0% found this document useful (0 votes)
83 views26 pagesUnderstanding Electrocardiography Basics
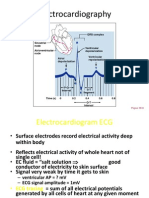
The EKG is a technique for recording the electrical activity of the heart over 100 years after its introduction. It produces a graph called an electrocardiogram. The EKG detects positive and negative deflections that correspond to depolarization and repolarization of the heart muscles during each cardiac cycle. The normal EKG has three distinct waves - the P wave from atrial depolarization, the QRS complex from ventricular depolarization, and the T wave from ventricular repolarization. Analysis of the EKG can provide information on the size and function of the heart and detect any injuries or issues.
Uploaded by
yansliyaCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
83 views26 pagesUnderstanding Electrocardiography Basics
The EKG is a technique for recording the electrical activity of the heart over 100 years after its introduction. It produces a graph called an electrocardiogram. The EKG detects positive and negative deflections that correspond to depolarization and repolarization of the heart muscles during each cardiac cycle. The normal EKG has three distinct waves - the P wave from atrial depolarization, the QRS complex from ventricular depolarization, and the T wave from ventricular repolarization. Analysis of the EKG can provide information on the size and function of the heart and detect any injuries or issues.
Uploaded by
yansliyaCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd