Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Organisational Development Practitioner: Emphasis On Morale
The Organisational Development Practitioner: Emphasis On Morale
Uploaded by
Sam Kapoor0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views5 pagesOriginal Title
UploadedFile_129880155096093750
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
RTF, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as RTF, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views5 pagesThe Organisational Development Practitioner: Emphasis On Morale
The Organisational Development Practitioner: Emphasis On Morale
Uploaded by
Sam KapoorCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as RTF, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
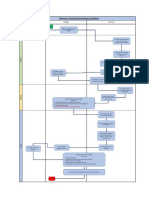
The Organisational development practitioner
The organisation development practitioner
Internal and external consultants Professionals from other disciplines who apply OD practices (e.g. TQM managers, IT/IS managers, compensation and benefits managers) Managers and administrators who apply OD from their line or staff positions
Consultant styles
HIGH Cheerleader Pathfinder
Emphasis on morale
Persuader
Stabiliser LOW LOW
Analyser
HIGH
Emphasis on effectiveness
Core and advanced skills
General consultation skills Intrapersonal skills Research and evaluation knowledge and skills/research design Data collection Organisation behaviour/organisation development knowledge and intervention skills Data analysis Presentation skills Experience as a line manager/major management knowledge areas Interpersonal skills Collateral knowledge areas
Basic knowledge and skills
Intrapersonal skills
Self- awareness
Interpersonal skills
Ability to work with others and groups
General consultation skills
Ability to get skills and knowledge used
Organisation development theory
Knowledge of change processes
The role of OD professionals
Position
Internal vs. external
Marginality
Ability to straddle boundaries
Emotional demands
Emotional intelligence
Use of knowledge and experience
Internal change agents (advantages)
They can save time identifying and understanding organisational problems They have intimate knowledge of the organisation and its dynamics They know their organisations culture, informal practices and sources of power They have access to a variety of information, including rumours, company reports and direct observations They are usually more easily accepted They are less threatening than outsiders They can more easily establish rapport and trust
External change agents (advantages)
Can provide particular expertise that is unavailable internally Bring a different and potentially more objective perspective into the organisation development process Their ability to probe difficult issues and to question the status quo They are also afforded some deference and power
External change agents (disadvantages)
Need extra time to enter the organisation and to gain a working knowledge of it Organisational members may be wary of outsiders They may also be viewed negatively because they are seen as having relatively little invested in the organisation Members believe that if problems arise, the external consultants can simply walk away with little negative consequence
Internal change agents (disadvantages)
Loss of objectivity because of their strong ties to the organisation They may be overly cautious, particularly when powerful others can affect their careers They may lack certain skills and experience in facilitating organisational change
Client vs. consultant knowledge
Use of consultants knowledge and experience
Plans implementation Recommends/prescribes Proposes criteria Feeds back data Probes and gathers data Clarifies and interprets Listens and reflects Refuses to become involved
Use of clients knowledge and experience
Professional ethics
Ethical guidelines Ethical dilemmas
Misrepresentation Misuse of data Coercion Value and goal conflict Technical ineptitude
A model of ethical dilemmas
Antecedents Role of the change agent Process Consequences
Role episode
Ethical dilemmas
Misrepresentation Misuse of data Coercion Value and goal conflict Technical ineptitude
Values Goals Needs Abilities
Role of the client system
Role conflict Role ambiguity
Kindred Todd and the ethics of OD
1. What ethical guidelines did the President Larry Stepchuck violate? (see Appendix, pages 66-70) 2. If you were in Todds place how would you react to such a situation? 3. Identify a work situation in which you were faced with a similar moral dilemma.
You might also like
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5813)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (844)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- WisdomDocument214 pagesWisdomHelio Nhampossa100% (1)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Marketing Micro and Macro EnvironmentDocument8 pagesMarketing Micro and Macro EnvironmentSumit Acharya100% (1)
- 1 TX Renfro 2009 The Practice of Econometrics + Computation PDFDocument328 pages1 TX Renfro 2009 The Practice of Econometrics + Computation PDFIvan Arandia TapiaNo ratings yet
- Artificial IntelligenceDocument2 pagesArtificial Intelligencehitiksha100% (1)
- Social PathologyDocument14 pagesSocial PathologyAnkit YadavNo ratings yet
- 0021 Performance EvaluationDocument21 pages0021 Performance Evaluationals1508No ratings yet
- Pearson Product-Moment Correlation: Correlation - Html#Ixzz293U1FdyeDocument3 pagesPearson Product-Moment Correlation: Correlation - Html#Ixzz293U1FdyeMClarissaENo ratings yet
- Primal Fear ReactionDocument2 pagesPrimal Fear ReactionCharlene M. GalenzogaNo ratings yet
- 0021-Performance Review ProcessDocument1 page0021-Performance Review Processals1508No ratings yet
- Grievance Redressal System - v1Document3 pagesGrievance Redressal System - v1als1508No ratings yet
- PMS ProcessDocument8 pagesPMS Processals1508No ratings yet
- Greivance Redressal MechanismDocument2 pagesGreivance Redressal Mechanismals1508No ratings yet
- GoodAid IncentiveDocument2 pagesGoodAid Incentiveals1508No ratings yet
- GD Topics & DatasetsDocument5 pagesGD Topics & Datasetsals1508No ratings yet
- Exit Process - StoresDocument3 pagesExit Process - Storesals1508No ratings yet
- Transfer NoteDocument1 pageTransfer Noteals1508No ratings yet
- Transfer PolicyDocument2 pagesTransfer Policyals1508No ratings yet
- Hul Bal SheetDocument2 pagesHul Bal Sheetals1508No ratings yet
- 8 1JSMill-FullDocument14 pages8 1JSMill-FullSudhir SinghNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Approach To Research A Review of Advantages and Disadvantages of Three Paradigms: Positivism, Interpretivism and Critical InquiryDocument7 pagesQualitative Approach To Research A Review of Advantages and Disadvantages of Three Paradigms: Positivism, Interpretivism and Critical InquiryKevin ChowNo ratings yet
- PINGLISH (Pakistani English)Document6 pagesPINGLISH (Pakistani English)rabiaNo ratings yet
- Lo 3 Motivation CH 5 Newstrom Ob 2011Document42 pagesLo 3 Motivation CH 5 Newstrom Ob 2011Liam ZandersNo ratings yet
- Getter: Speak To Persuade (Set 68) LMCE2092Document20 pagesGetter: Speak To Persuade (Set 68) LMCE2092Zulaikha HadiNo ratings yet
- OUTPUT 1 Description-of-a-mechanism-Lesson-5Document14 pagesOUTPUT 1 Description-of-a-mechanism-Lesson-5Yu ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Cem Güney ÖzverenDocument66 pagesCem Güney ÖzverenTubisNo ratings yet
- 7012 EhrDocument18 pages7012 EhrMansi RanaNo ratings yet
- Synonyms and AntonymsDocument8 pagesSynonyms and AntonymsCamille SalasNo ratings yet
- Generative GrammerDocument3 pagesGenerative Grammerullahbashir749No ratings yet
- I Don't Want You To GoDocument9 pagesI Don't Want You To GoJhardine Garcia Miniano100% (4)
- Statement of The Problem (Blue Ternatea)Document5 pagesStatement of The Problem (Blue Ternatea)Alexandria Ababon100% (1)
- Site PlanningDocument26 pagesSite PlanningNurul AfiqahNo ratings yet
- Team Building: Muhammad Syukri Bin Mohd NorDocument22 pagesTeam Building: Muhammad Syukri Bin Mohd NorUchiha SyukriNo ratings yet
- Human Factors and Ergonomics - WikipediaDocument12 pagesHuman Factors and Ergonomics - Wikipediabibilal bangaloreNo ratings yet
- Value Stream MappingDocument3 pagesValue Stream MappingMuhammad Fatah KaryadiNo ratings yet
- Charles Kittel Intro Solid State PhysicsDocument27 pagesCharles Kittel Intro Solid State PhysicsAndrés Escárraga CuéllarNo ratings yet
- Social Construction of RaceDocument4 pagesSocial Construction of Raceapi-340926637No ratings yet
- SSL Refrrence SivakamiDocument13 pagesSSL Refrrence SivakamiHarish KarthikNo ratings yet
- Activity 6 Ed 227Document1 pageActivity 6 Ed 227glezamaeNo ratings yet
- MBA For Executives: Marketing ManagementDocument57 pagesMBA For Executives: Marketing ManagementChandu De SilvaNo ratings yet
- BHIC-106: Indira Gandhi National Open University Maidan Garhi, New Delhi-68Document4 pagesBHIC-106: Indira Gandhi National Open University Maidan Garhi, New Delhi-68Ratnesh PillaiNo ratings yet
- An Understanding of Salat (SLW) From Al QuranDocument4 pagesAn Understanding of Salat (SLW) From Al QuranScottie GreenNo ratings yet