Professional Documents
Culture Documents
203 MDE ECG1 Lectuers
Uploaded by
rosefel0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views11 pagesTracing made by an electrocardiograph used especially in diagnosing abnormalities of heart action. Electrocardiograph an instrument for recording the changes of electrical potential occurring during the heartbeat.
Original Description:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentTracing made by an electrocardiograph used especially in diagnosing abnormalities of heart action. Electrocardiograph an instrument for recording the changes of electrical potential occurring during the heartbeat.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views11 pages203 MDE ECG1 Lectuers
Uploaded by
rosefelTracing made by an electrocardiograph used especially in diagnosing abnormalities of heart action. Electrocardiograph an instrument for recording the changes of electrical potential occurring during the heartbeat.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 11
Electrocardiogram The tracing made by an electrocardiograph Electrocardiograph an instrument for recording the changes of electrical potential occurring during
the heartbeat used especially in diagnosing abnormalities of heart action
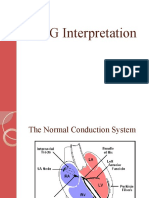
Cardiac conduction system
Sinoatrial Node (SA)
the impulse generating tissue located in the right atrium of the heart
Atrioventricular Node (AV)
the tissue between the atria and the ventricles of the heart, conducts the normal electrical impulse from the atria to the ventricles SA AV His bundle Purkinje fibers
2
Electrocardiogram (ECG) (cont.)
ECG Waves and Intervals
P wave: the sequential activation (depolarization) of the right and left atria QRS complex: right and left ventricular depolarization ST-T wave: ventricular repolarization U wave: probably represents "afterdepolarizations" in the ventricles PR interval: time interval from onset of atrial depolarization (P wave) to onset of ventricular depolarization (QRS complex) QRS duration: duration of ventricular muscle depolarization QT interval: duration of ventricular depolarization and repolarization RR interval: duration of ventricular cardiac cycle (an indicator of ventricular rate) PP interval: duration of atrial cycle (an indicator of atrial rate)
4
ECG Signal Characteristics
Signal is generated in the heart Amplitude range: -5 mV to +5 mV (usually the packed up signal on the body surface is 1 mV) Frequency range: 0.05 to 1500 Hz Acquisition by surface electrodes
Lead configurations for ECG Acquisition
1. Bipolar limb leads (Einthoven) 2. Unipolar limb leads or Augmented limb leads (Goldberg) 3. Unipolar chest leads (Wilson)
Bipolar limb leads (Einthoven)
Lead I
Lead II
Lead III
Signal shape of Bipolar limb leads (Einthoven)
Lead I
Lead II
Lead III
8
Unipolar limb leads or Augmented limb leads (Goldberg)
Lead aVR
Lead aVL
Lead aVF
Signal shape of Unipolar limb leads
Lead aVR
Lead aVL
Lead aVF
10
Signal processing of ECG
11
You might also like
- Lab Exercise 5 PDFDocument50 pagesLab Exercise 5 PDFE1- Villapaz, Aiemarie R. (Aie)No ratings yet
- ELECTROCARDIOGRAMDocument50 pagesELECTROCARDIOGRAMamitava2010No ratings yet
- ECG Guide: Understanding Heart Rhythms & EKG TestDocument10 pagesECG Guide: Understanding Heart Rhythms & EKG TestSilver Villota Magday Jr.No ratings yet
- ECG FILEDocument29 pagesECG FILEneha miriNo ratings yet
- Ecg 1Document198 pagesEcg 1hibaNo ratings yet
- Interpretasi EKG - Dr. HerickDocument189 pagesInterpretasi EKG - Dr. HerickDiana IdrisNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Output by N.Anisha MPT OrthoDocument53 pagesCardiac Output by N.Anisha MPT OrthoAnisha NallasamyNo ratings yet
- Normal ECG Waveforms and Intervals ExplainedDocument26 pagesNormal ECG Waveforms and Intervals ExplainedJan Christian AramburoNo ratings yet
- Electrocardiography: An Introduction To The ECGDocument76 pagesElectrocardiography: An Introduction To The ECGInnocent Clifford MaranduNo ratings yet
- Electrocardiography ECGDocument60 pagesElectrocardiography ECGSalman KhanNo ratings yet
- Introduction to ECGDocument6 pagesIntroduction to ECGAbigail ChristisnNo ratings yet
- I. The Standard 12 Lead ECGDocument2 pagesI. The Standard 12 Lead ECGapi-376925250% (2)
- ECG Basics and Normal ECG PatternsDocument40 pagesECG Basics and Normal ECG PatternsArslan KhanNo ratings yet
- Basic ECG LectureDocument148 pagesBasic ECG LectureAradhanaRamchandaniNo ratings yet
- 9 EcgDocument12 pages9 EcgTommy CharwinNo ratings yet
- Kuliah Ekg UnswagatiDocument75 pagesKuliah Ekg UnswagatiiikNo ratings yet
- Cheong Kuan Loong Medical Department Hospital Sultan Haji Ahmad Shah, Temerloh 12/5/10Document99 pagesCheong Kuan Loong Medical Department Hospital Sultan Haji Ahmad Shah, Temerloh 12/5/10Haq10No ratings yet
- ECG Interpretation in DogsDocument107 pagesECG Interpretation in DogsPLABITA GOSWAMI100% (2)
- Mechanical and Electrical Events of The Cardiac CycleDocument39 pagesMechanical and Electrical Events of The Cardiac CycleEdi HidayatNo ratings yet
- EcgDocument25 pagesEcgLaraib KanwalNo ratings yet
- ECG InterpretationDocument48 pagesECG InterpretationKervayse St.ClairNo ratings yet
- Hotel Dpalma, Bandung 16 Maret 2018: Dr. Benny Prasetya PDocument145 pagesHotel Dpalma, Bandung 16 Maret 2018: Dr. Benny Prasetya PkangheriNo ratings yet
- Mechanical and Electrical Events of The Cardiac CycleDocument39 pagesMechanical and Electrical Events of The Cardiac CyclecosedasapereNo ratings yet
- ECG Analysis of Coronary CirculationDocument155 pagesECG Analysis of Coronary CirculationDeepika PatelNo ratings yet
- DrAbnet ECG - BasicsDocument99 pagesDrAbnet ECG - BasicsAbnet WondimuNo ratings yet
- ECG Normal and AbnormalDocument74 pagesECG Normal and Abnormalawaniedream8391100% (1)
- DYSRHYTMIASDocument16 pagesDYSRHYTMIASVictor StevenNo ratings yet
- EcgDocument57 pagesEcgenii_ta100% (9)
- ECG Interpretation: Prepared byDocument16 pagesECG Interpretation: Prepared bypipoahmed51No ratings yet
- Dysrhythmia Interpretation GuideDocument26 pagesDysrhythmia Interpretation GuideSarah ChadnickNo ratings yet
- The ECG Guide: Understanding the Electrical Activity of the HeartDocument25 pagesThe ECG Guide: Understanding the Electrical Activity of the HeartFarhanNo ratings yet
- ECG Analysis and Cardiac DysrhythmiasDocument6 pagesECG Analysis and Cardiac Dysrhythmiasrui_kaNo ratings yet
- Interpretasi ElektrokardiografiDocument60 pagesInterpretasi ElektrokardiografiYogi GustriansyahNo ratings yet
- ECG Essentials Quick ReviewDocument45 pagesECG Essentials Quick Reviewjaikishan marathe 69No ratings yet
- ECG1Document67 pagesECG1Farhan RosliNo ratings yet
- The 12-Lead EKG: A Step-by-Step GuideDocument31 pagesThe 12-Lead EKG: A Step-by-Step GuideJay JiangNo ratings yet
- Electrocardiography-Blok Cardiorespi 1Document49 pagesElectrocardiography-Blok Cardiorespi 1ahmad syauqieNo ratings yet
- How To Read An EcgDocument86 pagesHow To Read An EcgmajdNo ratings yet
- Matrikulasi Interpretasi EkgDocument40 pagesMatrikulasi Interpretasi Ekgsupergirl2123No ratings yet
- ECG HorseDocument33 pagesECG HorseUNICORN TIMENo ratings yet
- Santosh DevDocument45 pagesSantosh Devdevdsantosh100% (1)
- ElectrocardiogramDocument52 pagesElectrocardiogramTuong HoangManhNo ratings yet
- EKG InterpretationDocument65 pagesEKG Interpretationpaskariatne probo dewi100% (1)
- Unit 1Document29 pagesUnit 1SasikumarNo ratings yet
- Electrocardiogra (M) PhyDocument26 pagesElectrocardiogra (M) PhyyansliyaNo ratings yet
- Ecg Physio LectureDocument60 pagesEcg Physio LectureAninze Chidera100% (1)
- ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHYDocument75 pagesELECTROCARDIOGRAPHYMeliaNo ratings yet
- Electrocardiogram (ECG)Document53 pagesElectrocardiogram (ECG)eric100% (1)
- Conduction System of Heart-FinalDocument69 pagesConduction System of Heart-FinalAshish ChavanNo ratings yet
- Electrophysiology of The HeartDocument27 pagesElectrophysiology of The HeartTsegaye HailuNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ECGDocument39 pagesIntroduction To ECGSingey LhendupNo ratings yet
- ECG WorldDocument139 pagesECG WorldsatyaNo ratings yet
- The Electrocardiogram: Normal Conduction PathwayDocument16 pagesThe Electrocardiogram: Normal Conduction PathwayFourth YearNo ratings yet
- Electrical Activity of The HeartDocument40 pagesElectrical Activity of The HeartMichael Ajak GhaiNo ratings yet
- Ecg BSTDocument204 pagesEcg BSTAnusha Verghese100% (1)
- KULIAH ECG Dinkes PurworejoDocument69 pagesKULIAH ECG Dinkes PurworejoVella NurfatimahNo ratings yet
- EKG | ECG Interpretation. Everything You Need to Know about 12-Lead ECG/EKG InterpretationFrom EverandEKG | ECG Interpretation. Everything You Need to Know about 12-Lead ECG/EKG InterpretationRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)