracia YamsonNo ratings yet
- Brain CancerDocument4 pagesBrain CancerLean LeonelNo ratings yet
- Selvaratnam2009 PDFDocument23 pagesSelvaratnam2009 PDFKinjal SharmaNo ratings yet
- Orthopedic Surgery - Farid Mahmud AditaDocument4 pagesOrthopedic Surgery - Farid Mahmud AditaMaria Widyaneni TrinastutiNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Essentials of Cardiopulmonary Physical Therapy 4th Edition by Ellen Hillegass Isbn 9780323430548Document8 pagesTest Bank For Essentials of Cardiopulmonary Physical Therapy 4th Edition by Ellen Hillegass Isbn 9780323430548Albert Ascher100% (41)
- Cognitive Rehabilitation For Older AdultsDocument4 pagesCognitive Rehabilitation For Older AdultsJosé Carlos Sánchez-RamirezNo ratings yet
- HerniaDocument13 pagesHerniarmt_01No ratings yet
- 17.alterations in Cognitive SystemsDocument46 pages17.alterations in Cognitive SystemsRoxana CioflîncNo ratings yet
- Autopsy Report For Wade WelchDocument8 pagesAutopsy Report For Wade WelchKOLD News 13No ratings yet