Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Vitamin Chart 2009
Uploaded by
Surpreet AroraOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Vitamin Chart 2009
Uploaded by
Surpreet AroraCopyright:
Available Formats
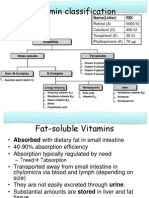
Vitamins RDA Letter Generic Name Female Male RDA UL Function Coenzymes Storage Absorption Sources Deficiency Disease
(look up symptoms) Vit Susceptibility Effects of Comments Hypervitaminosis
Water
Vit B1
Thiamin
1.1 mg/d
1.2mg/d
most exceed in nomal diet by 2 mg/d
NA
Energy Release from food, metabolism of carbs, branched AA's and pentoses, pyruvate dehydrogenase, TPP - carrier nerve function, synth of of active poorly stored, small amt in liver neurotransmitters aldehyde and muscles
actively in jujenum, transported by RBCs active during low intake, passive during high intake, HCl in stomach releases bound form readily in stomach and small intestine, active and passive,
BeriBeri - where polished rice is staple (peripheral neuropathy) Dry Beriberi- weakness, nerve degeneration, wet beriberi-edema, heart probs, Aribaflavinosis- stomatitis, cheilitis, glossitis, dermatitis; long-term uses of phenobarbitol susceptible Pellagra (diarrhea, demtia, dermatitis) - rough skin, untreated corn as staple is susceptible
readily excreted
Soluble
Vit B2
Riboflavin
1.1 mg/d
1.3 mg/d
(B complex
Vit B3
Niacin, nicotinic acid, nicotinamide, niacinamide 16 mg/d
14 mg/d
sources =
Vit B5
Pantothenic Acid
AI=5mg/d
AI=5mg/d
meat(organs),
Vit B6
Pyridoxine
1.3-1.7 mg/d 1.3-1.7 mg/d
coenenzymes in oxid/red rxns, metabolism of oxidized NA glutathoine catabolic in glycolisis and 35 mg/d of Krebs and anabolic in fatty supplemental acid synthesis metabolism of carbs, fat, protein, and alcohol, assiti in donating fatty acids to NA proteins several: heme synth, neurotransmitter synh, 100+ 100mg/d enzymatic rxns
FMN, FAD
small amt in liver
readily excreted
NAD, NADP
no storage
very heat stable
readily excreted
can be synthesized from Trp in body
coenzyme A PLP pyridoxal phosphate
minimal storage as coenzyme in liver
small intestine absorbed passively, binds to albumin for transport in the blood
Rare b/c so prevalent
readily excreted
stored in liver and muscle
rare, acoholics at risk
dairy, grains)
Vit B12
3 forms-Cyanocobolamin (free V B12), 2 coenzymes
2.4ug
2.4ug
NA
methylcobala min (coenzyme), 5deoxyadenos conenzymes move 1 carbon ylcobalamin group, maintain myelin sheath (coenzyme); liver
see slides - too much for here
synthesized by fungi, bacteria, and algae
vegans, Pernicious anemia(myelin sheeth sluff off), nerve malabsorptive degeneration, paralysis or death diseases
Folate
Folic Acid, Folacin
400ug
400ug
1mg/d
Biotin
30
30
NA
1 carbon unit transfers, DNA synthesis, homocysteine THFA metabolism, neurotransmitter tetrahydrofilic formation, AA metabolism acid some in liver add CO2 to compounds prosthetic metabolism of group small amt in muscle, liver, brain - carbohydrates, fatty acids, CoASH amino acids excreted via bile & urine - reducing agent - collagen synth (scurvy) - Fe absorption - Biosynthesis: carnitine, hormones, neurotransmitters, bile acids
absorbed in the monoglutamate from with help of folate conjugase, actively absorbed during low intake exists in free and protien bound biocytin forms. Must cleave from prtn b4 can be absorbed in sm int "&" low intake -> via specific energy dep transport system in sm intest synth by most animals, but not high intake-> passive tx humans. Eat citrus!!
Macrocytic anemia (#RBCprecurs O2) Deficiency is rare Don't eat 12 raw eggs, which have avidin which inhibits absorption
Vit C
Ascorbic Acid (reduced) Dehydroascorbic Acid (oxidized)
75mg
90mg small amt above may reduce cold symptoms
some pituitary, adrenal glands, WBC, eye, brain excrete via kidneys
Scurvy (fatique, pinpoint bruisin, bleeding, collagen loss) Note: need vC to make hydroxyproline, which reinforces collagen structure.
easily lost via cooking
2g
hard to get too much
3000ug fatal @ 12g Fat Soluble Vit A Retinol 800ug (eq) 1000ug Excess impedes vK uptake
Retinoids retinol - precursor retinal - vision (rhodopsin light -> nerve sig) retinoic acid - retina cone (bright) rod (dark), g&d (embryo/genes), ep cell, immunity
tx from chylomicrons -> liver store 90% in Liver
Retinoids (sm int) retinyl esters -> free retinol. Req bile, digestive enz, micelles. Once absorbed reform retinyl est in int cells
risk: kidney dis / old age animal (liver Night blind, eye bact, irreversible blindness, poor growth, dec immun Teratogenic (birth defects / abort)
removal Carotenoids - not excreted, some lost in urine absorbed intact, int cells convert carotenoids to retinoids
A most likely to cause toxicity one is more effective Preformed (animal) - Retinoids (retinol, retinal, retinoic acid) Provitamin A (plant) - Carotenoids (beta-carotene, alpha carotene) (int / liver split to 2x retinoids)
(sources =
Vit D2
Ergocalciferol (diet)
adult 5ug old adult 2 to 3x BF baby need supp sunlight usually enough
50 ug
regulate blood Ca levels - inc int absorpt of Ca - w/ parathyroid hormone, rel Ca from food cell differentiation - reduce cancer?
stored in fat excreted via bile
1. Skin: UV converts cholesterol to D3 (Pro vD3 -> Pre vD3 -> vD3) 2. Sm int: 80% D2 absorbed 3. Bound to prt carrier in blood 4. Metab in liver to 25-OH vD 5. Metab in kidney to 1,25 OH vD (active form)
poor bone mineralization - Osteomalacia(adult), Rickets(child) sun exposure vD resistance - due to prob with synth active form or receptor binding
hypercalcemia -> Ca dep in kidney, heart / vessels, excess sun not cause excess vD
prohormone derived from cholesterol
plant, animal,
Vit D3
Cholecalciferol (sun)
NA Antiox for unsat fatty acid 1000 mg 15mg (too much inhibit vK metabolism) found in Cell Memb and protects it from free radicals by donating electrons to oxidizing agents adipose, liver, muscle much excreted via bile & urine tx to liver via chylomicrons, then inc into lipoproteins not animal Sterility(lab animals); dep on dietary fat, bile, pancr enzymes vE def is rare no real direct disease, but decrease vK uptake so see vK diseases
bacterial)
Vit E
Tocopherol
K1 Phylloquinone (plant) K2 Menaquinone (animal, int bact) 90ug
NA only fat w/o upper limit
40-90% absorbed
Vit K
120ug
Criticl factor blood clotting
80% absorpt in sm intest. dep on Limited storage in Liver (via Breastmilk is poor bile, pancr enzymes. chylomicrons thru lymph system, source so babies not blood) need vK shots 10% of vK2 is synth by int bact and then absorbed by colon
Antibiotics kill vK producting intest bact Excess vA and vE impedes vK - lead to Bleeding disorders (prolonged clot time) due to importance in thrombin production
resists cooking loss
FEM<MALE ESSADDI - Estimated Safe & Adequate Daily Dietary Intake - for certain nutrients still being studied TPP FAD Niacin (1mg) B1 B2
Trp (60mg)
Notes: - Vitamins unstable to UV light, heat, oxy., H2O, or high/low pH - pay attn to freshness & ways to cook - Vitamins fcn in low concentrations as cofactors/regulators - not used up - RDA to replace normal T/O - Retinol synthesizable (human tissue) from provit A, carotenoids that are yellow-orange plant pigment in fruits and vegetables - 4 types: - Vit E activity found in 3 structures w/ diff activity:
You might also like
- Food Chemistry Part 1Document30 pagesFood Chemistry Part 1Dhigna LuthfiyaniNo ratings yet
- VitaminsDocument77 pagesVitaminsEsosa OdighizuwaNo ratings yet
- Vitamin Chart.2Document3 pagesVitamin Chart.2ashdmb217No ratings yet
- Biochemistry of Nutrition: Bruno SopkoDocument64 pagesBiochemistry of Nutrition: Bruno SopkoMamtaNo ratings yet
- VITAMINSDocument58 pagesVITAMINSRazvan DinuNo ratings yet
- Agussalim Bukhari Department of Nutrition Faculty of Medicine, Hasanuddin UniversityDocument37 pagesAgussalim Bukhari Department of Nutrition Faculty of Medicine, Hasanuddin Universitynini100% (1)
- Water SolubleDocument12 pagesWater SolubleLara, Beverly B.No ratings yet
- Biochemistry of VitaminsDocument64 pagesBiochemistry of VitaminsConrado CatimbangNo ratings yet
- Micronutrients, VitaminsDocument32 pagesMicronutrients, VitaminsEsdras DountioNo ratings yet
- VitaminsDocument37 pagesVitaminsMaryNo ratings yet
- Vitamins: Nutrition Departement Faculty of Medicine - North Sumatera UniversityDocument54 pagesVitamins: Nutrition Departement Faculty of Medicine - North Sumatera UniversityMuhammad FaizNo ratings yet
- VitaminsDocument77 pagesVitaminsLoredana100% (1)
- Animal Nutrition LectureDocument66 pagesAnimal Nutrition Lecturemovie nightsNo ratings yet
- VADD - StudentsDocument38 pagesVADD - Studentsonline masterNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10. Basic Concepts of Vitaminology. Biochemistry of Water-Soluble and Fat-Soluble VitaminsDocument58 pagesLecture 10. Basic Concepts of Vitaminology. Biochemistry of Water-Soluble and Fat-Soluble VitaminsВіталій Михайлович НечипорукNo ratings yet
- Nutrition All Info For MidtermDocument8 pagesNutrition All Info For Midtermpashnera0211No ratings yet
- Vitamin A, Vitamin D, Thiamine, Riboflavine, Pyridoxine, Niacinamide, Folic Acid, Ascorbic Acid, Panth. AcidDocument130 pagesVitamin A, Vitamin D, Thiamine, Riboflavine, Pyridoxine, Niacinamide, Folic Acid, Ascorbic Acid, Panth. AcidsalinaNo ratings yet
- Bioche VitaminsDocument7 pagesBioche Vitaminsharips motupalliNo ratings yet
- Micronutrients - VitaminsDocument9 pagesMicronutrients - VitaminsKate SantosNo ratings yet
- Vitamin I & II - Noor WaseemDocument49 pagesVitamin I & II - Noor Waseemqueenmasa191No ratings yet
- Nutritional Management On HepatitisDocument15 pagesNutritional Management On HepatitisFebby ShabrinaNo ratings yet
- Dietary Vitamins: Agussalim Bukhari Department of Nutrition Faculty of Medicine, Hasanuddin UniversityDocument37 pagesDietary Vitamins: Agussalim Bukhari Department of Nutrition Faculty of Medicine, Hasanuddin UniversityNurul fatimahNo ratings yet
- Dietary Vitamins: Agussalim Bukhari Department of Nutrition Faculty of Medicine, Hasanuddin UniversityDocument37 pagesDietary Vitamins: Agussalim Bukhari Department of Nutrition Faculty of Medicine, Hasanuddin UniversityindahirmawatiNo ratings yet
- Gizi Vitamin EDocument97 pagesGizi Vitamin EMaya DasmaselaNo ratings yet
- Vitamins 2011 PDFDocument121 pagesVitamins 2011 PDFIshan Lakhwani100% (3)
- Vitamins and MineralsDocument91 pagesVitamins and MineralsPyaesone AungNo ratings yet
- Classification of VitaminsDocument26 pagesClassification of VitaminsRajesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Vitamin Deficiency in FishesDocument40 pagesVitamin Deficiency in FishesDuong Vu TungNo ratings yet
- Vitamin B12 and FolateDocument12 pagesVitamin B12 and FolateAllessandria DimaggioNo ratings yet
- Dietary Vitamins: Agussalim Bukhari Department of Nutrition Faculty of Medicine, Hasanuddin UniversityDocument37 pagesDietary Vitamins: Agussalim Bukhari Department of Nutrition Faculty of Medicine, Hasanuddin UniversityindahirmawatiNo ratings yet
- Fats and Water Soluble VitaminsDocument31 pagesFats and Water Soluble VitaminshafizahhoshniNo ratings yet
- Produk Senyawa Aktif Sumber Keterangan LainDocument5 pagesProduk Senyawa Aktif Sumber Keterangan LainAnastasia AliesaNo ratings yet
- Nutritional Biochemistry: Vitamins Dr. Bidhan Chandra KonerDocument50 pagesNutritional Biochemistry: Vitamins Dr. Bidhan Chandra KonerElenanana100% (1)
- Water Soluble Vitamin: Dept. of Nutrition Medical School Universitas PadjadjaranDocument49 pagesWater Soluble Vitamin: Dept. of Nutrition Medical School Universitas PadjadjaranHadiyatussalamah Pusfa KencanasariNo ratings yet
- Nutrition and VitaminDocument70 pagesNutrition and VitaminTob JurNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Lesson PlanDocument10 pagesBiochemistry Lesson Planchristian jade quijanoNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of VitaminsDocument93 pagesPharmacology of VitaminsDelphine NjokuNo ratings yet
- CarotenoidsDocument22 pagesCarotenoidsVanitha Reddy P100% (4)
- A Presentation On: Presented byDocument67 pagesA Presentation On: Presented byOlufemi KolawoleNo ratings yet
- Vitamin-A: M.Prasad Naidu MSC Medical Biochemistry, PH.DDocument42 pagesVitamin-A: M.Prasad Naidu MSC Medical Biochemistry, PH.DDr. M. Prasad NaiduNo ratings yet
- VitaminsDocument191 pagesVitaminsAyush JainNo ratings yet
- Poisons of Plant OriginDocument46 pagesPoisons of Plant OriginThe AbyssinicansNo ratings yet
- Fat Soluble VitaminsDocument20 pagesFat Soluble VitaminsWati WindayaniNo ratings yet
- Lec 15Document23 pagesLec 15jayNo ratings yet
- 5 LIPIDS Lee - ModifiedDocument72 pages5 LIPIDS Lee - ModifiedPelrNo ratings yet
- Vitamins and Vitamin Containing DrugsDocument17 pagesVitamins and Vitamin Containing DrugsMohamed EzzatNo ratings yet
- Vitamins, Water and Minerals MetabolismDocument171 pagesVitamins, Water and Minerals Metabolismfitri syamNo ratings yet
- The Eldoret National Polytechnic, Diploma in Pharmaceutical TechnologyDocument20 pagesThe Eldoret National Polytechnic, Diploma in Pharmaceutical TechnologyGerald Limo Arap ChebiiNo ratings yet
- Biology in EnglishDocument19 pagesBiology in EnglishRameshNo ratings yet
- Micronutrients 2020Document44 pagesMicronutrients 2020Arsyi ZahwaNo ratings yet
- Vitamins (Handout)Document34 pagesVitamins (Handout)Danna DaniNo ratings yet
- NFS 382 Final ReviewDocument56 pagesNFS 382 Final ReviewAya ThairNo ratings yet
- RSC Digestive SystemDocument4 pagesRSC Digestive SystemDan Rey OsiasNo ratings yet
- Vitamin Deficeiency and DisceasesDocument1 pageVitamin Deficeiency and DisceasesavadcsNo ratings yet
- Derangements of Potassium - Emergency Medicine 2014Document19 pagesDerangements of Potassium - Emergency Medicine 2014Michael AmarilloNo ratings yet
- VITAMINSDocument6 pagesVITAMINSJohn Rick OrineNo ratings yet
- Lecture 33 - Vitamins & Trace ElementsDocument35 pagesLecture 33 - Vitamins & Trace Elementsapi-3703352100% (1)
- Basic of Nutrition/ Nutrients Ii: Hikmah Mohamad Idi Foundation Biochemistry Sem 2/2021Document53 pagesBasic of Nutrition/ Nutrients Ii: Hikmah Mohamad Idi Foundation Biochemistry Sem 2/2021Noor Syaqirah Abdul WahabNo ratings yet
- Vitamins Final YrDocument37 pagesVitamins Final YrPooja ReddyNo ratings yet
- Bacteria GroupsDocument3 pagesBacteria GroupsSurpreet AroraNo ratings yet
- Gross Anatomy Board ReviewDocument1 pageGross Anatomy Board ReviewSurpreet AroraNo ratings yet
- Nasal Obstruction and Facial Growth: The Strength of Evidence For Clinical AssumptionsDocument9 pagesNasal Obstruction and Facial Growth: The Strength of Evidence For Clinical AssumptionsSurpreet AroraNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Muscle PropertiesDocument4 pagesCardiac Muscle PropertiesSurpreet AroraNo ratings yet
- Copy of Quiz-Glycolysis and FermentationDocument6 pagesCopy of Quiz-Glycolysis and FermentationParisa YahyaieNo ratings yet
- Protein Nutrition (David Bender)Document68 pagesProtein Nutrition (David Bender)Anonymous 8h8Rw6YmAnNo ratings yet
- 10 3389@fimmu 2020 01100 PDFDocument22 pages10 3389@fimmu 2020 01100 PDFvalinaNo ratings yet
- Plant Hormone ReceptorsDocument12 pagesPlant Hormone ReceptorsJitendra MishraNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument24 pagesBiologyTom KiloitNo ratings yet
- 12 Fire Letters - 1 DNA Strand Template (1 Fire Letter Sequence 144 Vector Codes)Document1 page12 Fire Letters - 1 DNA Strand Template (1 Fire Letter Sequence 144 Vector Codes)RobertNo ratings yet
- CHOLESTEROL EstimationDocument20 pagesCHOLESTEROL EstimationRsraoNo ratings yet
- Illumina Dye SequencingDocument5 pagesIllumina Dye SequencingNguyen TaNo ratings yet
- Karl Lohmann (1929) Discovered ATP in Muscle Cells. Fritz Lipmann and Herman Kalckar (1941) Were The First To Recognize The Role of ATP in Energy MetabolismDocument12 pagesKarl Lohmann (1929) Discovered ATP in Muscle Cells. Fritz Lipmann and Herman Kalckar (1941) Were The First To Recognize The Role of ATP in Energy Metabolismمحمد جانNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 12 March 30 Biology Chapter 11 Biotechnology Principles and ProcessesDocument8 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 12 March 30 Biology Chapter 11 Biotechnology Principles and ProcessesRahul ThakurNo ratings yet
- Physeo Biochemistry 2019 PDFDocument168 pagesPhyseo Biochemistry 2019 PDFBo Min Kim75% (4)
- Proteins AS Biology Questions AQA OCR EdexcelDocument3 pagesProteins AS Biology Questions AQA OCR EdexceljanaNo ratings yet
- ExotoxinDocument27 pagesExotoxinSyeda MaryamNo ratings yet
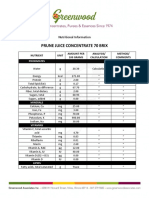
- Prune Juice Concentrate 70 Brix Nutritional InformationDocument2 pagesPrune Juice Concentrate 70 Brix Nutritional Informationborn2dive 9702No ratings yet
- Application of Biotechnology On Genetic Engineering (DNA Cloning)Document4 pagesApplication of Biotechnology On Genetic Engineering (DNA Cloning)Jerome MagnoNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes - 2. Molecular BiologyDocument31 pagesBiology Notes - 2. Molecular BiologyKhansa Shafa LuthfiyaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 The Nucleus and DNA Organization and PBL Write Shops 5 6Document15 pagesLesson 4 The Nucleus and DNA Organization and PBL Write Shops 5 6Macky IbayNo ratings yet
- Tugas Formulasi Pakan BabiDocument8 pagesTugas Formulasi Pakan BabiAldrin NdunNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry and Biophysics Reports: Alakesh Bera, Sajal BiringDocument11 pagesBiochemistry and Biophysics Reports: Alakesh Bera, Sajal BiringPaula Manalo-SuliguinNo ratings yet
- Semester Test 1 Without Memo-2Document1 pageSemester Test 1 Without Memo-2Lencelot MalopeNo ratings yet
- BIOMOLECULES-ACTIVITY - by PartnerDocument2 pagesBIOMOLECULES-ACTIVITY - by PartnerANGELICA LITONNo ratings yet
- Bioreactor: Chemical Reaction Engineering (CRE) Is TheDocument25 pagesBioreactor: Chemical Reaction Engineering (CRE) Is ThekhunafaNo ratings yet
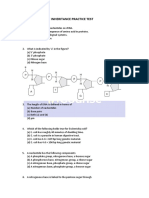
- Molecular Basis of Inheritance Practice TestDocument13 pagesMolecular Basis of Inheritance Practice TestPartha Shee100% (1)
- ICD 10 Diagnosis GiziDocument2 pagesICD 10 Diagnosis Gizigizi cgcNo ratings yet
- Alpha-Calcidol Vs CalcitriolDocument8 pagesAlpha-Calcidol Vs Calcitriolamin138irNo ratings yet
- Biochemical Energy ProductionDocument58 pagesBiochemical Energy ProductionAlyana GabiniNo ratings yet
- Honors Biology AssignmentDocument8 pagesHonors Biology AssignmentMatt WedekindNo ratings yet
- Cloning - PCR Strategy - Optimising PCR - EMBLDocument3 pagesCloning - PCR Strategy - Optimising PCR - EMBLNathan IbaleNo ratings yet
- CLS Aipmt 15 16 XIII Bot Study Package 4 Set 1 Chapter 16 PDFDocument30 pagesCLS Aipmt 15 16 XIII Bot Study Package 4 Set 1 Chapter 16 PDFMoumita SarkarNo ratings yet
- Douglas Ultra Preventive XDocument4 pagesDouglas Ultra Preventive XGary MollerNo ratings yet